Abstract
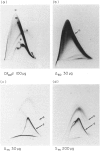
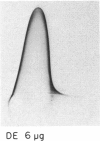
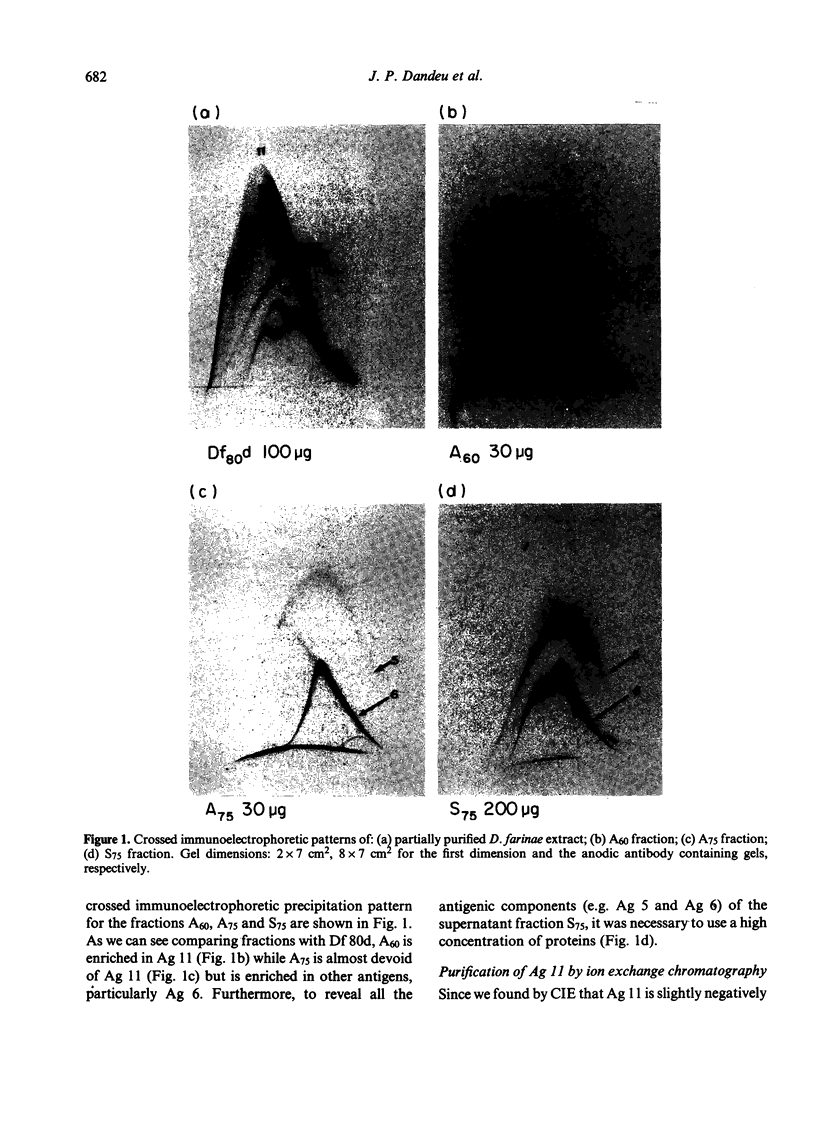
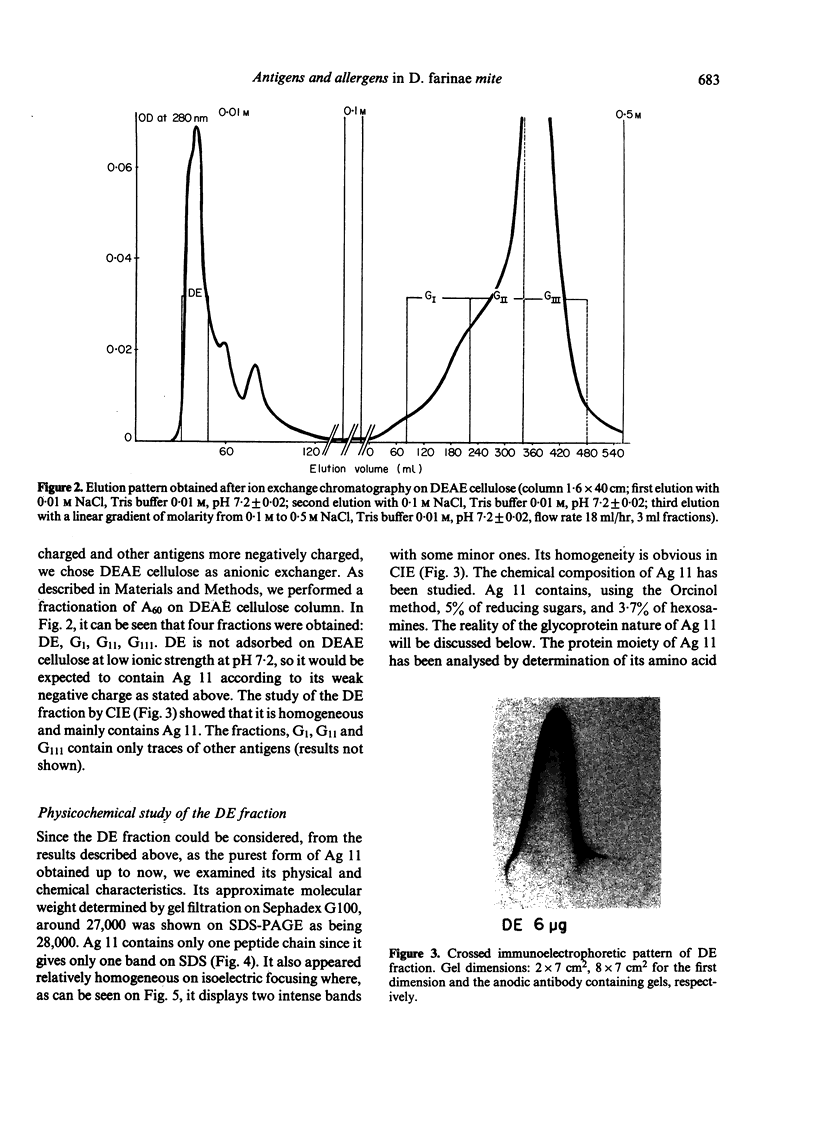
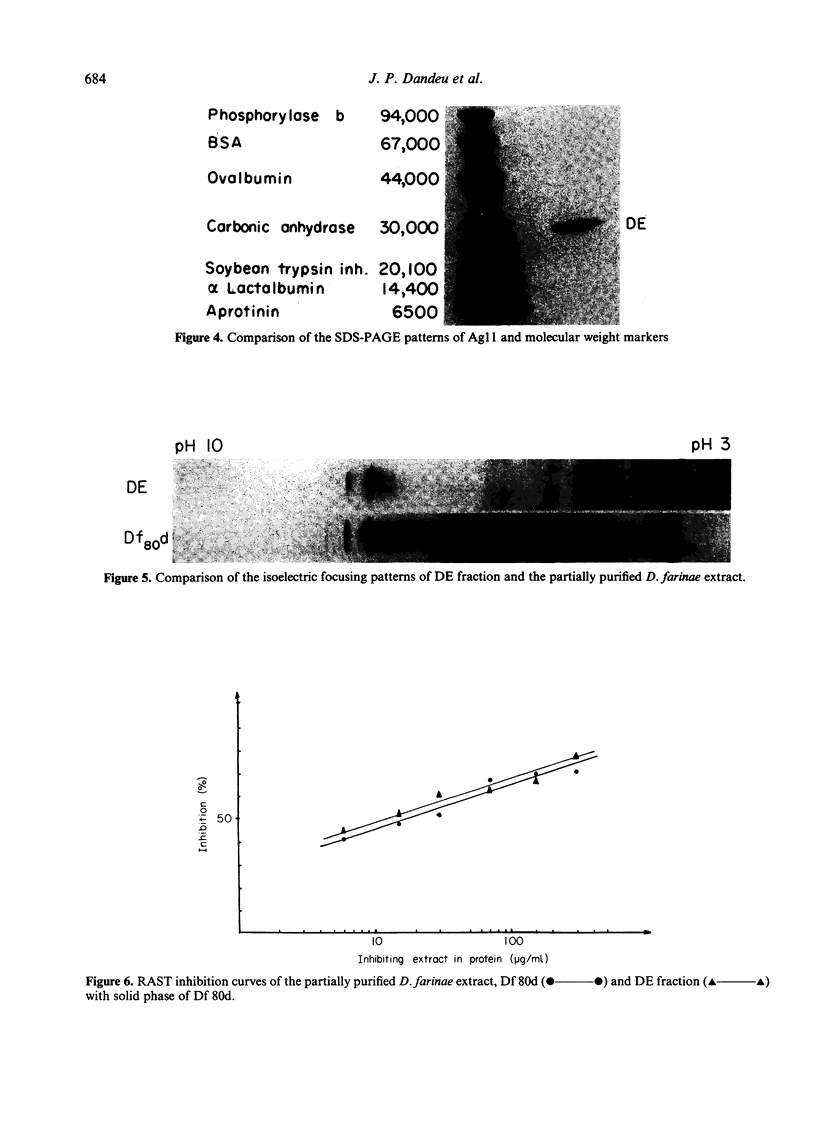
Ammonium sulphate precipitation and DEAE chromatography is an efficient way of purifying Ag 11, the main allergen in Dermatophagoïdes farinae mites, which has already been characterized by crossed radioimmunoelectrophoresis. At 60% of saturation in ammonium sulphate, a precipitate is formed which, dissolved and dialysed has been named fraction A 60. It is mainly composed of Ag 11. In the fraction DE obtained by DEAE chromatography of the ammonium sulphate fraction A 60, Ag 11 appears homogeneous on crossed-immunoelectrophoresis. Isoelectrofocusing results indicate an average isoelectric point near neutrality in agreement with the non-absorbtion of Ag 11 on the DEAE cellulose at a weak ionic strength (0.01, at pH 7.2). By sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and gel filtration Ag 11 has a molecular weight of 28,000.
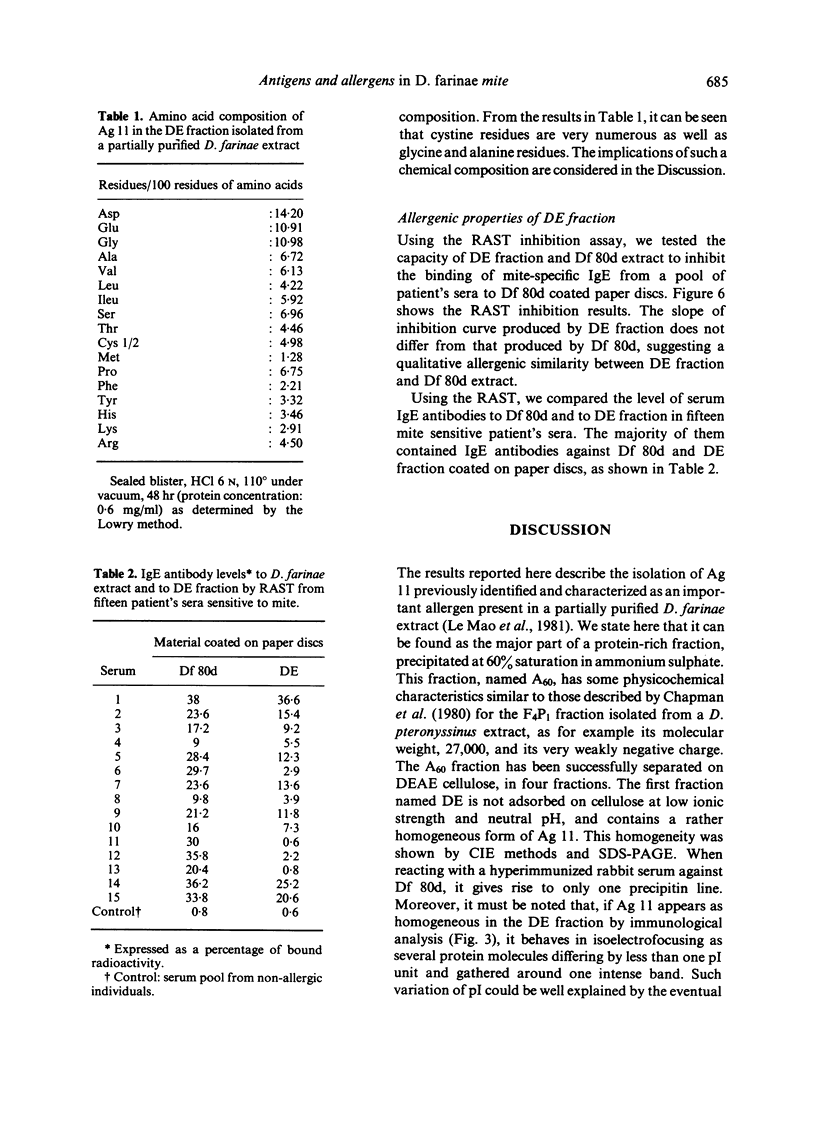
Ag 11 appears as a single polypeptidic chain with numerous dithio-bonds implying a highly folded and resistant structure. Oligosaccharides could be present as constituting molecules as well as contaminating ones as was assumed for hexosamines. These results are discussed with reference to a similar study performed on the major allergen of Dermatophagoïdes pteronyssinus. The allergenic properties of Ag 11 as present in fraction DE were tested by RAST-based methods. Fraction DE is an inhibitor as good as Df 80d and when it is coated on paper discs it can bind specific IgE in sera from the majority of mite sensitive patients. The results suggest that Ag 11 is a major allergen from D. farinae.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ceska M., Eriksson R., Varga J. M. Radioimmunosorbent assay of allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1972 Jan;49(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(72)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman M. D., Platts-Mills T. A. Measurement of IgG, IgA and IgE antibodies to Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus by antigen-binding assay, using a partially purified fraction of mite extract (F4P1). Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Oct;34(1):126–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman M. D., Platts-Mills T. A. Purification and characterization of the major allergen from Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus-antigen P1. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):587–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson L. A., Morgan W. T. A colorimetric method for the determination of glucosamine and chondrosamine. Biochem J. 1933;27(6):1824–1828. doi: 10.1042/bj0271824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holford-Strevens V., Wide L., Milne J. F., Pepys J. Allergens and antigens of Dermatophagoides farinae. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Jan;6(1):49–59. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Mao J., Dandeu J. P., Rabillon J., Lux M., David B. Antigens and allergens in Dermatophagoïdes farinae mite. I. Immunochemical and physicochemical study of two allergenic fractions from a partially-purified Dermatophagoïdes farinae mite extract. Immunology. 1981 Oct;44(2):239–247. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Mao J., Weyer A., Pauli G., Lebel B., David B. Studies on Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus allergens: measurement of the relative potencies of D. pteronyssinus purified extracts by in vitro and in vivo methods. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1980 May;65(5):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(80)90217-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Kudo K., Okudaira H., Miyamoto T., Horiuchi Y. Characterization of the allergenic components of the house dust mite, Dermatophagoides farinae. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;55(1-6):47–53. doi: 10.1159/000231907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S., Biliotti G., Passaleva A., Ricci M. Mites and house dust allergy. II. Relationship between house dust and mite (Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and D. farinae) allergens by fractionation methods. Clin Allergy. 1972 Jun;2(2):115–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1972.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S., Boccaccini P., Amadori A., Ricci M. Studies on allergens of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus by direct and indirect RAST. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;50(5):525–535. doi: 10.1159/000231557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson A. R. Antibody isoelectric spectra. Analysis of the heterogeneity of antibody molecules in serum by isoelectric focusing in gel and specific detection with hapten. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Nov;1(5):390–394. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson A. R., Salaman M. R., Kreth H. W. Microheterogeneity and allomorphism of proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Jun 15;209:210–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb47530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]