Abstract
Inbred mouse strains and their F1 hybrids infected intravenously with Mycobacterium lepraemurium showed different mean survival times (MST). BALB/c and C57BL mice were particularly susceptible, whereas C3H, CBA and DBA/2 mice were relatively resistant. Resistance as judged by MST was dominant in the F1 hybrids. A similar ranking order was obtained by comparing the doubling time of the bacillus in the bone marrow, the increase in spleen weight between 4 and 12 weeks after infection, and the pathology of the liver during infection. The general pattern suggests that mouse resistance to M. lepraemurium is, at least in part, controlled by a gene with the same strain distribution as the genes for resistance to Salmonella typhimurium (Ity') and Leishmania donovani (Lsh') and the gene controlling resistance to Mycobacterium bovis BCG (Bcg). Ity, Lsh and Bcg are all known to be on chromosome 1, suggesting a centre controlling reactions to intracellular infections.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J., Curtis J. Development of delayed hypersensitivity responses in Mycobacterium lepraemurium infections in resistant and susceptible strains of mice. Immunology. 1979 Mar;36(3):563–567. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J. Letter: Genetic control of natural resistance to Leishmania donovani. Nature. 1974 Jul 26;250(464):353–354. doi: 10.1038/250353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Taylor B. A., Blackwell J., Evans E. P., Freeman J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. III. Mapping of the locus controlling susceptibility to visceral leishmaniasis in the mouse. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):7–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
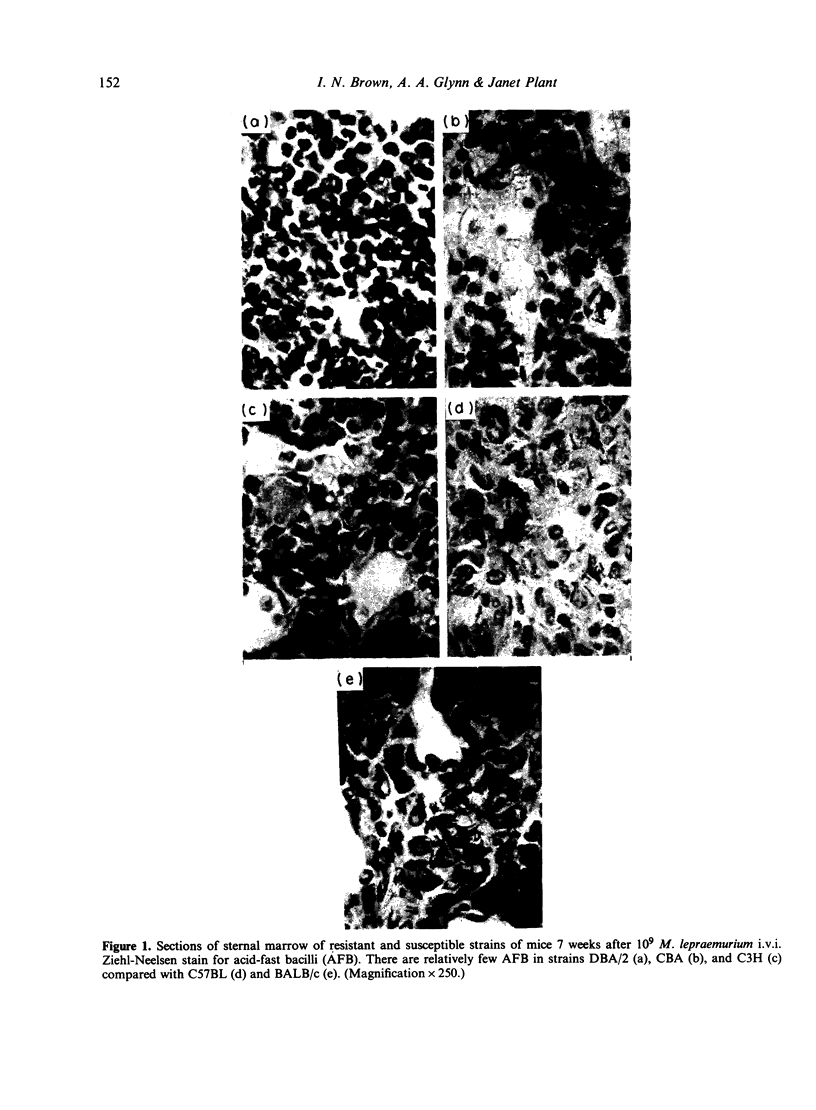
- Brown I. N., Krenzien H. N. Systemic Mycobacterium lepraemurium infection in mice: differences in doubling time in liver, spleen, and bone marrow, and a method for measuring the proportion of viable organisms in an inoculum. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):480–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.480-486.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., McKenzie I. F. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: genetics of listeriosis. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):755–762. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.755-762.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Closs O., Haugen O. A. Experimental murine leprosy. 2. Further evidence for varying susceptibility of outbred mice and evaluation of the response of 5 inbred mouse strains to infection with Mycobacterium lepraemurium. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1974 Jul;82(4):459–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Skamene E., Forget A. Genetic control of natural resistance to Mycobacterium bovis (BCG) in mice. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2417–2421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. G., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: genetics of natural resistance to infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):583–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.583-588.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrange P. H., Closs O. Protective immunity to chronic bacterial infection. Scand J Immunol. 1979;10(4):285–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb01352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrange P. H., Hurtrel B. Local immune response to Mycobacterium lepraemurium in C3H and C57Bl/6 mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Dec;38(3):461–474. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefford M. J., Patel P. J., Poulter L. W., Mackaness G. B. Induction of cell-mediated immunity to Mycobacterium lepraemurium in susceptible mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):654–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.654-659.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Locating salmonella resistance gene on mouse chromosome 1. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):1–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Natural resistance to Salmonella infection, delayed hypersensitivity and Ir genes in different strains of mice. Nature. 1974 Mar 22;248(446):345–347. doi: 10.1038/248345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Kongshavn P. A., Sachs D. H. Resistance to Listeria monocytogenes in mice: genetic control by genes that are not linked to the H-2 complex. J Infect Dis. 1979 Feb;139(2):228–231. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]