Abstract
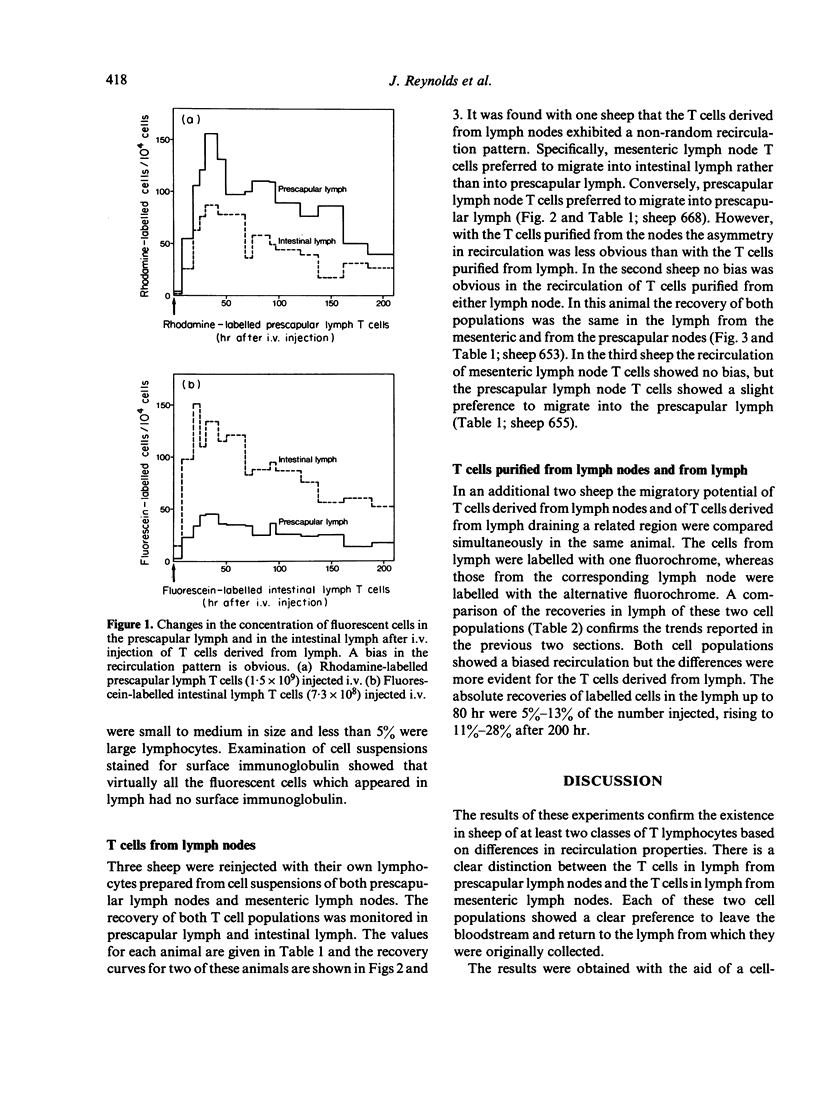
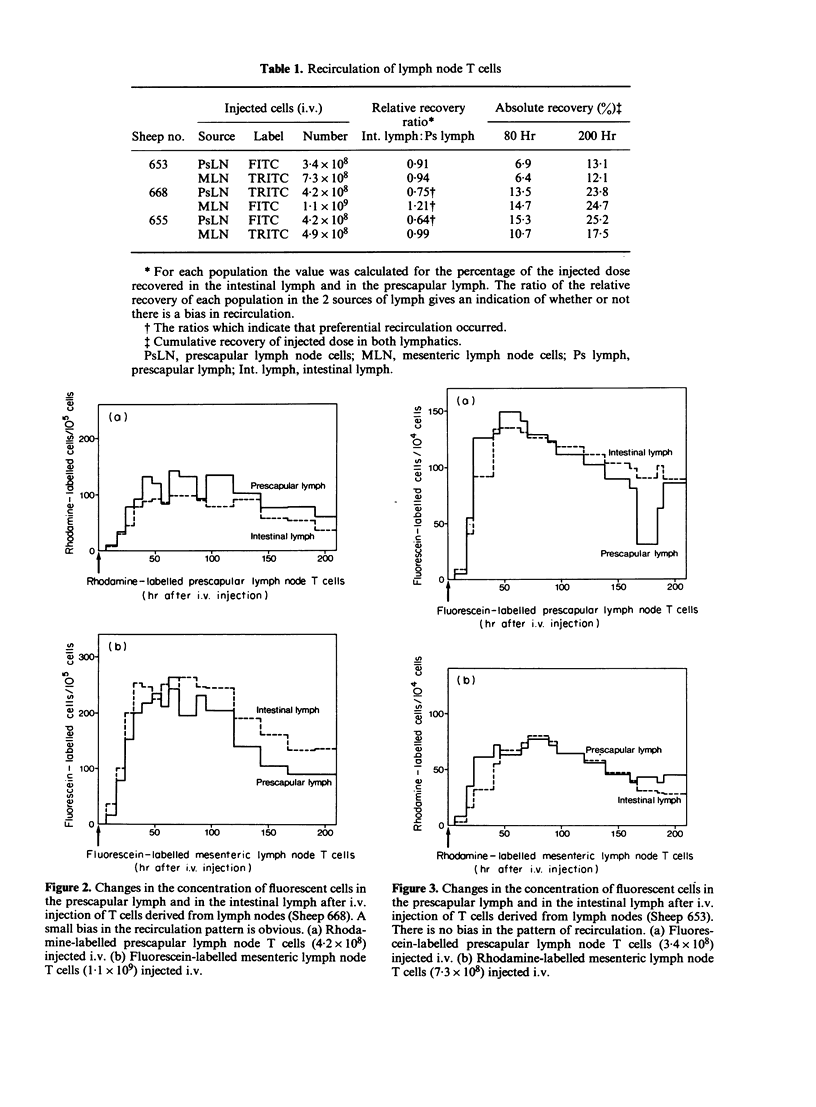
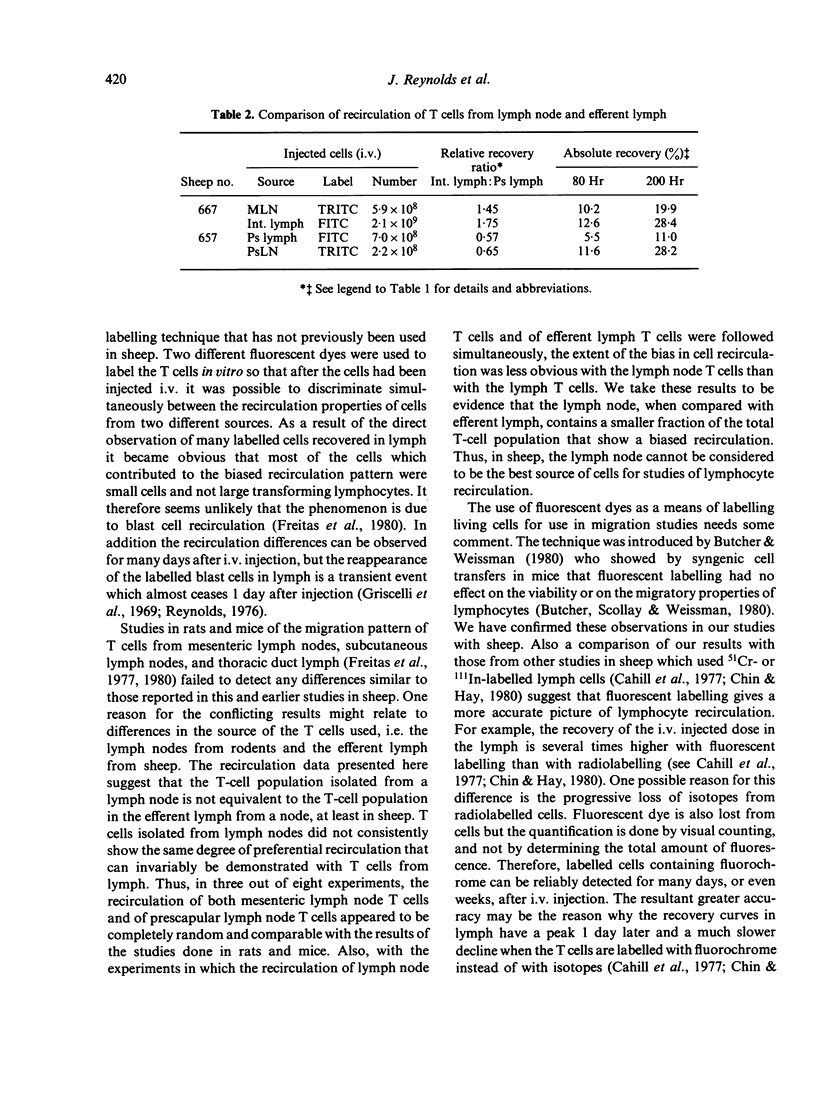
T lymphocytes derived from different sources in sheep were compared for their ability to recirculate from blood to lymph. Nylon wool columns were used to prepare T-cell-enriched populations from efferent intestinal lymph, efferent prescapular lymph and from cell suspensions of mesenteric lymph nodes and prescapular lymph nodes. With each animal, T cells from two of the above sources were labelled in vitro, one population with fluorescein isothiocyanate the other with rhodamine isothiocyanate; both populations were returned to the animal at the same time by intravenous injection. The intestinal lymph and prescapular lymph were continuously monitored to compare the recirculating properties of the two populations of T cells. This technique led to confirmation of the earlier reports in sheep of a preferential recovery of intestinal lymph T cells and of prescapular lymph T cells in the lymph from which the cells were originally collected. This phenomenon was much less evident with T cells from mesenteric nodes and prescapular nodes and in a number of experiments a random pattern of recirculation occurred. It is concluded that there are differences in the composition of the T-cell population in a node compared with that of the lymph draining the node. The advantages of using fluorescently-labelled cells to study lymphocyte migration are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butcher E. C., Scollay R. G., Weissman I. L. Direct fluorescent labeling of cells with fluorescein or rhodamine isothiocyanate. II. Potential application to studies of lymphocyte migration and maturation. J Immunol Methods. 1980;37(2):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90196-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill R. N., Poskitt D. C., Frost D. C., Trnka Z. Two distinct pools of recirculating T lymphocytes: migratory characteristics of nodal and intestinal T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):420–428. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill R. N., Poskitt D. C., Frost H., Julius M. H., Trnka Z. Behaviour of sheep-immunoglobulin-bearing and non-immunoglobulin-bearing lymphocytes isolated by nylon wool columns. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1978;57(1):90–96. doi: 10.1159/000232088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin W., Hay J. B. A comparison of lymphocyte migration through intestinal lymph nodes, subcutaneous lymph nodes, and chronic inflammatory sites of sheep. Gastroenterology. 1980 Dec;79(6):1231–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas A. A., Rose M., Rocha B. Random recirculation of small T lymphocytes from thoracic duct lymph in the mouse. Cell Immunol. 1980 Nov;56(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griscelli C., Vassalli P., McCluskey R. T. The distribution of large dividing lymph node cells in syngeneic recipient rats after intravenous injection. J Exp Med. 1969 Dec 1;130(6):1427–1451. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.6.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G. An essay on lymphocyte circulation and the gut. Monogr Allergy. 1980;16:100–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins J., Hall J. G. Selective entry of immunoblasts into gut from intestinal lymph. Nature. 1976 Jan 29;259(5541):308–309. doi: 10.1038/259308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scollay R., Hopkins J., Hall J. Possible role of surface Ig in non-random recirculation of small lymphocytes. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):528–529. doi: 10.1038/260528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Freitas A. A., Rose M. L., Parrott D. M. Murine mesenteric and peripheral lymph nodes: a common pool of small T cells. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):731–733. doi: 10.1038/270731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


