Abstract
Thoracic duct lymph (TDL) of nonimmune rats and mice was examined for the presence of antigen-carrying cells immediately following a single injection of 125I-labelled or fluorescence-labelled serum protein antigens. Small numbers of cells laden with antigen (approximately 1/2000 to 1/5000) were identified in TDL and blood by autoradiography or fluorescence microscopy. The antigen-laden (Ag-L) cells resembled macrophages in that a large number adhered to plastic, they phagocytosed bacteria or a particulate dye, were non-specific esterase positive, radioresistant and could take up more than one antigen at one time in vivo. Surface phenotyping using monoclonal antibodies against rat cell markers established that Ag-L cells did not express Ia determinants. The results suggest the existence of a subpopulation of macrophage-related cells that may be involved in the transport of antigen and in stimulation of antibody responses.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOAK J. L., WOODRUFF M. F. A MODIFIED TECHNIQUE FOR COLLECTING MOUSE THORACIC DUCT LYMPH. Nature. 1965 Jan 23;205:396–397. doi: 10.1038/205396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barclay A. N. The localization of populations of lymphocytes defined by monoclonal antibodies in rat lymphoid tissues. Immunology. 1981 Apr;42(4):593–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
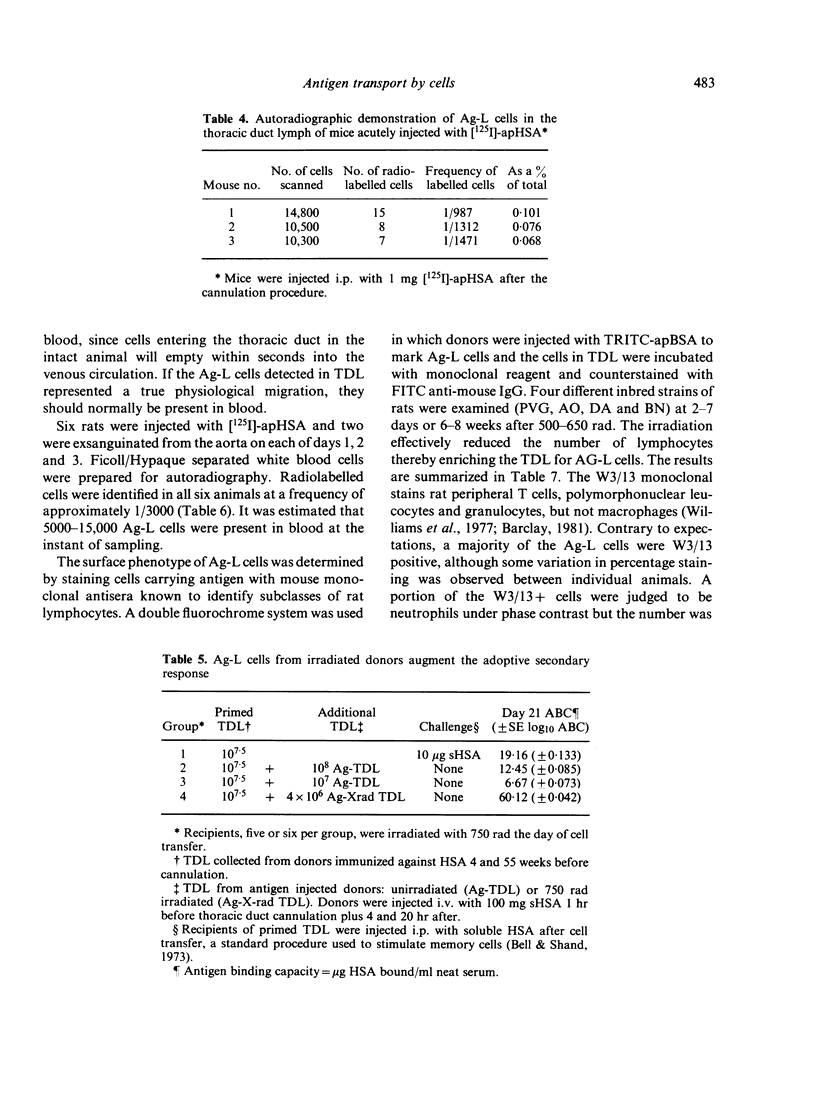
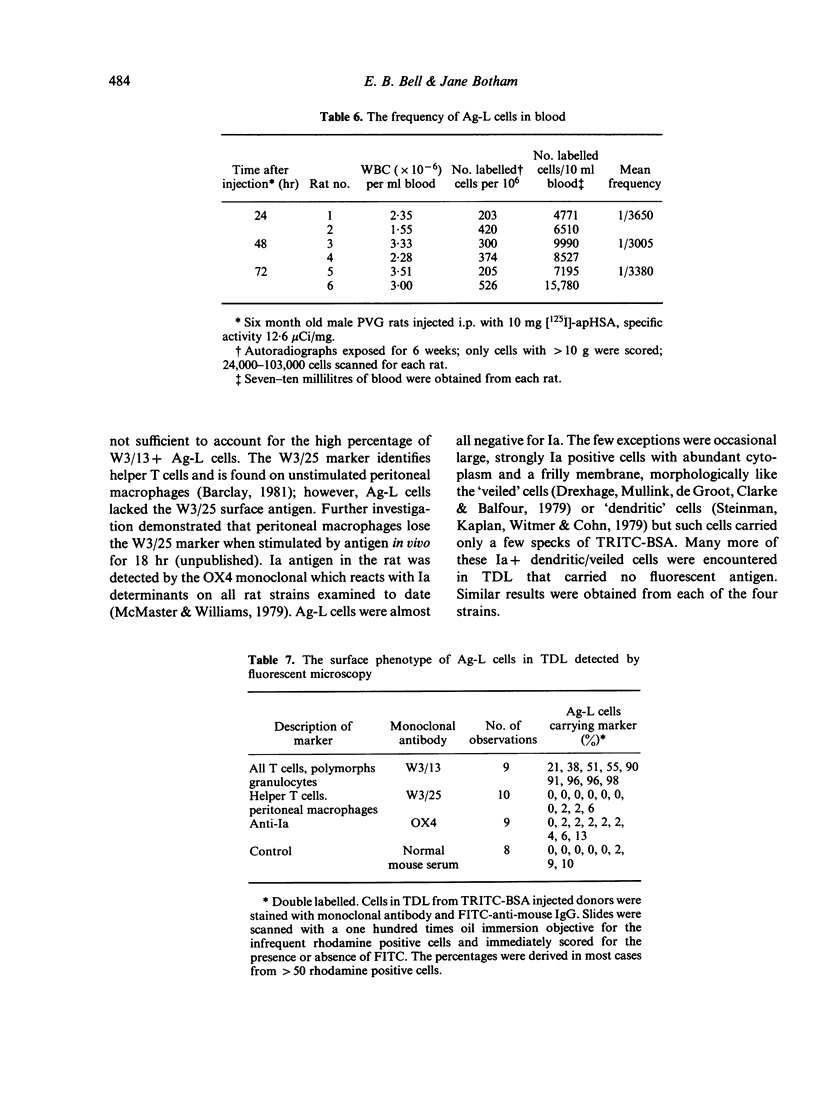
- Bell E. B. Antigen-laden cells in thoracic duct lymph. Implications for adoptive transfer experiments. Immunology. 1979 Dec;38(4):797–808. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E. B., Shand F. L. A search for lymphocyte-derived macrophages during xenogeneic graft-verus-host reactions induced by rat thoracic duct cells. Immunology. 1972 Apr;22(4):537–547. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E. B., Shand F. L. Cellular events in protein tolerant inbred rats. I. The fate of thoracic duct lymphocytes and memory cells during tolerance induction to human serum albumin. Eur J Immunol. 1973 May;3(5):259–267. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Regulation of macrophage populations. I. Preferential induction of Ia-rich peritoneal exudates by immunologic stimuli. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1426–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I., Unanue E. R. Regulation of macrophage populations. II. Synthesis and expression of Ia antigens by peritoneal exudate macrophages is a transient event. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):263–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drexhage H. A., Mullink H., de Groot J., Clarke J., Balfour B. M. A study of cells present in peripheral lymph of pigs with special reference to a type of cell resembling the Langerhans cell. Cell Tissue Res. 1979 Nov;202(3):407–430. doi: 10.1007/BF00220434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOWANS J. L. The effect of the continuous re-infusion of lymph and lymphocytes on the output of lymphocytes from the thoracic duct of unanaesthetized rats. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Feb;38(1):67–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H., Grennan D. Different macrophage populations distinguished by means of fluorescent polysaccharides. Recognition and properties of marginal-zone macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Mar;11(3):221–228. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. H., Balfour B. M., Armstrong J. A., Griffiths S. Functional anatomy of lymph nodes. II. Peripheral lymph-borne mononuclear cells. Anat Rec. 1978 Jan;190(1):5–21. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091900103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinkert W. E., LaBadie J. H., O'Brien J. P., Beyer C. F., Bowers W. E. Rat dendritic cells function as accessory cells and control the production of a soluble factor required for mitogenic responses of T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. C., Wong M. Functional heterogeneity of culture-grown bone marrow-derived macrophages. I. Antigen presenting function. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):86–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Gallico G. G. Tissue distribution and quantitation of Ia-like antigens in the rat. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Oct;8(10):741–748. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830081013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Identification of Ia glycoproteins in rat thymus and purification from rat spleen. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):426–433. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIN T., SALDEEN T. THE LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS FROM THE PERITONEAL CAVITY: A LYMPHANGIOGRAPHIC STUDY IN THE RAT. Cancer Res. 1964 Nov;24:1700–1711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roser B. J. The origin and significance of macrophages in thoracic duct lymph. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1976 Dec;54(6):541–550. doi: 10.1038/icb.1976.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roser B. The origins, kinetics, and fate of macrophage populations. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Aug;8(2):139–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberberg-Sinakin I., Thorbecke G. J., Baer R. L., Rosenthal S. A., Berezowsky V. Antigen-bearing langerhans cells in skin, dermal lymphatics and in lymph nodes. Cell Immunol. 1976 Aug;25(2):137–151. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Kaplan G., Witmer M. D., Cohn Z. A. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. V. Purification of spleen dendritic cells, new surface markers, and maintenance in vitro. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):1–16. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Nogueira N., Witmer M. D., Tydings J. D., Mellman I. S. Lymphokine enhances the expression and synthesis of Ia antigens on cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1248–1261. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Witmer M. D. Lymphoid dendritic cells are potent stimulators of the primary mixed leukocyte reaction in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5132–5136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunshine G. H., Katz D. R., Feldmann M. Dendritic cells induce T cell proliferation to synthetic antigens under Ir gene control. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1817–1822. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Søeberg B., Sumerska T., Binns R. M., Balfour B. M. Contact sensitivity in the pig. II. Induction by intralymphatic infusion of DNP conjugated cells. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1978;57(2):114–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Askonas B. A. The immune response of mice to antigen in macrophages. Immunology. 1968 Aug;15(2):287–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Galfrè G., Milstein C. Analysis of cell surfaces by xenogeneic myeloma-hybrid antibodies: differentiation antigens of rat lymphocytes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita U., Shevach E. M. The expression of Ia antigens on immunocompetent cells in the guinea pig. II. Ia antigens on macrophages. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1584–1588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]