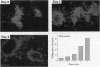
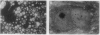
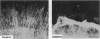
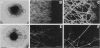
Abstract
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is the enzyme that hydrolyzes the neurotransmitter acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses and neuromuscular junctions. However, results from our laboratory and others indicate that AChE has an extrasynaptic, noncholinergic role during neural development. This article is a review of our findings demonstrating the morphogenic role of AChE, using a neuronal cell culture model. We also discuss how these data suggest that AChE has a cell adhesive function during neural development. These results could have additional significance as AChE is the target enzyme of agricultural organophosphate and carbamate pesticides as well as the commonly used household organophosphate chlorpyrifos (Dursban). Prenatal exposure to these agents could have adverse effects on neural development by interfering with the morphogenic function of AChE.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bataillé S., Portalier P., Coulon P., Ternaux J. P. Influence of acetylcholinesterase on embryonic spinal rat motoneurones growth in culture: a quantitative morphometric study. Eur J Neurosci. 1998 Feb;10(2):560–572. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1998.00065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender B. L., Ghatak N. R. Light and electron microscopic observations on a ganglioneuroma. Acta Neuropathol. 1978 Apr 26;42(1):7–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01273259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biagioni S., Odorisio T., Poiana G., Scarsella G., Augusti-Tocco G. Acetylcholinesterase in the development of chick dorsal root ganglia. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1989;7(3):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(89)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimijoin S., Hammond P. Transient expression of acetylcholinesterase messenger RNA and enzyme activity in developing rat thalamus studied by quantitative histochemistry and in situ hybridization. Neuroscience. 1996 Mar;71(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00457-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanda S. M., Pope C. N. Neurochemical and neurobehavioral effects of repeated gestational exposure to chlorpyrifos in maternal and developing rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1996 Apr;53(4):771–776. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(95)02105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochard P., Coltey P. Cholinergic traits in the neural crest: acetylcholinesterase in crest cells of the chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1983 Jul;98(1):221–238. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90351-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupree J. L., Bigbee J. W. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor treatment delays recovery from axotomy in cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurocytol. 1996 Aug;25(8):439–454. doi: 10.1007/BF02284814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupree J. L., Bigbee J. W. Retardation of neuritic outgrowth and cytoskeletal changes accompany acetylcholinesterase inhibitor treatment in cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurosci Res. 1994 Dec 1;39(5):567–575. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490390508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupree J. L., Maynor E. N., Bigbee J. W. Inverse correlation of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity with the presence of neurofilament inclusions in dorsal root ganglion neurons cultured in the presence of a reversible inhibitor of AChE. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Sep 1;197(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)11895-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L., COURTNEY K. D., ANDRES V., Jr, FEATHER-STONE R. M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Jul;7:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Badawi A., Schenk E. A. Histochemical methods for separate, consecutive and simultaneous demonstration of acetylcholinesterase and norepinephrine in cryostat sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1967 Oct;15(10):580–588. doi: 10.1177/15.10.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Engel A. G., Rosenberry T. L. Acetylcholinesterase of human erythrocytes and neuromuscular junctions: homologies revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1078–1082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta J. J., Bigbee J. W. Substratum-induced modulation of acetylcholinesterase activity in cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurosci Res. 1992 Mar;31(3):454–461. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490310307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W. Multiple forms of acetylcholinesterase and their distribution in endplate and non-endplate regions of rat diaphragm muscle. J Neurobiol. 1973;4(4):343–361. doi: 10.1002/neu.480040404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel M., Schalk I., Ehret-Sabatier L., Bouet F., Goeldner M., Hirth C., Axelsen P. H., Silman I., Sussman J. L. Quaternary ligand binding to aromatic residues in the active-site gorge of acetylcholinesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9031–9035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. A., Holmes C., Budd T. C., Greenfield S. A. The effect of acetylcholinesterase on outgrowth of dopaminergic neurons in organotypic slice culture of rat mid-brain. Cell Tissue Res. 1995 Feb;279(2):323–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00318488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOELLE G. B. The histochemical identification of acetylcholinesterase in cholinergic, adrenergic and sensory neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1955 Jun;114(2):167–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpel R., Sternfeld M., Ginzberg D., Guhl E., Graessmann A., Soreq H. Overexpression of alternative human acetylcholinesterase forms modulates process extensions in cultured glioma cells. J Neurochem. 1996 Jan;66(1):114–123. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.66010114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenigsberger C., Chiappa S., Brimijoin S. Neurite differentiation is modulated in neuroblastoma cells engineered for altered acetylcholinesterase expression. J Neurochem. 1997 Oct;69(4):1389–1397. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1997.69041389.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenigsberger C., Hammond P., Brimijoin S. Developmental expression of acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase in the rat: enzyme and mRNA levels in embryonic dorsal root ganglia. Brain Res. 1998 Mar 23;787(2):248–258. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(97)01507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostovic I., Goldman-Rakic P. S. Transient cholinesterase staining in the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus and its connections in the developing human and monkey brain. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Oct 1;219(4):431–447. doi: 10.1002/cne.902190405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristt D. A. Acetylcholinesterase in the ventrobasal thalamus: transience and patterning during ontogenesis. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):923–939. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layer P. G. Cholinesterases preceding major tracts in vertebrate neurogenesis. Bioessays. 1990 Sep;12(9):415–420. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layer P. G., Kaulich S. Cranial nerve growth in birds is preceded by cholinesterase expression during neural crest cell migration and the formation of an HNK-1 scaffold. Cell Tissue Res. 1991 Sep;265(3):393–407. doi: 10.1007/BF00340862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layer P. G., Weikert T., Alber R. Cholinesterases regulate neurite growth of chick nerve cells in vitro by means of a non-enzymatic mechanism. Cell Tissue Res. 1993 Aug;273(2):219–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00312823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layer P. G., Willbold E. Novel functions of cholinesterases in development, physiology and disease. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 1995;29(3):1–94. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6336(11)80046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Pezzementi L., Bon S., Krejci E., Vallette F. M. Molecular and cellular biology of cholinesterases. Prog Neurobiol. 1993 Jul;41(1):31–91. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(93)90040-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody S. A., Stein D. B. The development of acetylcholinesterase activity in the embryonic nervous system of the frog, Xenopus laevis. Brain Res. 1988 Apr 1;467(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(88)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen S. R., Hooper M. J., Padilla S. Rat brain acetylcholinesterase activity: developmental profile and maturational sensitivity to carbamate and organophosphorus inhibitors. Toxicology. 1998 Jan 16;125(1):13–19. doi: 10.1016/s0300-483x(97)00157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto M. A., Lobelle F., Jr, Bidanset J. H., Wurpel J. N. Embryotoxicity and neurotoxicity in rats associated with prenatal exposure to DURSBAN. Vet Hum Toxicol. 1992 Dec;34(6):498–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega M., Marani E. Acetylcholinesterase in the developing rat spinal cord: an enzyme histochemical study. Eur J Morphol. 1990;28(2-4):379–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. T. A morphogenic role for transiently expressed acetylcholinesterase in developing thalamocortical systems? Neurosci Lett. 1987 Apr 10;75(3):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robitzki A., Mack A., Hoppe U., Chatonnet A., Layer P. G. Regulation of cholinesterase gene expression affects neuronal differentiation as revealed by transfection studies on reaggregating embryonic chicken retinal cells. Eur J Neurosci. 1997 Nov;9(11):2394–2405. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1997.tb01656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma K. V., Bigbee J. W. Acetylcholinesterase antibody treatment results in neurite detachment and reduced outgrowth from cultured neurons: further evidence for a cell adhesive role for neuronal acetylcholinesterase. J Neurosci Res. 1998 Aug 15;53(4):454–464. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19980815)53:4<454::AID-JNR7>3.0.CO;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman J. D. Chlorpyrifos (Dursban)-associated birth defects: report of four cases. Arch Environ Health. 1996 Jan-Feb;51(1):5–8. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1996.9935986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. H., Reed G., Whitefield B., Nurcombe V. Cholinergic regulation of neurite outgrowth from isolated chick sympathetic neurons in culture. J Neurosci. 1995 Jan;15(1 Pt 1):144–151. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-01-00144.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivatsan M., Peretz B. Acetylcholinesterase promotes regeneration of neurites in cultured adult neurons of Aplysia. Neuroscience. 1997 Apr;77(3):921–931. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(96)00458-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternfeld M., Ming G., Song H., Sela K., Timberg R., Poo M., Soreq H. Acetylcholinesterase enhances neurite growth and synapse development through alternative contributions of its hydrolytic capacity, core protein, and variable C termini. J Neurosci. 1998 Feb 15;18(4):1240–1249. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-04-01240.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennyson V. M., Brzin M. The appearance of acetylcholinesterase in the dorsal root neuroblast of the rabbit embryo. A study by electron microscope cytochemistry and microgasometric analysis with the magnetic diver. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jul;46(1):64–80. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
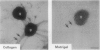
- Weikert T., Rathjen F. G., Layer P. G. Developmental maps of acetylcholinesterase and G4-antigen of the early chicken brain: long-distance tracts originate from AChE-producing cell bodies. J Neurobiol. 1990 Apr;21(3):482–498. doi: 10.1002/neu.480210309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]