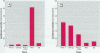Abstract
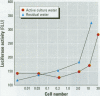
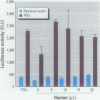
Collaborative studies were performed to develop a functional assay for fish-killing activity produced by Pfiesteria piscicida. Eight cell lines were used to screen organic fractions and residual water fraction by using a 3-[4, 5-dimethylthiazol-(2-4)]-diphenyltetrazolium bromide cytotoxicity assay. Diethyl ether and a residual water fraction were cytotoxic to several cell lines including rat pituitary (GH(4)C(1)) cells. Residual water as well as preextracted culture water containing P. piscicida cells induced c-fos-luciferase expressed in GH(4)C(1) cells with a rapid time course of induction and sensitive detection. The reporter gene assay detected activity in toxic isolates of P. piscicida from several North Carolina estuaries in 1997 and 1998 and may also be suitable for detecting toxic activity in human and animal serum.
Full text
PDF
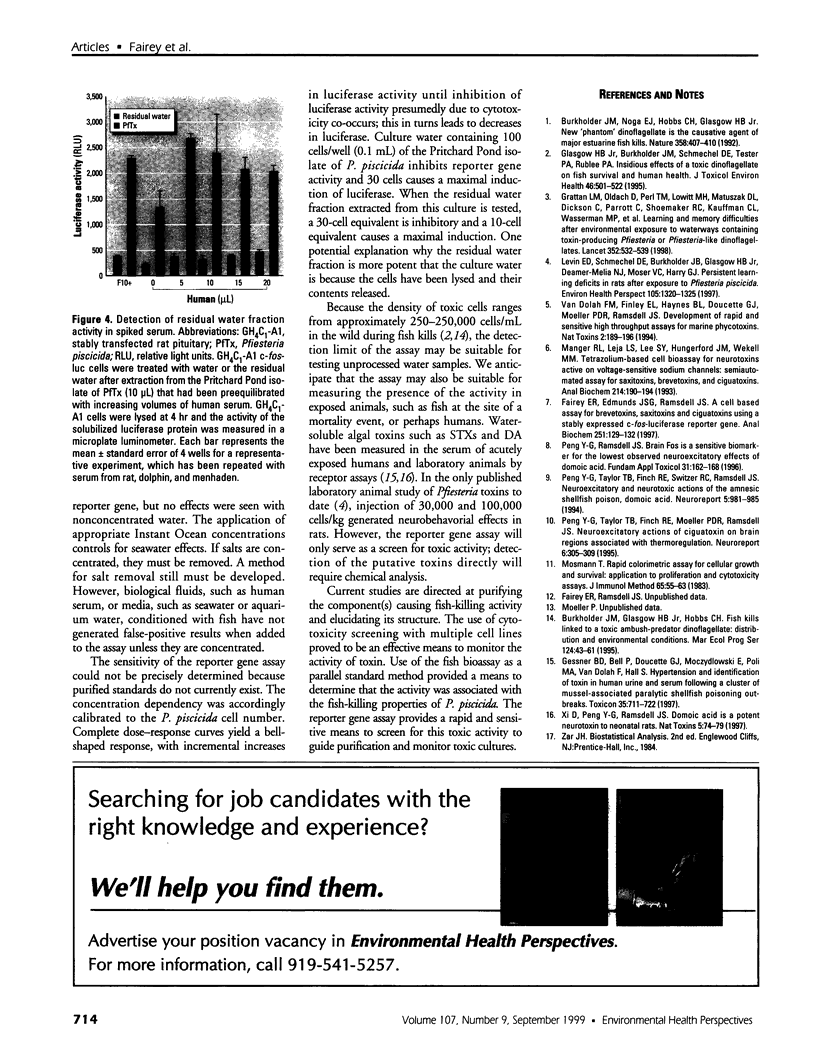
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burkholder J. M., Noga E. J., Hobbs C. H., Glasgow H. B., Jr, Smith S. A. New 'phantom' dinoflagellate is the causative agent of major estuarine fish kills. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):407–410. doi: 10.1038/358407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairey E. R., Edmunds J. S., Ramsdell J. S. A cell-based assay for brevetoxins, saxitoxins, and ciguatoxins using a stably expressed c-fos-luciferase reporter gene. Anal Biochem. 1997 Aug 15;251(1):129–132. doi: 10.1006/abio.1997.2264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessner B. D., Bell P., Doucette G. J., Moczydlowski E., Poli M. A., Van Dolah F., Hall S. Hypertension and identification of toxin in human urine and serum following a cluster of mussel-associated paralytic shellfish poisoning outbreaks. Toxicon. 1997 May;35(5):711–722. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(96)00154-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow H. B., Jr, Burkholder J. M., Schmechel D. E., Tester P. A., Rublee P. A. Insidious effects of a toxic estuarine dinoflagellate on fish survival and human health. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1995 Dec;46(4):501–522. doi: 10.1080/15287399509532051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grattan L. M., Oldach D., Perl T. M., Lowitt M. H., Matuszak D. L., Dickson C., Parrott C., Shoemaker R. C., Kauffman C. L., Wasserman M. P. Learning and memory difficulties after environmental exposure to waterways containing toxin-producing Pfiesteria or Pfiesteria-like dinoflagellates. Lancet. 1998 Aug 15;352(9127):532–539. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)02132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. D., Schmechel D. E., Burkholder J. B., Deamer-Melia N. J., Moser V. C., Harry G. J. Persisting learning deficits in rats after exposure to Pfiesteria piscicida. Environ Health Perspect. 1997 Dec;105(12):1320–1325. doi: 10.1289/ehp.971051320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manger R. L., Leja L. S., Lee S. Y., Hungerford J. M., Wekell M. M. Tetrazolium-based cell bioassay for neurotoxins active on voltage-sensitive sodium channels: semiautomated assay for saxitoxins, brevetoxins, and ciguatoxins. Anal Biochem. 1993 Oct;214(1):190–194. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Y. G., Ramsdell J. S. Brain Fos induction is a sensitive biomarker for the lowest observed neuroexcitatory effects of domoic acid. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1996 Jun;31(2):162–168. doi: 10.1006/faat.1996.0087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Y. G., Taylor T. B., Finch R. E., Moeller P. D., Ramsdell J. S. Neuroexcitatory actions of ciguatoxin on brain regions associated with thermoregulation. Neuroreport. 1995 Jan 26;6(2):305–309. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199501000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng Y. G., Taylor T. B., Finch R. E., Switzer R. C., Ramsdell J. S. Neuroexcitatory and neurotoxic actions of the amnesic shellfish poison, domoic acid. Neuroreport. 1994 Apr 14;5(8):981–985. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199404000-00032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dolah F. M., Finley E. L., Haynes B. L., Doucette G. J., Moeller P. D., Ramsdell J. S. Development of rapid and sensitive high throughput pharmacologic assays for marine phycotoxins. Nat Toxins. 1994;2(4):189–196. doi: 10.1002/nt.2620020407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xi D., Peng Y. G., Ramsdell J. S. Domoic acid is a potent neurotoxin to neonatal rats. Nat Toxins. 1997;5(2):74–79. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)(1997)5:2<74::AID-NT4>3.0.CO;2-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]