Abstract
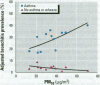
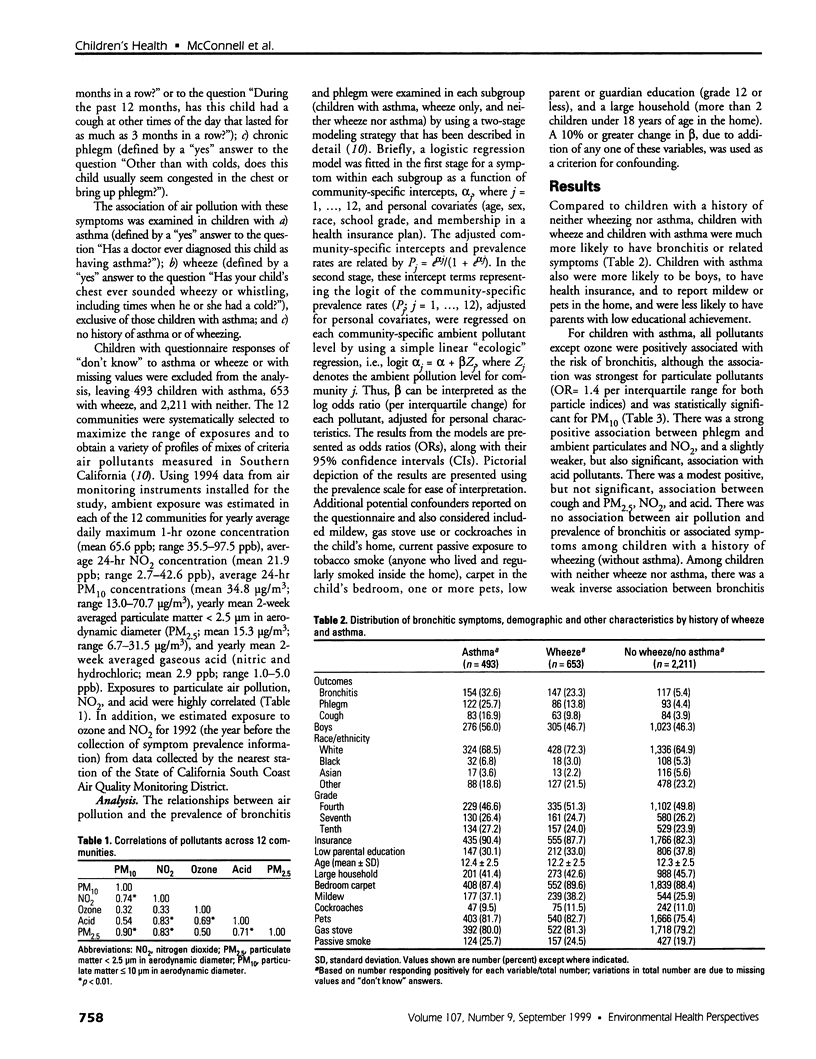
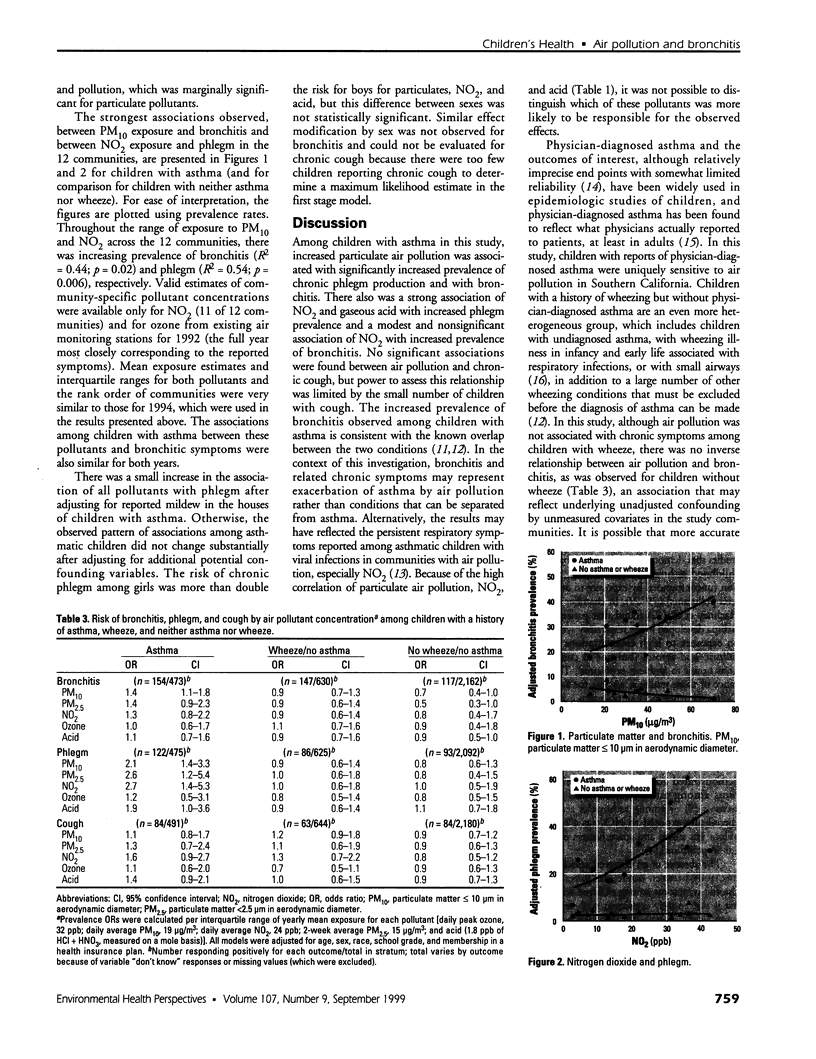
The association of air pollution with the prevalence of chronic lower respiratory tract symptoms among children with a history of asthma or related symptoms was examined in a cross-sectional study. Parents of a total of 3,676 fourth, seventh, and tenth graders from classrooms in 12 communities in Southern California completed questionnaires that characterized the children's histories of respiratory illness and associated risk factors. The prevalences of bronchitis, chronic phlegm, and chronic cough were investigated among children with a history of asthma, wheeze without diagnosed asthma, and neither wheeze nor asthma. Average ambient annual exposure to ozone, particulate matter (PM(10) and PM(2.5); [less than/equal to] 10 microm and < 2.5 microm in aerodynamic diameter, respectively), acid vapor, and nitrogen dioxide (NO(2)) was estimated from monitoring stations in each community. Positive associations between air pollution and bronchitis and phlegm were observed only among children with asthma. As PM(10) increased across communities, there was a corresponding increase in the risk per interquartile range of bronchitis [odds ratio (OR) 1.4/19 microg/m(3); 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.1-1.8). Increased prevalence of phlegm was significantly associated with increasing exposure to all ambient pollutants except ozone. The strongest association was for NO(2), based on relative risk per interquartile range in the 12 communities (OR 2.7/24 ppb; CI, 1.4-5.3). The results suggest that children with a prior diagnosis of asthma are more likely to develop persistent lower respiratory tract symptoms when exposed to air pollution in Southern California.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. J. Air pollution and asthma. Postgrad Med J. 1994 May;70(823):319–325. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.70.823.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boezen M., Schouten J., Rijcken B., Vonk J., Gerritsen J., van der Zee S., Hoek G., Brunekreef B., Postma D. Peak expiratory flow variability, bronchial responsiveness, and susceptibility to ambient air pollution in adults. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 Dec;158(6):1848–1854. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.158.6.9804072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody R. P., Weisel C. P., Birnbaum G., Lioy P. J. The effect of ozone associated with summertime photochemical smog on the frequency of asthma visits to hospital emergency departments. Environ Res. 1992 Aug;58(2):184–194. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(05)80214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delfino R. J., Coate B. D., Zeiger R. S., Seltzer J. M., Street D. H., Koutrakis P. Daily asthma severity in relation to personal ozone exposure and outdoor fungal spores. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996 Sep;154(3 Pt 1):633–641. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.154.3.8810598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockery D. W., Cunningham J., Damokosh A. I., Neas L. M., Spengler J. D., Koutrakis P., Ware J. H., Raizenne M., Speizer F. E. Health effects of acid aerosols on North American children: respiratory symptoms. Environ Health Perspect. 1996 May;104(5):500–505. doi: 10.1289/ehp.96104500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockery D. W., Speizer F. E., Stram D. O., Ware J. H., Spengler J. D., Ferris B. G., Jr Effects of inhalable particles on respiratory health of children. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Mar;139(3):587–594. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.3.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer J. R., Abbey D. E., Burchette R. J. Asthma related to occupational and ambient air pollutants in nonsmokers. J Occup Med. 1993 Sep;35(9):909–915. doi: 10.1097/00043764-199309000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney J. D., Linn W. S., Avol E. L. Acid fog: effects on respiratory function and symptoms in healthy and asthmatic volunteers. Environ Health Perspect. 1989 Feb;79:159–162. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8979159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfon N., Newacheck P. W. Trends in the hospitalization for acute childhood asthma, 1970-84. Am J Public Health. 1986 Nov;76(11):1308–1311. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.11.1308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S. Associations between criteria air pollutants and asthma. Environ Health Perspect. 1995 Sep;103 (Suppl 6):235–242. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103s6235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez F. D., Wright A. L., Taussig L. M., Holberg C. J., Halonen M., Morgan W. J. Asthma and wheezing in the first six years of life. The Group Health Medical Associates. N Engl J Med. 1995 Jan 19;332(3):133–138. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199501193320301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. J., Taussig L. M. The chronic bronchitis complex in children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1984 Aug;31(4):851–864. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)34649-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peat J. K., Salome C. M., Toelle B. G., Bauman A., Woolcock A. J. Reliability of a respiratory history questionnaire and effect of mode of administration on classification of asthma in children. Chest. 1992 Jul;102(1):153–157. doi: 10.1378/chest.102.1.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. M., Avol E., Navidi W., London S. J., Gauderman W. J., Lurmann F., Linn W. S., Margolis H., Rappaport E., Gong H. A study of twelve Southern California communities with differing levels and types of air pollution. I. Prevalence of respiratory morbidity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999 Mar;159(3):760–767. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.159.3.9804143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope C. A., 3rd, Dockery D. W., Spengler J. D., Raizenne M. E. Respiratory health and PM10 pollution. A daily time series analysis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Sep;144(3 Pt 1):668–674. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.3_Pt_1.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope C. A., 3rd Respiratory hospital admissions associated with PM10 pollution in Utah, Salt Lake, and Cache Valleys. Arch Environ Health. 1991 Mar-Apr;46(2):90–97. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1991.9937434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romieu I., Meneses F., Ruiz S., Huerta J., Sienra J. J., White M., Etzel R., Hernandez M. Effects of intermittent ozone exposure on peak expiratory flow and respiratory symptoms among asthmatic children in Mexico City. Arch Environ Health. 1997 Sep-Oct;52(5):368–376. doi: 10.1080/00039899709602213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romieu I., Meneses F., Ruiz S., Sienra J. J., Huerta J., White M. C., Etzel R. A. Effects of air pollution on the respiratory health of asthmatic children living in Mexico City. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996 Aug;154(2 Pt 1):300–307. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.154.2.8756798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romieu I., Meneses F., Sienra-Monge J. J., Huerta J., Ruiz Velasco S., White M. C., Etzel R. A., Hernandez-Avila M. Effects of urban air pollutants on emergency visits for childhood asthma in Mexico City. Am J Epidemiol. 1995 Mar 15;141(6):546–553. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedal S., Petkau J., White R., Blair J. Acute effects of ambient inhalable particles in asthmatic and nonasthmatic children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 Apr;157(4 Pt 1):1034–1043. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.157.4.9609008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]