Abstract
Meta-analysis has seen increasing use as a tool in epidemiology over the past five years. Although this method is relatively well accepted for use in clinical trials, its use has proved somewhat more controversial in epidemiology. If meta-analysis is viewed as an evolutionary improvement over the review article, it may become more widely acceptable. Meta-analysis should incorporate the concern for study quality and differences in study design seen in classic review articles with the concern for rigor, objectivity, and quantitative precision characteristic of meta-analysis. Available tools for consideration of differences among studies are described with several examples from the literature. The extent to which various methods are used in published meta-analyses is described. Methods for assessing publication bias, and tools for combining dose-response data, are discussed also. Evaluation of risk factors and protective factors for cancer must be based on the weight of the evidence. Tools such as meta-analysis are essential if we are to interpret the vast number of completed studies in cancer epidemiology.
Full text
PDF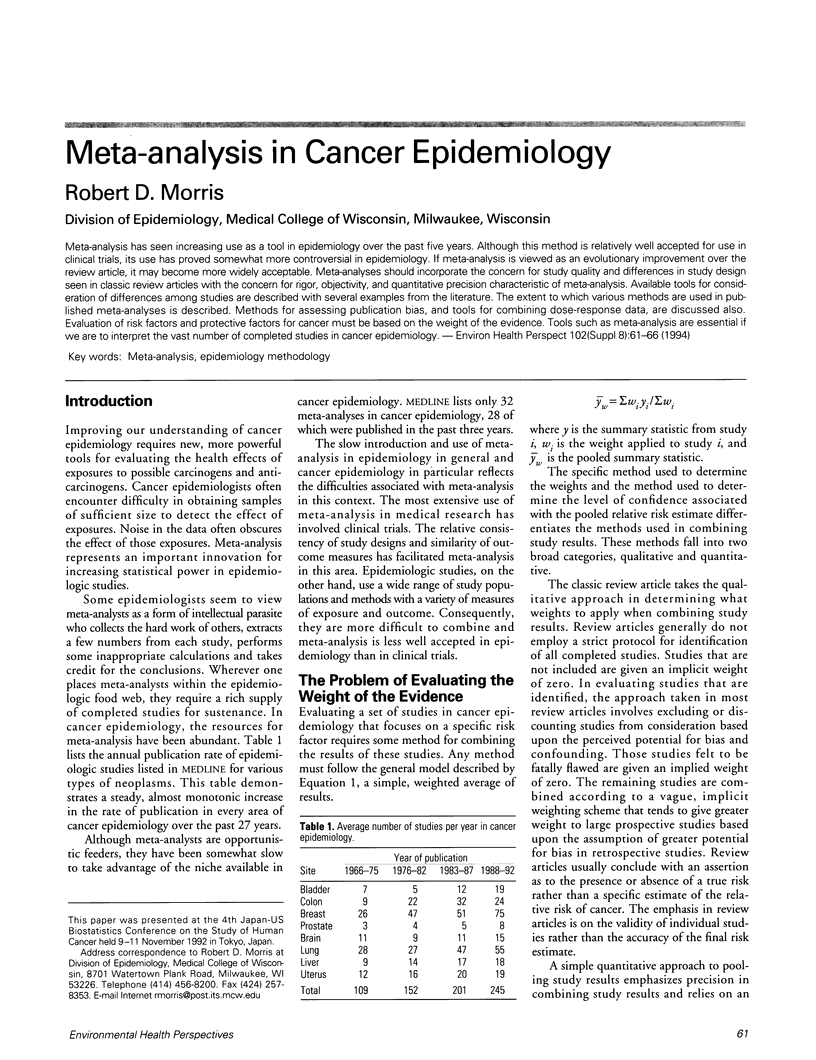


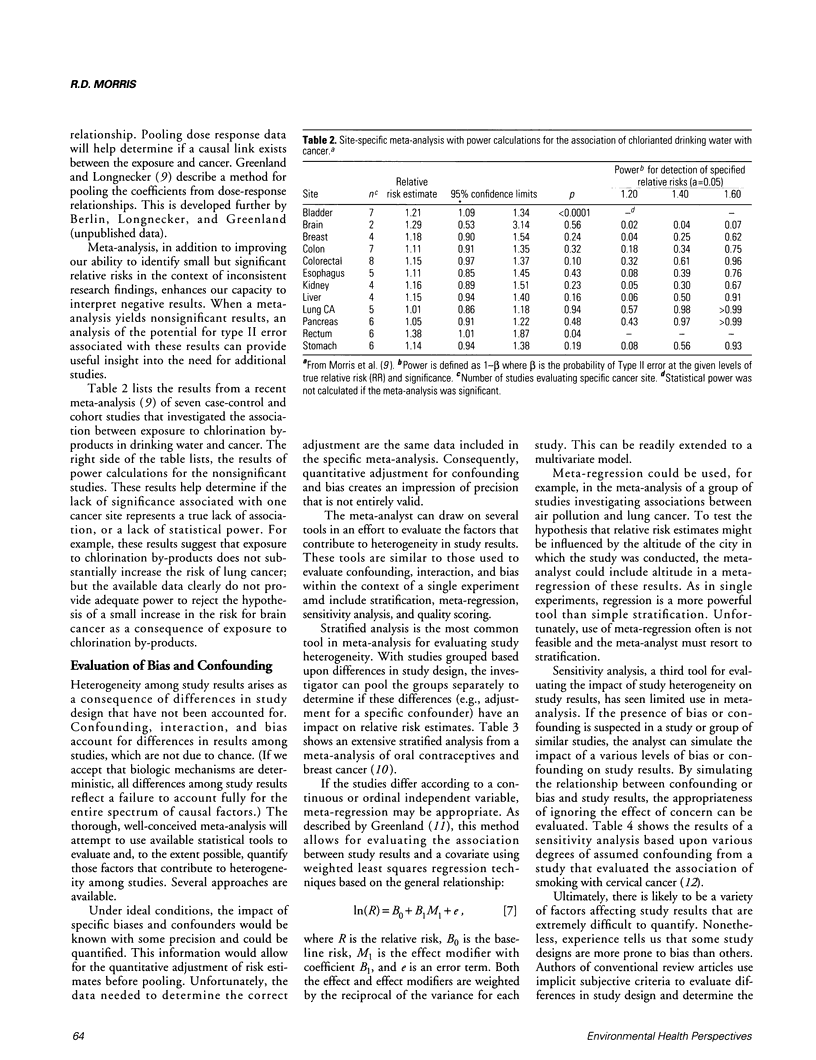
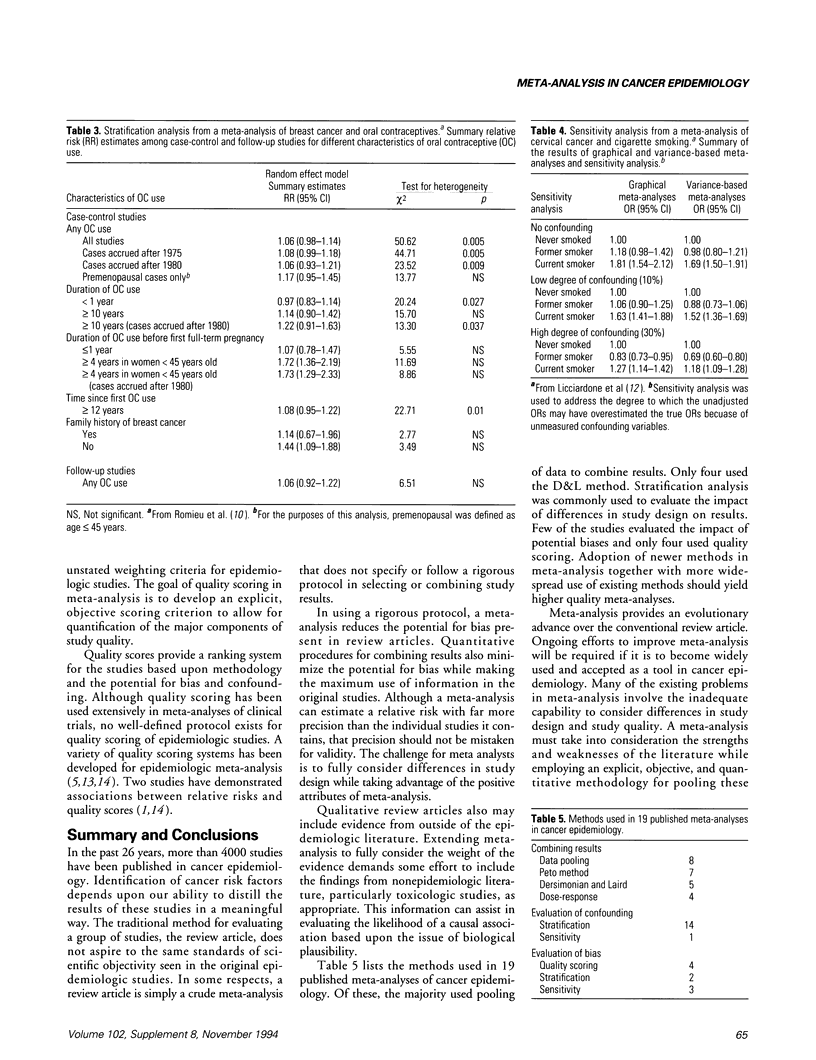

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berlin J. A., Colditz G. A. A meta-analysis of physical activity in the prevention of coronary heart disease. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Oct;132(4):612–628. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DerSimonian R., Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986 Sep;7(3):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickersin K., Min Y. I., Meinert C. L. Factors influencing publication of research results. Follow-up of applications submitted to two institutional review boards. JAMA. 1992 Jan 15;267(3):374–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenland S., Longnecker M. P. Methods for trend estimation from summarized dose-response data, with applications to meta-analysis. Am J Epidemiol. 1992 Jun 1;135(11):1301–1309. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenland S. Quantitative methods in the review of epidemiologic literature. Epidemiol Rev. 1987;9:1–30. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licciardone J. C., Brownson R. C., Chang J. C., Wilkins J. R., 3rd Uterine cervical cancer risk in cigarette smokers: a meta-analytic study. Am J Prev Med. 1990 Sep-Oct;6(5):274–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker M. P., Berlin J. A., Orza M. J., Chalmers T. C. A meta-analysis of alcohol consumption in relation to risk of breast cancer. JAMA. 1988 Aug 5;260(5):652–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. D., Audet A. M., Angelillo I. F., Chalmers T. C., Mosteller F. Chlorination, chlorination by-products, and cancer: a meta-analysis. Am J Public Health. 1992 Jul;82(7):955–963. doi: 10.2105/ajph.82.7.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romieu I., Berlin J. A., Colditz G. Oral contraceptives and breast cancer. Review and meta-analysis. Cancer. 1990 Dec 1;66(11):2253–2263. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19901201)66:11<2253::aid-cncr2820661102>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer W. O., Lawrence V., Dales R., Hill G., Archer M. C., Clark P., Abenhaim L., Hardy J., Sampalis J., Pinfold S. P. Links between passive smoking and disease: a best-evidence synthesis. A report of the Working Group on Passive Smoking. Clin Invest Med. 1990 Feb;13(1):17–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita M., Kanamori M., Izuno T., Miyakawa M. Estimating a summarized odds ratio whilst eliminating publication bias in meta-analysis. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1992 Oct;22(5):354–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf S., Peto R., Lewis J., Collins R., Sleight P. Beta blockade during and after myocardial infarction: an overview of the randomized trials. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1985 Mar-Apr;27(5):335–371. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(85)80003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


