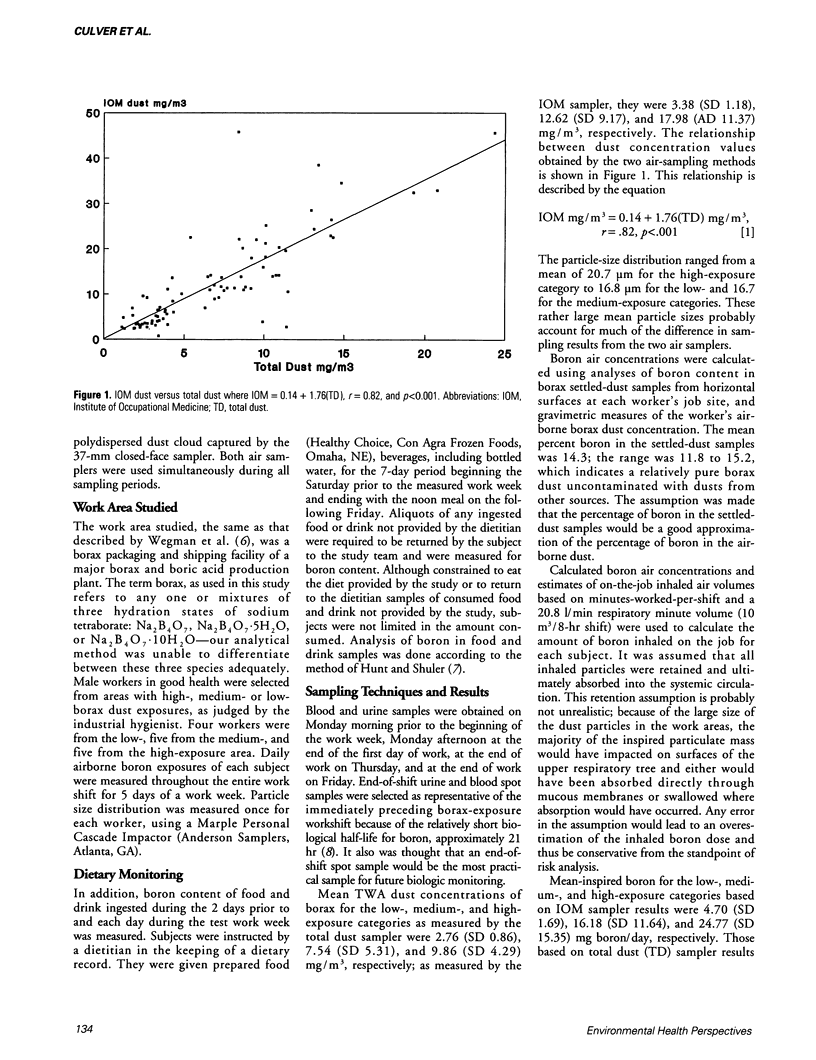
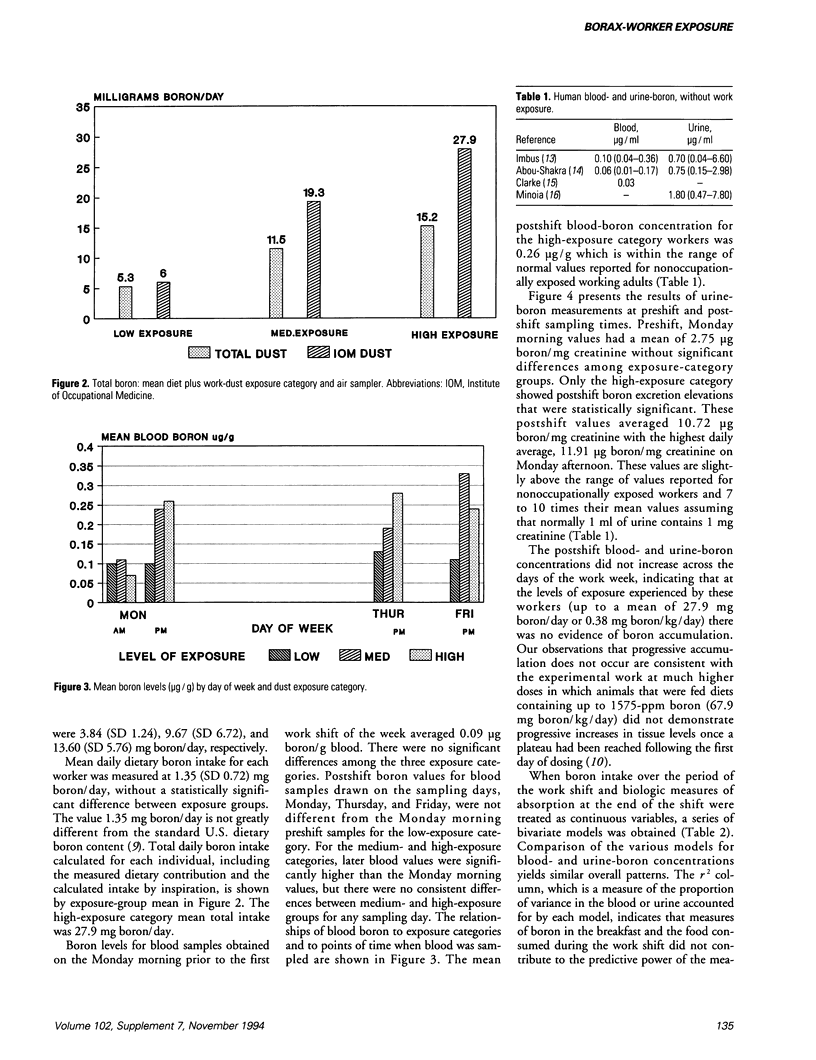
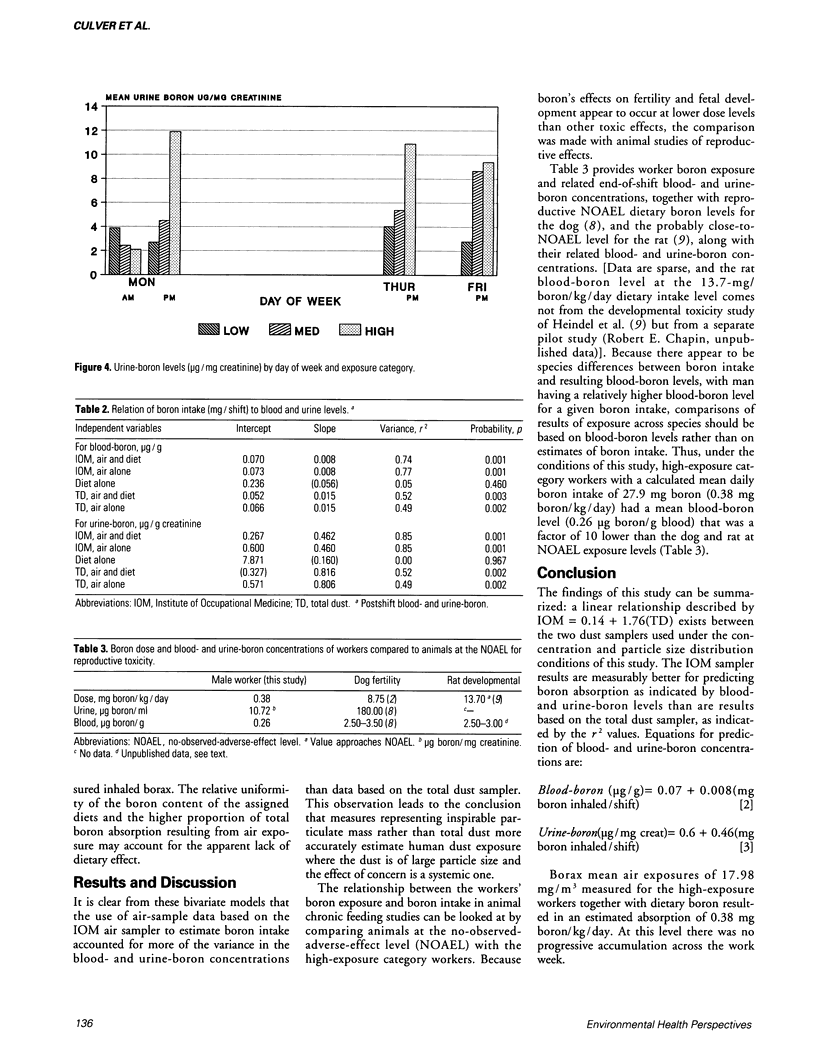
Abstract
Daily dietary-boron intake and on-the-job inspired boron were compared with blood- and urine-boron concentrations in workers engaged in packaging and shipping borax. Fourteen workers handling borax at jobs of low, medium, and high dust exposures were sampled throughout full shifts for 5 consecutive days each. Airborne borax concentrations ranged from means of 3.3 mg/m3 to 18 mg/m3, measured gravimetrically. End-of-shift mean blood-boron concentrations ranged from 0.11 to 0.26 microgram/g; end-of-shift mean urine concentrations ranged from 3.16 to 10.72 micrograms/mg creatinine. Creatinine measures were used to adjust for differences in urine-specific gravity such that 1 ml of urine contains approximately 1 mg creatinine. There was no progressive increase in end-of-shift blood- or urine-boron concentrations across the days of the week. Urine testing done at the end of the work shift gave a somewhat better estimate of borate exposure than did blood testing, was sampled more easily, and was analytically less difficult to perform. Personal air samplers of two types were used: one, the 37-mm closed-face, two-piece cassette to estimate total dust and the other, the Institute of Occupational Medicine (IOM) sampler to estimate inspirable particulate mass. Under the conditions of this study, the IOM air sampler more nearly estimated human exposure as measured by blood- and urine-boron levels than did the sampler that measured total dust.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarke W. B., Koekebakker M., Barr R. D., Downing R. G., Fleming R. F. Analysis of ultratrace lithium and boron by neutron activation and mass-spectrometric measurement of 3He and 4He. Int J Rad Appl Instrum A. 1987;38(9):735–743. doi: 10.1016/0883-2889(87)90255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heindel J. J., Price C. J., Field E. A., Marr M. C., Myers C. B., Morrissey R. E., Schwetz B. A. Developmental toxicity of boric acid in mice and rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1992 Feb;18(2):266–277. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(92)90055-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. A., Andersen J., Schou J. S. Boric acid single dose pharmacokinetics after intravenous administration to man. Arch Toxicol. 1984 Mar;55(1):64–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00316588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. A., Schou J. S., Aggerbeck B. Gastro-intestinal absorption and in vitro release of boric acid from water-emulsifying ointments. Food Chem Toxicol. 1984 Jan;22(1):49–53. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(84)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku W. W., Chapin R. E., Moseman R. F., Brink R. E., Pierce K. D., Adams K. Y. Tissue disposition of boron in male Fischer rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;111(1):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(91)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minoia C., Sabbioni E., Apostoli P., Pietra R., Pozzoli L., Gallorini M., Nicolaou G., Alessio L., Capodaglio E. Trace element reference values in tissues from inhabitants of the European community. I. A study of 46 elements in urine, blood and serum of Italian subjects. Sci Total Environ. 1990 Jun;95:89–105. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(90)90055-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseman R. F. Chemical disposition of boron in animals and humans. Environ Health Perspect. 1994 Nov;102 (Suppl 7):113–117. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102s7113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegman D. H., Eisen E. A., Hu X., Woskie S. R., Smith R. G., Garabrant D. H. Acute and chronic respiratory effects of sodium borate particulate exposures. Environ Health Perspect. 1994 Nov;102 (Suppl 7):119–128. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102s7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir R. J., Jr, Fisher R. S. Toxicologic studies on borax and boric acid. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1972 Nov;23(3):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(72)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


