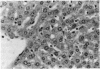
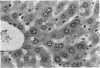
Abstract
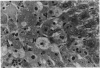
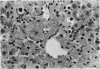
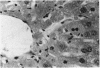
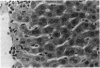
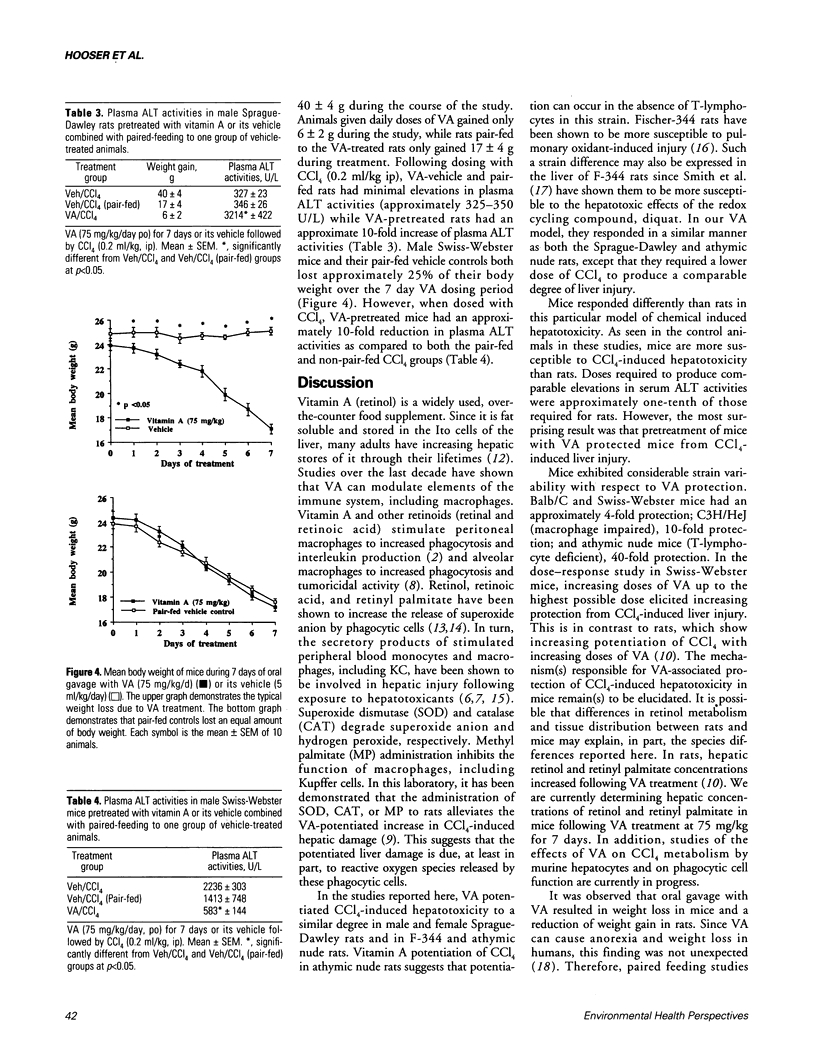
Vitamin A (VA, retinol) has been shown to modulate cells of the immune system. When rats are pretreated with VA (75 mg/kg/day) for 7 days, there is greatly potentiated liver damage upon subsequent exposure to hepatotoxicants such as CCl4. This potentiated damage can be blocked by superoxide dismutase or catalase, suggesting that reactive oxygen species are playing a major role in the increased liver injury. The studies reported here examined VA-induced modulation of CCl4 hepatotoxicity in different strains of male rats, female rats, and different strains of male mice. Also, the role of VA-induced weight loss on potentiation of CCl4 injury was investigated. Rats or mice were dosed with VA (retinol) at 75 mg/kg/day, po, for 7 days. In an additional VA dose-response study, mice were given VA at 18.8, 37.5, or 75 mg/kg/day, po, for 7 days. On day 8 they were given a dose of CCl4 which elicited mild hepatic damage. On day 9 they were necropsied. Male and female Sprague-Dawley rats, and male Fischer-344 and athymic nude rats pretreated with VA had an approximately 10-fold increase in liver damage as compared to vehicle controls. Pretreatment of male Balb/C, C3H/HeJ, Swiss-Webster, or athymic nude mice resulted in a marked reduction of CCl4-induced hepatic damage. In the dose-response study in mice, increasing doses of VA elicited increasing amounts of protection from CCl4-induced liver injury. Paired feeding studies revealed that VA-induced weight loss (or decreased weight gain) had no effect on subsequent VA-induced potentiation (rats) or protection (mice) from hepatic damage caused by CCl4.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badwey J. A., Robinson J. M., Curnutte J. T., Karnovsky M. J., Karnovsky M. L. Retinoids stimulate the release of superoxide by neutrophils and change their morphology. J Cell Physiol. 1986 May;127(2):223–228. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041270206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathcock J. N., Hattan D. G., Jenkins M. Y., McDonald J. T., Sundaresan P. R., Wilkening V. L. Evaluation of vitamin A toxicity. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990 Aug;52(2):183–202. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/52.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He L. S., Chang S. W., Ortiz de Montellano P., Burke T. J., Voelkel N. F. Lung injury in Fischer but not Sprague-Dawley rats after short-term hyperoxia. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):L451–L458. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.259.6.L451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemilä H., Wikström M. Retinoids activate superoxide production by polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Mar;21(3):227–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskin D. L. Nonparenchymal cells and hepatotoxicity. Semin Liver Dis. 1990 Nov;10(4):293–304. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren D. S. The luxus vitamins--A and B12. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Aug;34(8):1611–1616. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.8.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriguchi S., Werner L., Watson R. R. High dietary vitamin A (retinyl palmitate) and cellular immune functions in mice. Immunology. 1985 Sep;56(1):169–177. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiratori Y., Kawase T., Shiina S., Okano K., Sugimoto T., Teraoka H., Matano S., Matsumoto K., Kamii K. Modulation of hepatotoxicity by macrophages in the liver. Hepatology. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):815–821. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. V., Hughes H., Lauterburg B. H., Mitchell J. R. Oxidant stress and hepatic necrosis in rats treated with diquat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Oct;235(1):172–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana K., Sone S., Tsubura E., Kishino Y. Stimulatory effect of vitamin A on tumoricidal activity of rat alveolar macrophages. Br J Cancer. 1984 Mar;49(3):343–348. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- elSisi A. E., Hall P., Sim W. L., Earnest D. L., Sipes I. G. Characterization of vitamin A potentiation of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1993 Apr;119(2):280–288. doi: 10.1006/taap.1993.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]