Abstract
Ionizing radiation produces a variety of damaging insults to nucleic acids, including the promutagenic lesion 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine. In the present study, the 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine content of peripheral blood leukocyte DNA isolated from individuals exposed to therapeutic doses of ionizing radiation was determined by a HPLC-coupled 32P-postlabeling assay. Peripheral blood leukocyte DNA from individuals irradiated with 180-200 cGy were observed to contain 2-4.5 times as much 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine as that from unexposed individuals. These results were confirmed by the use of a HPLC-coupled electrochemical detection system. Thus, human exposure to ionizing radiation significantly increased the circulating leukocyte DNA content of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine.
Full text
PDF
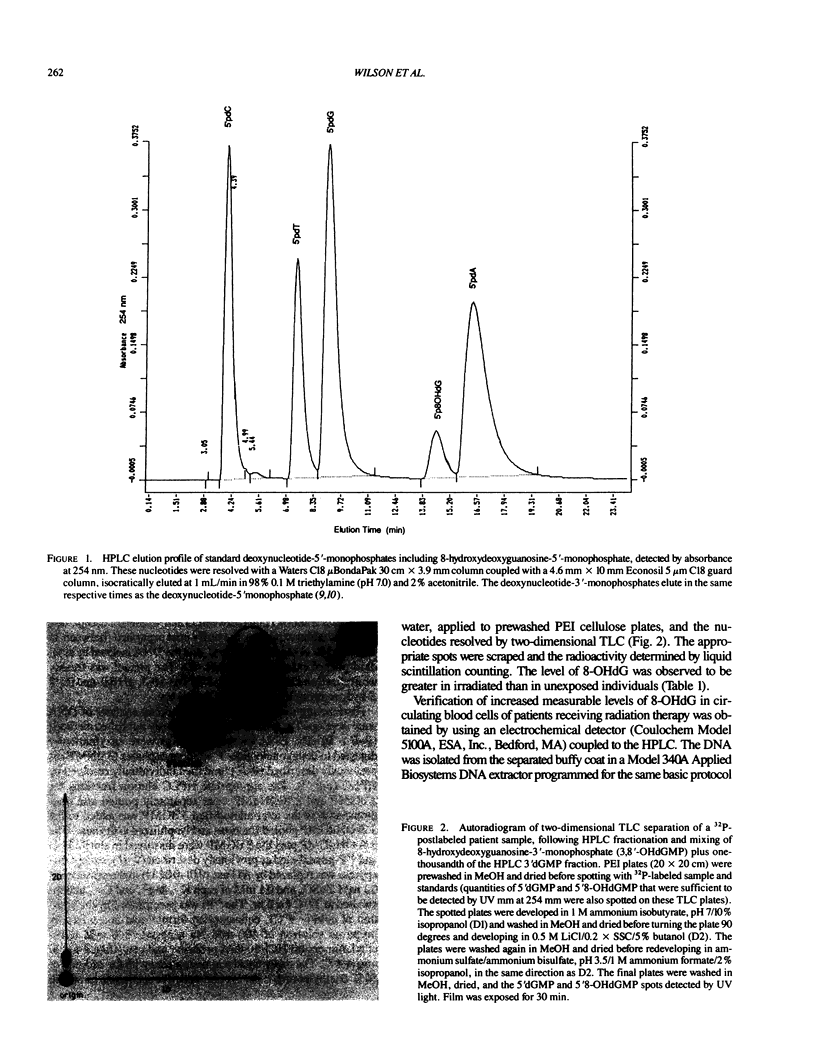

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Floyd R. A. Role of oxygen free radicals in carcinogenesis and brain ischemia. FASEB J. 1990 Jun;4(9):2587–2597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Crain P. F., Kuchino Y., Nishimura S., Ootsuyama A., Tanooka H. Formation of 8-hydroxyguanine moiety in cellular DNA by agents producing oxygen radicals and evidence for its repair. Carcinogenesis. 1986 Nov;7(11):1849–1851. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.11.1849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter C., Park J. W., Ames B. N. Normal oxidative damage to mitochondrial and nuclear DNA is extensive. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6465–6467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibutani S., Takeshita M., Grollman A. P. Insertion of specific bases during DNA synthesis past the oxidation-damaged base 8-oxodG. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):431–434. doi: 10.1038/349431a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchou J., Kasai H., Shibutani S., Chung M. H., Laval J., Grollman A. P., Nishimura S. 8-oxoguanine (8-hydroxyguanine) DNA glycosylase and its substrate specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4690–4694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. F. DNA damage produced by ionizing radiation in mammalian cells: identities, mechanisms of formation, and reparability. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:95–125. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60611-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V. L., Basu A. K., Essigmann J. M., Smith R. A., Harris C. C. O6-alkyldeoxyguanosine detection by 32P-postlabeling and nucleotide chromatographic analysis. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 15;48(8):2156–2161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V. L., Smith R. A., Autrup H., Krokan H., Musci D. E., Le N. N., Longoria J., Ziska D., Harris C. C. Genomic 5-methylcytosine determination by 32P-postlabeling analysis. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):275–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood M. L., Dizdaroglu M., Gajewski E., Essigmann J. M. Mechanistic studies of ionizing radiation and oxidative mutagenesis: genetic effects of a single 8-hydroxyguanine (7-hydro-8-oxoguanine) residue inserted at a unique site in a viral genome. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 31;29(30):7024–7032. doi: 10.1021/bi00482a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]