Abstract
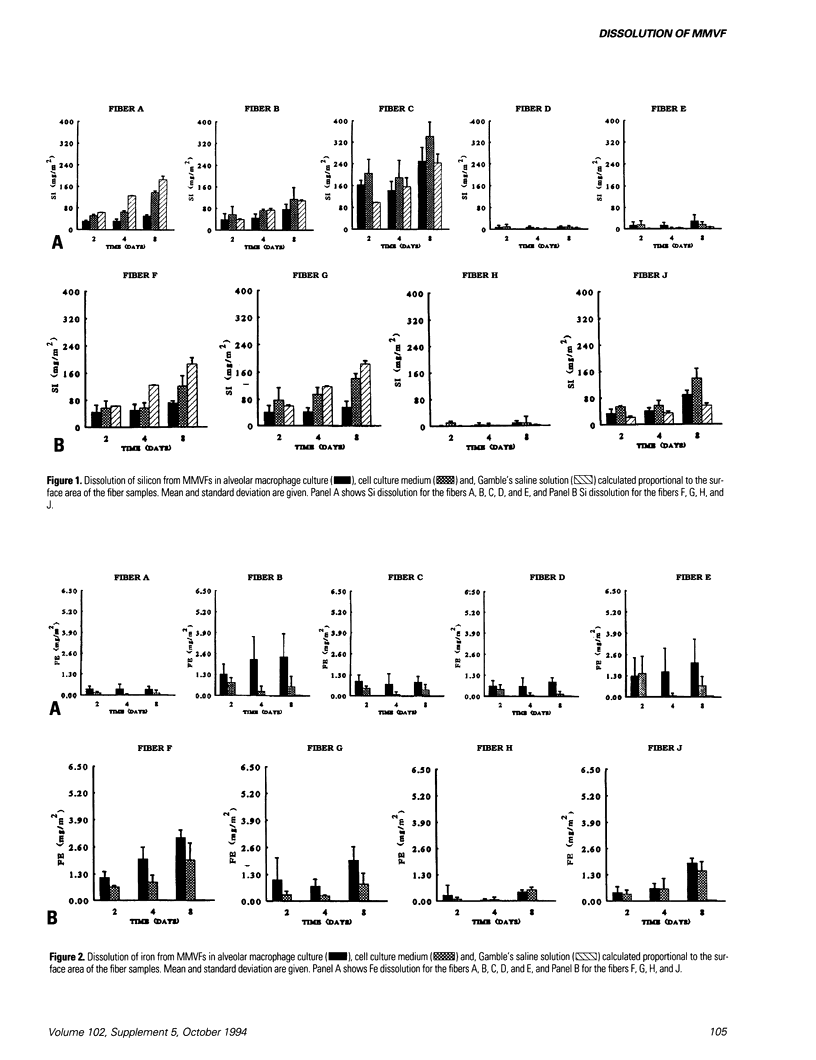
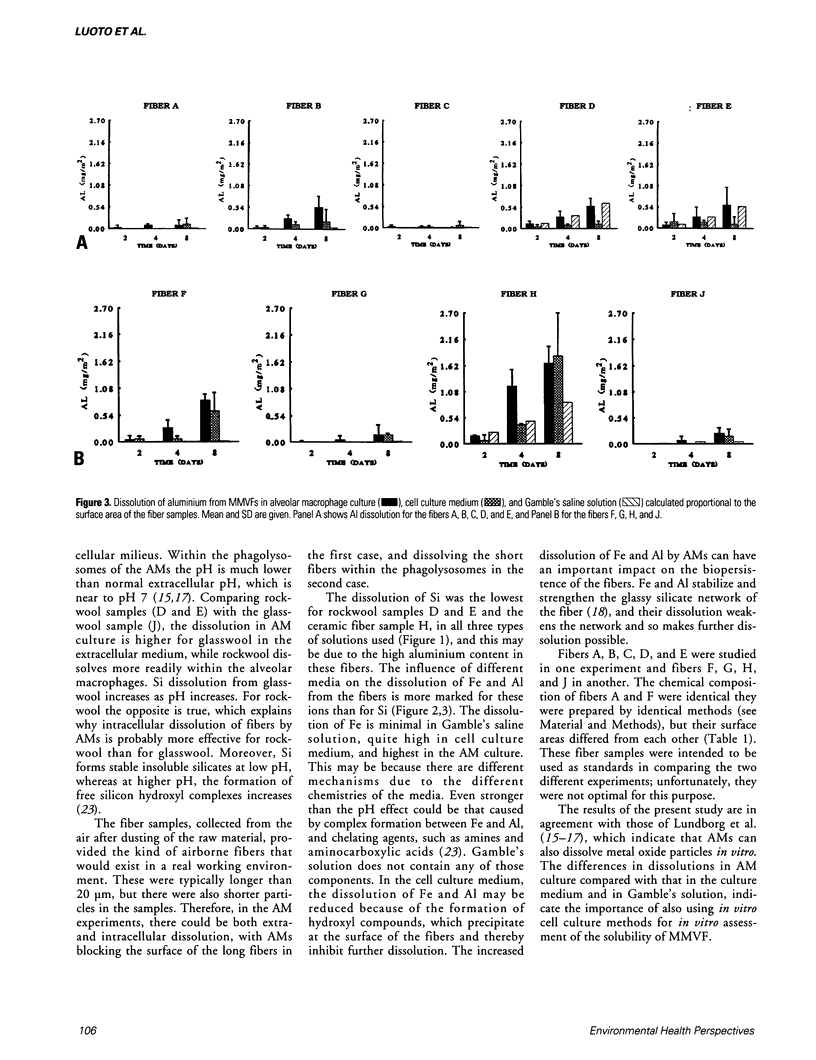
The effect of different chemical compositions of man-made vitreous fibers (MMVF) on their dissolution by alveolar macrophages (AM) in culture and in Gamble's solution was studied. The fibers were exposed to cultured rat AMs, culture medium alone; or Gamble's saline solution for 2, 4, or 8 days. The dissolution of the fibers was studied by measuring the amount of silicon (Si), iron (Fe), and aluminum (Al) in each medium. The AMs in culture dissolved Fe and Al from the fibers but the dissolution of Si was more marked in the cell culture medium without cells and in the Gamble's solution. The dissolution of Si, Fe, and Al was different for different fibers, and increased as a function of time. The Fe and Al content of the fibers correlated negatively with the dissolution of Si by AMs from the MMVF, i.e., when the content of Fe and Al of the fibers increased the dissolution of Si decreased. These results suggest that the chemical composition of MMVFs has a marked effect on their dissolution. AMs seem to affect the dissolution of Fe and Al from the fibers. This suggests that in vitro models with cells in the media rather than only culture media or saline solutions would be preferable in dissolution studies of MMVFs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brain J. D., Frank N. R. Recovery of free cells from rat lungs by repeated washings. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Jul;25(1):63–69. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.25.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundborg M., Eklund A., Lind B., Camner P. Dissolution of metals by human and rabbit alveolar macrophages. Br J Ind Med. 1985 Sep;42(9):642–645. doi: 10.1136/oem.42.9.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundborg M., Holma B. In vitro phagocytosis of fungal spores by rabbit lung macrophages. Sabouraudia. 1972 Jul;10(2):152–156. doi: 10.1080/00362177285190301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundborg M., Lind B., Camner P. Ability of rabbit alveolar macrophages to dissolve metals. Exp Lung Res. 1984;7(1):11–22. doi: 10.3109/01902148409087905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYRVIK Q., LEAKE E. S., FARISS B. Studies on pulmonary alveolar macrophages from the normal rabbit: a technique to procure them in a high state of purity. J Immunol. 1961 Feb;86:128–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marafante E., Lundborg M., Vahter M., Camner P. Dissolution of two arsenic compounds by rabbit alveolar macrophages in vitro. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1987 Apr;8(3):382–388. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(87)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pott F. Problems in defining carcinogenic fibres. Ann Occup Hyg. 1987;31(4B):799–802. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/31.4b.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pott F., Schlipköter H. W., Roller M., Rippe R. M., Germann P. G., Mohr U., Bellmann B. Kanzerogenität von Glasfasern mit unterschiedlicher Beständigkeit. Zentralbl Hyg Umweltmed. 1990 May;189(6):563–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurny K. R. Measurement and analysis of chemically changed mineral fibers after experiments in vitro and in vivo. Environ Health Perspect. 1983 Sep;51:343–355. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8351343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler C. S. Exposure to man-made mineral fibers: a summary of current animal data. Toxicol Ind Health. 1990 Mar;6(2):293–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


