Abstract
This paper summarizes two roundtable discussions held at the conclusion of the International Conference on Biopersistence of Respirable Synthetic Fibres and Minerals. The first round table addressed the role of biopersistence in the pathogenicity of fiber-induced disease. The panel included T. W. Hesterberg (Chairman), J.M.G. Davis, K. Donaldson, B. Fubini, N.F. Johnson, G. Oberdoerster, P. Sébastien, and D. Warheit. The second panel addressed the issue of methods for assessing biopersistence. It included R.O. McClellan (Chairman), J. Brain, A. Langer, A. Morgan, C. Morscheidt, H. Muhle, and R. Musselman. The two chairmen acknowledge the excellent contributions of all the members of the panels, whose comments formed the basis of this summary. Nonetheless, the authors assume full responsibility for the written text, recognizing that it was not reviewed by the discussants of the two panels.—Environ Health Perspect 102(Suppl 5):277–283 (1994)
Keywords: fibers, lung cancer, mesothelioma, biopersistence, fiber dissolution, risk, hazard
Full text
PDF

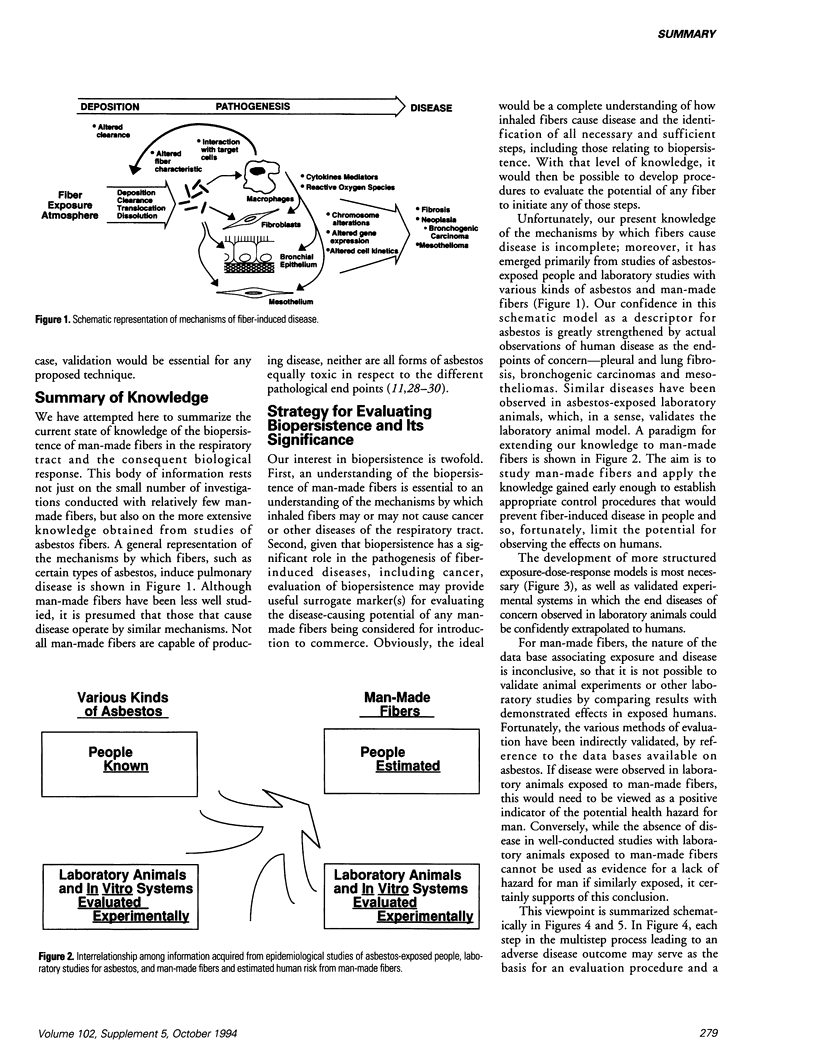
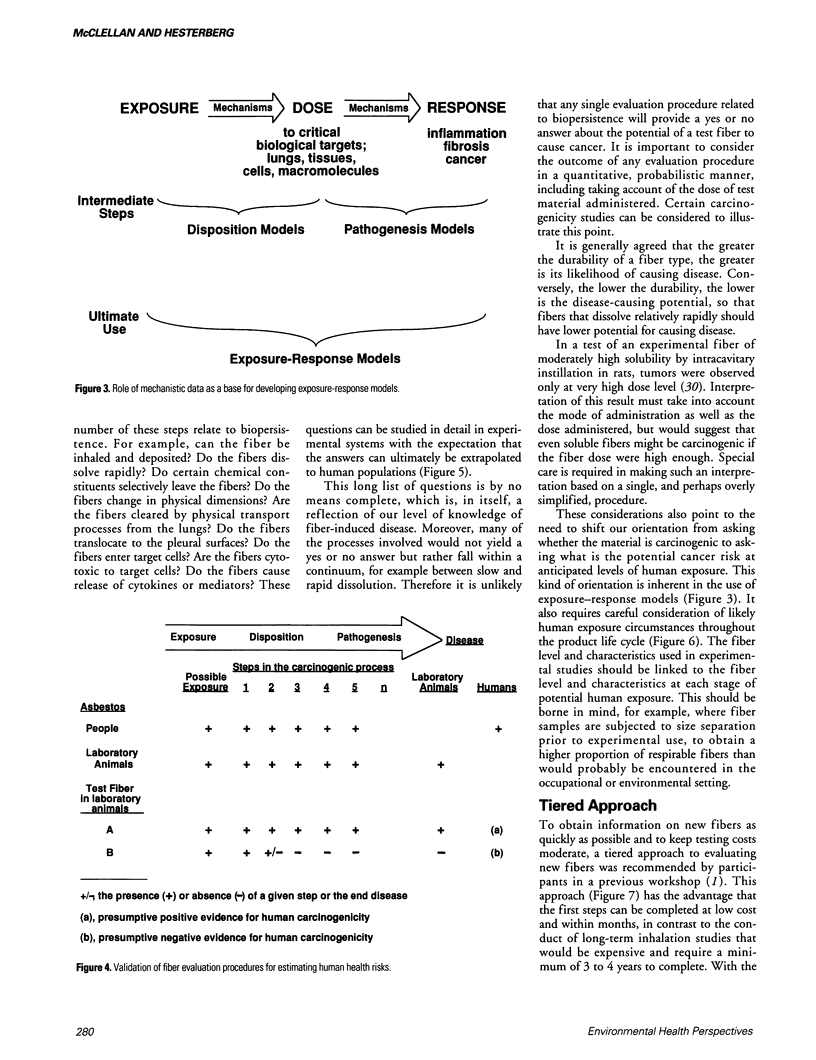
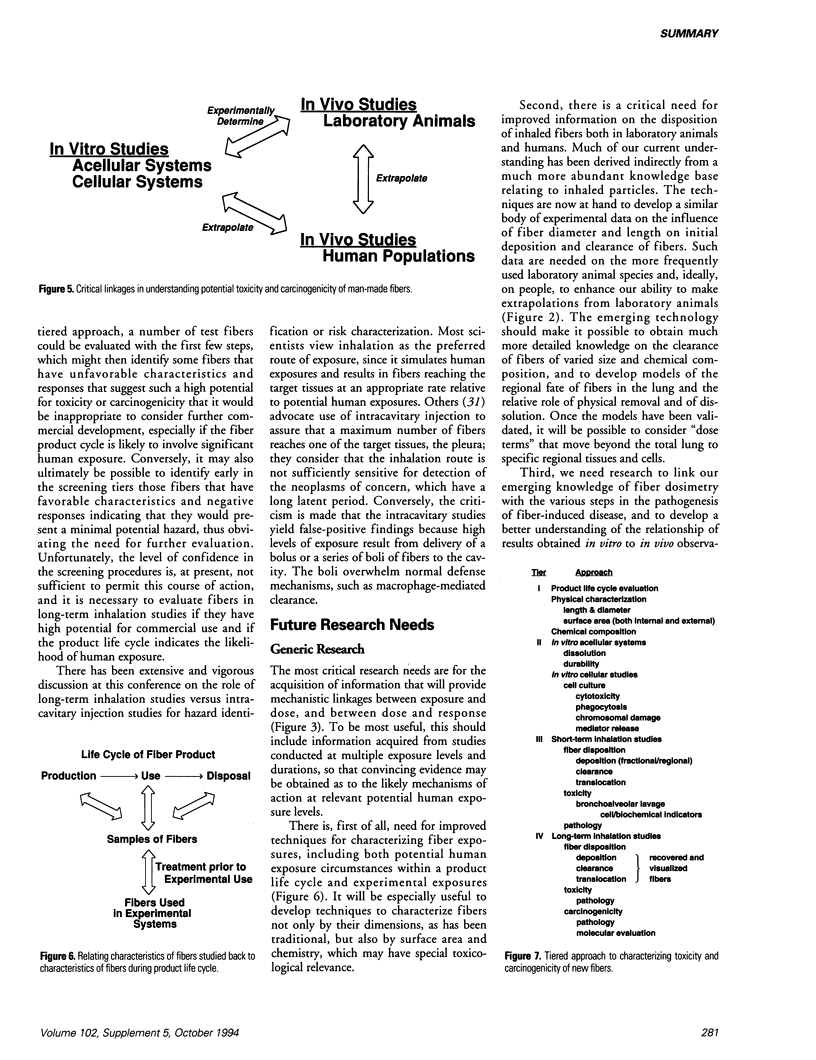


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellmann B., Muhle H., Pott F., König H., Klöppel H., Spurny K. Persistence of man-made mineral fibres (MMMF) and asbestos in rat lungs. Ann Occup Hyg. 1987;31(4B):693–709. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/31.4b.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody A. R., Hill L. H., Adkins B., Jr, O'Connor R. W. Chrysotile asbestos inhalation in rats: deposition pattern and reaction of alveolar epithelium and pulmonary macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jun;123(6):670–679. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.6.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs A. R., Stephens M., Griffiths D. M., Blight B. J., Pooley F. D. Fibre distribution in the lungs and pleura of subjects with asbestos related diffuse pleural fibrosis. Br J Ind Med. 1991 Nov;48(11):762–770. doi: 10.1136/oem.48.11.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesterberg T. W., Miiller W. C., Mast R., McConnell E. E., Bernstein D. M., Anderson R. Relationship between lung biopersistence and biological effects of man-made vitreous fibers after chronic inhalation in rats. Environ Health Perspect. 1994 Oct;102 (Suppl 5):133–137. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102s5133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesterberg T. W., Miiller W. C., McConnell E. E., Chevalier J., Hadley J. G., Bernstein D. M., Thevenaz P., Anderson R. Chronic inhalation toxicity of size-separated glass fibers in Fischer 344 rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1993 May;20(4):464–476. doi: 10.1006/faat.1993.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. P., Barras C. E., Griffith F. D., Waritz R. S., Lapin C. A. Comparative pulmonary responses to inhaled inorganic fibers with asbestos and fiberglass. Environ Res. 1981 Feb;24(1):167–191. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(81)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippmann M. Asbestos exposure indices. Environ Res. 1988 Jun;46(1):86–106. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(88)80061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippmann M., Yeates D. B., Albert R. E. Deposition, retention, and clearance of inhaled particles. Br J Ind Med. 1980 Nov;37(4):337–362. doi: 10.1136/oem.37.4.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClellan R. O., Miller F. J., Hesterberg T. W., Warheit D. B., Bunn W. B., Kane A. B., Lippmann M., Mast R. W., McConnell E. E., Reinhardt C. F. Approaches to evaluating the toxicity and carcinogenicity of man-made fibers: summary of a workshop held November 11-13, 1991, Durham, North Carolina. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;16(3):321–364. doi: 10.1016/0273-2300(92)90011-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Black A., Evans N., Holmes A., Pritchard J. N. Deposition of sized glass fibres in the respiratory tract of the rat. Ann Occup Hyg. 1980;23(4):353–366. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/23.4.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Holmes A. Solubility of asbestos and man-made mineral fibers in vitro and in vivo: its significance in lung disease. Environ Res. 1986 Apr;39(2):475–484. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(86)80071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pott F., Roller M., Kamino K., Bellmann B. Significance of durability of mineral fibers for their toxicity and carcinogenic potency in the abdominal cavity of rats in comparison with the low sensitivity of inhalation studies. Environ Health Perspect. 1994 Oct;102 (Suppl 5):145–150. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102s5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger R. B. Comparative deposition of inhaled aerosols in experimental animals and humans: a review. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1985;15(2):197–214. doi: 10.1080/15287398509530647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton M. F., Layard M., Tegeris A., Miller E., May M., Morgan E., Smith A. Relation of particle dimension to carcinogenicity in amphibole asbestoses and other fibrous minerals. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Nov;67(5):965–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timbrell V. Human exposure to asbestos: dust controls and standards. The inhalation of fibrous dusts. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Dec 31;132(1):255–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb41107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warheit D. B., Hwang H. C., Achinko L. Assessments of lung digestion methods for recovery of fibers. Environ Res. 1991 Apr;54(2):183–193. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(05)80100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warheit D. B., Kellar K. A., Hartsky M. A. Pulmonary cellular effects in rats following aerosol exposures to ultrafine Kevlar aramid fibrils: evidence for biodegradability of inhaled fibrils. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;116(2):225–239. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(92)90302-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


