Abstract
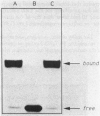
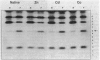
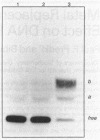
Metal replacement studies were used to investigate the metal requirement of a bacterially expressed polypeptide encoding the zinc finger DNA binding domain of the estrogen receptor. Apopolypeptide was generated by dialysis of native polypeptide against low-pH buffer under reducing conditions. Specific DNA binding can be restored by refolding the apopolypeptide in the presence of ionic zinc, cadmium, or cobalt. However, refolding in the presence of copper or nickel fails to regenerate DNA binding activity. While cobalt-reconstituted polypeptide has a reduced affinity for its AGGTCA-binding site compared to zinc- or cadmium-polypeptide, it has the surprising property of increased cooperative DNA binding. Our work indicates that metal substitution results in a range of effects upon DNA binding in vitro. The potential biological significance of metal substitution in vivo is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aruoma O. I., Halliwell B., Gajewski E., Dizdaroglu M. Copper-ion-dependent damage to the bases in DNA in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):601–604. doi: 10.1042/bj2730601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunce G. E., Vessal M. Effect of zinc and/or pyridoxine deficiency upon oestrogen retention and oestrogen receptor distribution in the rat uterus. J Steroid Biochem. 1987 Mar;26(3):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(87)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou S. H. DNA- and protein-scission activities of ascorbate in the presence of copper ion and a copper-peptide complex. J Biochem. 1983 Oct;94(4):1259–1267. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Bredt D. S., Pabo C. O. Tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus forms a metal-linked dimer. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):70–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2832944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P., Luisi B. F., Korszun Z. R., Basavappa R., Sigler P. B., Yamamoto K. R. The function and structure of the metal coordination sites within the glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):543–546. doi: 10.1038/334543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchens T. W., Li C. M., Sato Y., Yip T. T. Multiple DNA-binding estrogen receptor forms resolved by interaction with immobilized metal ions. Identification of a metal-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17206–17212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härd T., Kellenbach E., Boelens R., Maler B. A., Dahlman K., Freedman L. P., Carlstedt-Duke J., Yamamoto K. R., Gustafsson J. A., Kaptein R. Solution structure of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):157–160. doi: 10.1126/science.2115209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Schorpp M., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. An estrogen-responsive element derived from the 5' flanking region of the Xenopus vitellogenin A2 gene functions in transfected human cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klock G., Strähle U., Schütz G. Oestrogen and glucocorticoid responsive elements are closely related but distinct. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):734–736. doi: 10.1038/329734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Predki P. F., Sarkar B. Effect of replacement of "zinc finger" zinc on estrogen receptor DNA interactions. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5842–5846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe J. W., Neuhaus D., Rhodes D. Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of the oestrogen receptor. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):458–461. doi: 10.1038/348458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunderman F. W., Jr, Barber A. M. Finger-loops, oncogenes, and metals. Claude Passmore Brown memorial lecture. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1988 Jul-Aug;18(4):267–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiesen H. J., Bach C. Transition metals modulate DNA-protein interactions of SP1 zinc finger domains with its cognate target site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 30;176(2):551–557. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80219-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkeshelashvili L. K., McBride T., Spence K., Loeb L. A. Mutation spectrum of copper-induced DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6401–6406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]