Abstract
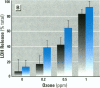
In this study, we compared the cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of hydrogen peroxide and ozone on cultured human airway epithelial cells in primary culture. Both agents caused a dose-dependent loss in the replicative ability of epithelial cells and at higher levels of exposure caused acute cytotoxicity as measured by release of lactate dehydrogenase. Differences were seen, however, between the agents' effects with regard to induction of DNA single strand breaks as measured by alkaline elution:; whereas single-strand breaks were detected in significant amounts at concentration of hydrogen peroxide that cause acute cytotoxicity, none were detected at any of the levels of ozone exposure examined. A difference was also seen in the ability of the iron chelator deferoxamine to protect cells from the effect of the two oxidants. Preincubation of cultures with deferoxamine appreciably attenuated the toxicity of hydrogen peroxide but not of ozone. These data suggest that ozone has significant toxic effects on bronchial epithelial cells not mediated through the generation of hydrogen peroxide or hydroxyl radical. Furthermore, the data indicate that the inhibiting action of ozone on cell replicative ability is not mediated through a mechanism related to DNA single strand breaks.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Koren H. S., Devlin R. B., Graham D. E., Mann R., McGee M. P., Horstman D. H., Kozumbo W. J., Becker S., House D. E., McDonnell W. F. Ozone-induced inflammation in the lower airways of human subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Feb;139(2):407–415. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozumbo W. J., Agarwal S. Induction of DNA damage in cultured human lung cells by tobacco smoke arylamines exposed to ambient levels of ozone. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Dec;3(6):611–618. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/3.6.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden M. C., Friedman M., Hanley N., Siegler E., Quay J., Becker S., Devlin R., Koren H. S. Chemical nature and immunotoxicological properties of arachidonic acid degradation products formed by exposure to ozone. Environ Health Perspect. 1993 Jun;101(2):154–164. doi: 10.1289/ehp.93101154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor W. A., Church D. F. Aldehydes, hydrogen peroxide, and organic radicals as mediators of ozone toxicity. Free Radic Biol Med. 1991;11(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(91)90186-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor W. A., Das B., Church D. F. The ozonation of unsaturated fatty acids: aldehydes and hydrogen peroxide as products and possible mediators of ozone toxicity. Chem Res Toxicol. 1991 May-Jun;4(3):341–348. doi: 10.1021/tx00021a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddel R. R., Ke Y., Gerwin B. I., McMenamin M. G., Lechner J. F., Su R. T., Brash D. E., Park J. B., Rhim J. S., Harris C. C. Transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells by infection with SV40 or adenovirus-12 SV40 hybrid virus, or transfection via strontium phosphate coprecipitation with a plasmid containing SV40 early region genes. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1904–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schraufstatter I. U., Hyslop P. A., Hinshaw D. B., Spragg R. G., Sklar L. A., Cochrane C. G. Hydrogen peroxide-induced injury of cells and its prevention by inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4908–4912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer J., Bigby B. G., Stulbarg M., Holtzman M. J., Nadel J. A., Ueki I. F., Leikauf G. D., Goetzl E. J., Boushey H. A. O3-induced change in bronchial reactivity to methacholine and airway inflammation in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Apr;60(4):1321–1326. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.4.1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spragg R. G. DNA strand break formation following exposure of bovine pulmonary artery and aortic endothelial cells to reactive oxygen products. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Jan;4(1):4–10. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.1.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. F., Blakely W. F., Joner E. I. Mammalian cells are not killed by DNA single-strand breaks caused by hydroxyl radicals from hydrogen peroxide. Radiat Res. 1985 Sep;103(3):383–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X. Y., Schofield B. H., Croxton T., Takahashi N., Gabrielson E. W., Spannhake E. W. Physiologic modulation of bronchial epithelial cell barrier function by polycationic exposure. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1994 Aug;11(2):188–198. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.11.2.8049079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]