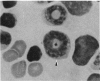
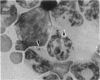
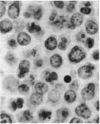
Abstract
Previous studies have revealed marked differences in the incidence of leukemia between rats and mice exposed to 1,3-butadiene that do not appear to be readily explained on the basis of pharmacokinetics or metabolism. Chronic exposure to 1,3-butadiene results in a high incidence of thymic lymphoma in B6C3F1 mice that is not observed in Sprague-Dawley rats. Studies at the Chemical Industry Institute of Toxicology have focused on evaluating the potential of endogenous ecotropic retroviral background to influence susceptibility to 1,3-butadiene leukemogenesis. These studies have compared the pathogenesis and incidence of thymic lymphoma between B6C3F1 and NIH Swiss mice. Proviral ecotropic sequences are truncated in the NIH Swiss mouse, and the virus is not expressed. Chronic exposure to 1,3-butadiene (1250 ppm) for up to 1 year resulted in a fourfold difference in the incidence of thymic lymphoma between B6C3F1 and NIH Swiss mice. These results provide presumptive evidence for retrovirus involvement since NIH Swiss mice lack ecotropic viruses and appear to be relatively resistant to induction of lymphoma by 1,3-butadiene. Other explanations appear to be less likely in light of the fact that target organ toxicity has been determined to be virtually identical between the two strains during the preleukemic phase of 1,3-butadiene exposure.
Full text
PDF
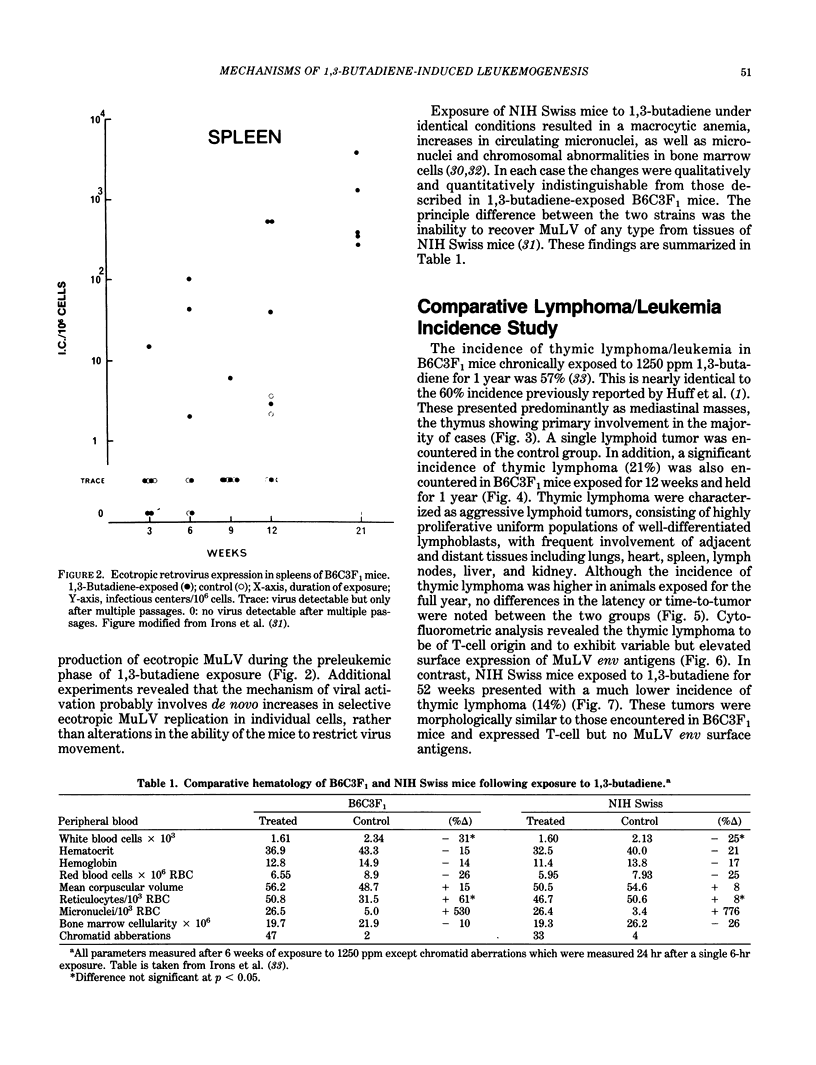
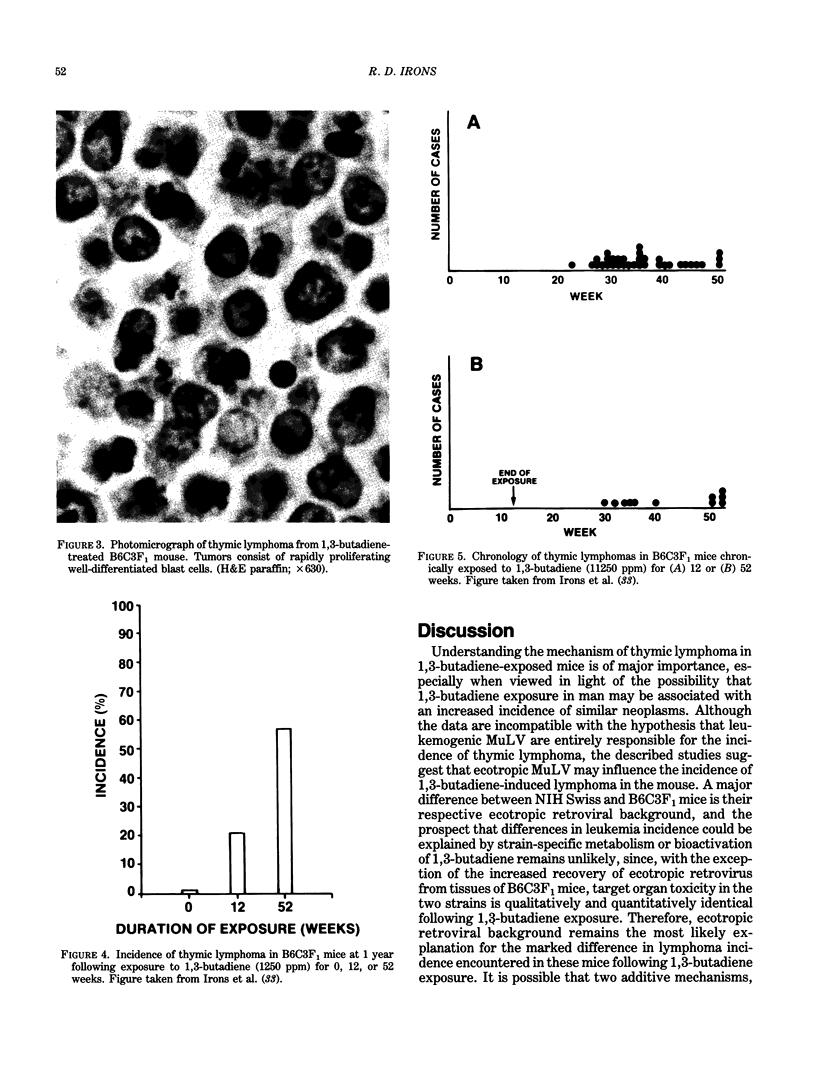
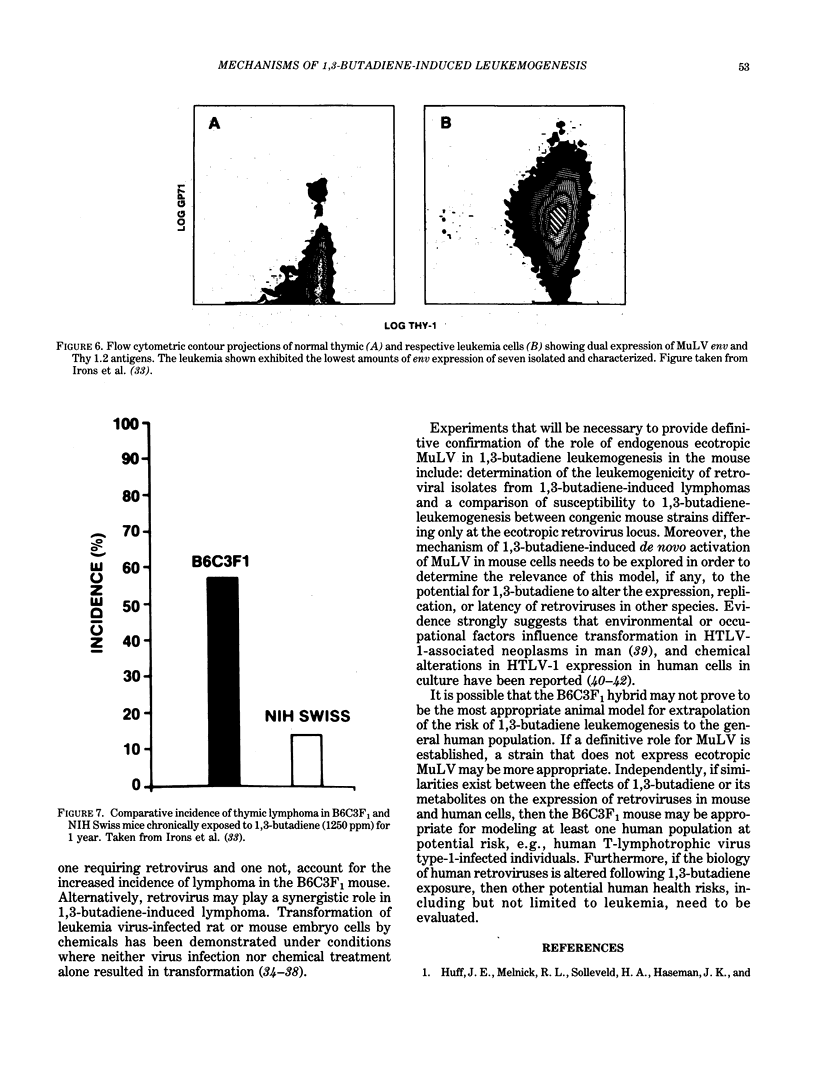


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball J. K., McCarter J. A. Repeated demonstration of a mouse leukemia virus after treatment with chemical carcinogens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Apr;46(4):751–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeslee J. R., Jr, Yamamoto N., Hinuma Y. Human T-cell leukemia virus I induction by 5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine and N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine: inhibition by retinoids, L-ascorbic acid, and DL-alpha-tocopherol. Cancer Res. 1985 Aug;45(8):3471–3476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. A., Dahl A. R., Henderson R. F., Birnbaum L. S. Species differences in the distribution of inhaled butadiene in tissues. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1987 Oct;48(10):867–872. doi: 10.1080/15298668791385723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boniver J., Declève A., Lieberman M., Honsik C., Travis M., Kaplan H. S. Marrow-thymus interactions during radiation leukemogenesis in C57BL/Ka mice. Cancer Res. 1981 Feb;41(2):390–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Cloyd M. W., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Cellular origin and role of mink cell focus-forming viruses in murine thymic lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):25–31. doi: 10.1038/295025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Structure of endogenous murine leukemia virus DNA in mouse genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5774–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinsky J., Goodenow M. M., Jackson M., Lilly F., Leinwand L., Childs G. Comparison of endogenous murine leukemia virus proviral organization and RNA expression in 3-methylcholanthrene-induced and spontaneous thymic lymphomas in RF and AKR mice. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):94–99. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.94-99.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W. Characterization of target cells for MCF viruses in AKR mice. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90512-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Evans L. H. Endogenous retroviral env expression in primary murine leukemias: lack of xenotropic antigens but presence of distinct mink cell focus-forming env subtypes correlating with ecotropic virus inoculated and mouse strain. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Jan;78(1):181–189. doi: 10.1093/jnci/78.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Gautsch J. W., Jensen F. C., Lerner R. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Biochemical evidence that MCF murine leukemia viruses are envelope (env) gene recombinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4676–4680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman A. E., Gilden R. V., Vernon M. L., Wolford R. G., Hugunin P. E., Huebner R. J. 5-Bromo-2'-deoxyuridine potentiation of transformation of rat-embryo cells induced in vitro by 3-methylcholanthrene: induction of rat leukemia virus gs antigen in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2415–2419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman A. E., Price P. J., Zimmerman E. M., Kelloff G. J., Huebner R. J. RNA tumor virus genomes as determinants of chemically-induced transformation in vitro. Bibl Haematol. 1973;39:617–634. doi: 10.1159/000427890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS L. [Serial cell-free passage of a radiation-activated mouse leukemia agent]. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jan;100(1):102–105. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenow M. M., Lilly F. Expression of differentiation and murine leukemia virus antigens on cells of primary tumors and cell lines derived from chemically induced lymphomas of RF/J mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7612–7616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haran-Ghera N., Peled A. The mechanism of radiation action in leukaemogenesis. Isolation of a leukaemogenic filtrable agent from tissues of irradiated and normal C57BL mice. Br J Cancer. 1967 Dec;21(4):730–738. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1967.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Nagata K., Hanaoka M., Nakai M., Matsumoto T., Kinoshita K. I., Shirakawa S., Miyoshi I. Adult T-cell leukemia: antigen in an ATL cell line and detection of antibodies to the antigen in human sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6476–6480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff J. E., Melnick R. L., Solleveld H. A., Haseman J. K., Powers M., Miller R. A. Multiple organ carcinogenicity of 1,3-butadiene in B6C3F1 mice after 60 weeks of inhalation exposure. Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):548–549. doi: 10.1126/science.3966163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igel H. J., Huebner R. J., Turner H. C., Kotin P., Falk H. L. Mouse leukemia virus activation by chemical carcinogens. Science. 1969 Dec 26;166(3913):1624–1626. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3913.1624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irons R. D., Cathro H. P., Stillman W. S., Steinhagen W. H., Shah R. S. Susceptibility to 1,3-butadiene-induced leukemogenesis correlates with endogenous ecotropic retroviral background in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;101(1):170–176. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(89)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irons R. D., Oshimura M., Barrett J. C. Chromosome aberrations in mouse bone marrow cells following in vivo exposure to 1,3-butadiene. Carcinogenesis. 1987 Nov;8(11):1711–1714. doi: 10.1093/carcin/8.11.1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irons R. D., Smith C. N., Stillman W. S., Shah R. S., Steinhagen W. H., Leiderman L. J. Macrocytic-megaloblastic anemia in male B6C3F1 mice following chronic exposure to 1,3-butadiene. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1986 Mar 30;83(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(86)90326-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irons R. D., Smith C. N., Stillman W. S., Shah R. S., Steinhagen W. H., Leiderman L. J. Macrocytic-megaloblastic anemia in male NIH Swiss mice following repeated exposure to 1,3-butadiene. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1986 Sep 30;85(3):450–455. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(86)90352-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irons R. D., Stillman W. S., Cloyd M. W. Selective activation of endogenous ecotropic retrovirus in hematopoietic tissues of B6C3F1 mice during the preleukemic phase of 1,3-butadiene exposure. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):457–462. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. S. On the natural history of the murine leukemias: presidential address. Cancer Res. 1967 Aug;27(8):1325–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN M., KAPLAN H. S. Leukemogenic activity of filtrates from radiation-induced lymphoid tumors of mice. Science. 1959 Aug 14;130(3372):387–388. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3372.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiderman L. J., Stillman W. S., Shah R. S., Steinhagen W. H., Irons R. D. Altered hematopoietic stem cell development in male B6C3F1 mice following exposure to 1,3-butadiene. Exp Mol Pathol. 1986 Feb;44(1):50–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(86)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Spirtas R., Gamble J. F., Tousey P. M. Mortality among rubber workers: Relationship to specific jobs. J Occup Med. 1976 Mar;18(3):178–185. doi: 10.1097/00043764-197603000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinhardt T. J., Lemen R. A., Crandall M. S., Young R. J. Environmental epidemiologic investigation of the styrene-butadiene rubber industry. Mortality patterns with discussion of the hematopoietic and lymphatic malignancies. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1982 Dec;8(4):250–259. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra N. K., Pant K. J., Thomas F. O., Price P. J. Chemical-viral co-carcinogenesis: requirement for leukemia virus expression in accelerated transformation. Int J Cancer. 1976 Dec 15;18(6):852–858. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. J., Suk W. A., Peters R. L., Gilden R. V., Huebner R. J. Chemical transformation of rat cells infected with xenotropic type-C RNA virus and its suppression by virus-specific antiserum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):579–581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim J. S., Cho H. Y., Rabstein L., Gordon R. J., Bryan R. J., Gardner M. B., Huebner R. J. Transformation of mouse cells infected with AKR leukaemia virus induced by smog extracts. Nature. 1972 Sep 8;239(5367):103–107. doi: 10.1038/239103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UPTON A. C., WOLFF F. F., FURTH J., KIMBALL A. W. A comparison of the induction of myeloid and lymphoid leukemias in x-radiated RF mice. Cancer Res. 1958 Aug;18(7):842–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyth-Dreese F. A., de Vries J. E. Enhanced expression of human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus in neoplastic T cells induced to proliferate by phorbol ester and interleukin-2. Int J Cancer. 1983 Jul 15;32(1):53–59. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910320109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]