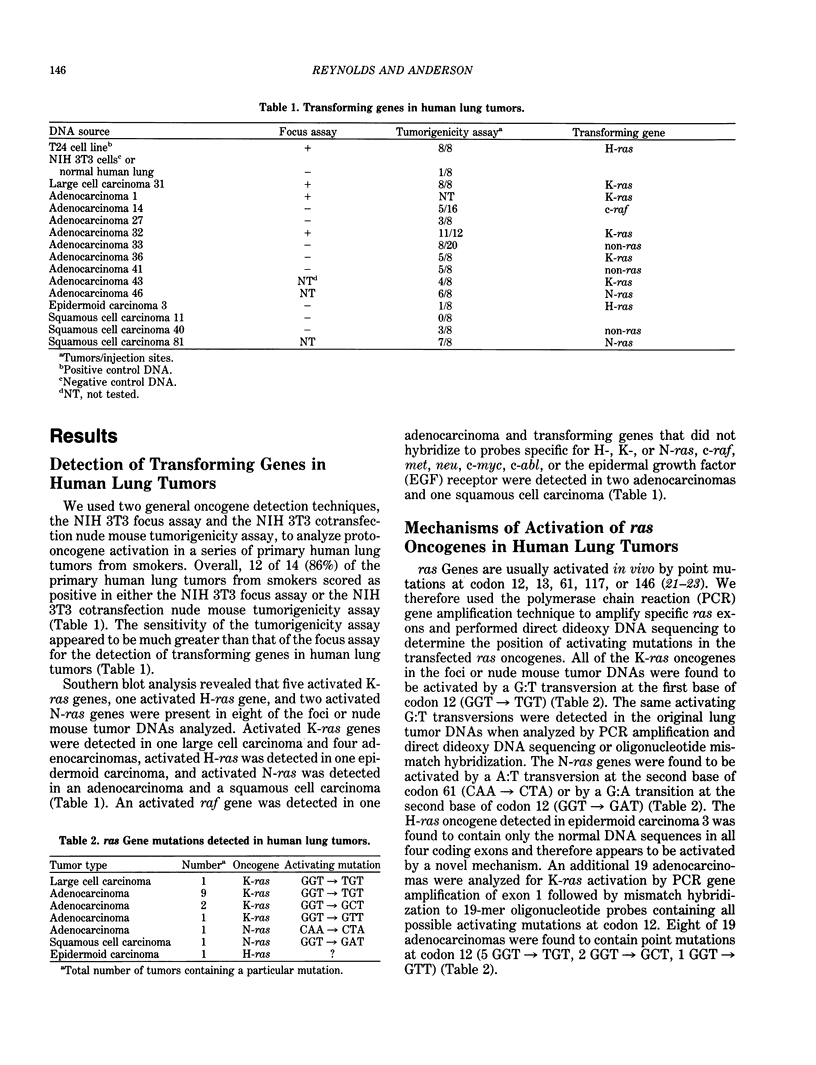
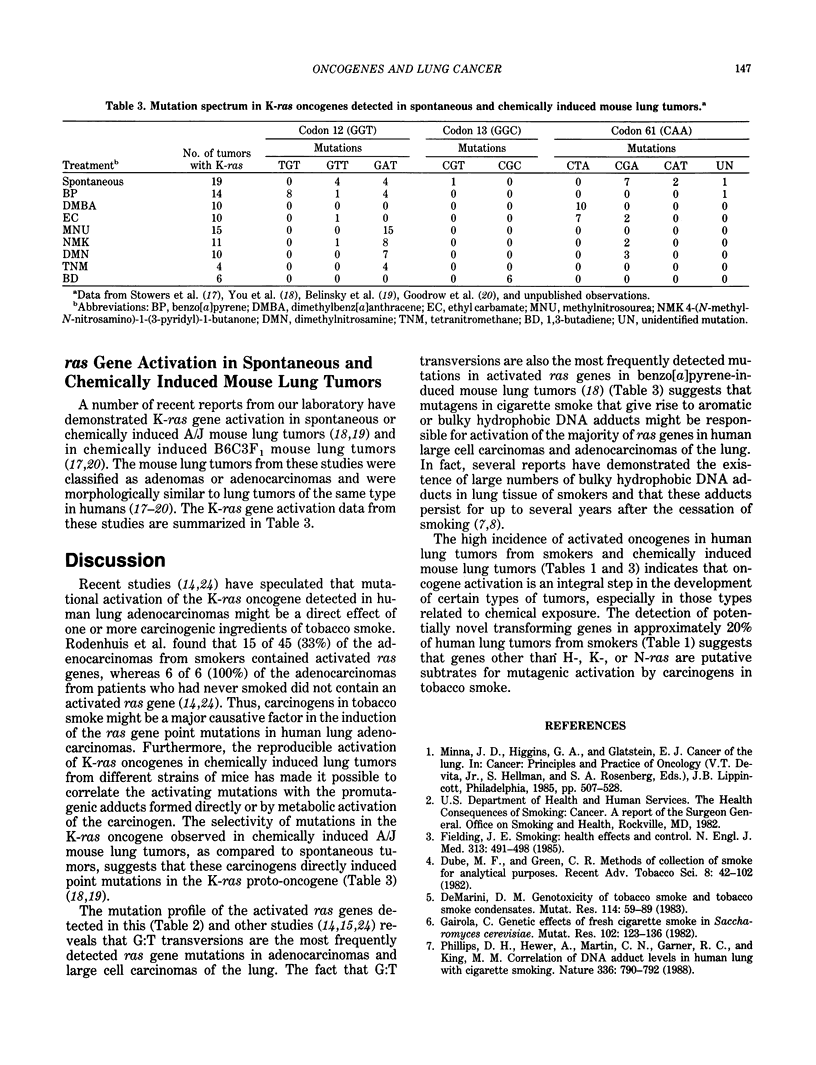
Abstract
Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths in several nations. Epidemiological studies have indicated that 85% of all lung cancer deaths and 30% of all cancer deaths in the U.S. are associated with tobacco smoking. Various chemicals in tobacco smoke are thought to react with DNA and to ultimately yield heritable mutations. In an effort to understand the molecular mechanisms involved in lung tumorigenesis, we have analyzed proto-oncogene activation in a series of human lung tumors from smokers and spontaneously occurring and chemically induced lung tumors in mice. Approximately 86% of the human lung tumors and greater than 90% of the mouse lung tumors were found to contain activated oncogenes. ras Oncogenes activated by point mutations were detected in many of the human lung adenocarcinomas and virtually all of the mouse lung adenomas and adenocarcinomas. The mutation profiles of the activated K-ras genes detected in the chemically induced mouse lung tumors suggest that the observed mutations result from genotoxic effects of the chemicals. Comparison of the K-ras mutations observed in the human lung adenocarcinomas with mutation profiles observed in the mouse lung tumors suggest that bulky hydrophobic DNA adducts may be responsible for the majority of the mutations observed in the activated human K-ras genes. Other data indicate that approximately 20% of human lung tumors contain potentially novel transforming genes that may also be targets for mutagens in cigarette smoke.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belinsky S. A., Devereux T. R., Maronpot R. R., Stoner G. D., Anderson M. W. Relationship between the formation of promutagenic adducts and the activation of the K-ras protooncogene in lung tumors from A/J mice treated with nitrosamines. Cancer Res. 1989 Oct 1;49(19):5305–5311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. The molecular genetics of cancer. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):305–311. doi: 10.1126/science.3541204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarini D. M. Genotoxicity of tobacco smoke and tobacco smoke condensate. Mutat Res. 1983 Jan;114(1):59–89. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(83)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding J. E. Smoking: health effects and control (1). N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 22;313(8):491–498. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508223130807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gairola C. Genetic effects of fresh cigarette smoke in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mutat Res. 1982 Sep;102(2):123–136. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(82)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrow T., Reynolds S., Maronpot R., Anderson M. Activation of K-ras by codon 13 mutations in C57BL/6 X C3H F1 mouse tumors induced by exposure to 1,3-butadiene. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 1;50(15):4818–4823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. H., Hewer A., Martin C. N., Garner R. C., King M. M. Correlation of DNA adduct levels in human lung with cigarette smoking. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):790–792. doi: 10.1038/336790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath E., Miller R. H., Mittal D., Avitts T. A., Dunsford H. A., Randerath K. Covalent DNA damage in tissues of cigarette smokers as determined by 32P-postlabeling assay. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Mar 1;81(5):341–347. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.5.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds S. H., Stowers S. J., Patterson R. M., Maronpot R. R., Aaronson S. A., Anderson M. W. Activated oncogenes in B6C3F1 mouse liver tumors: implications for risk assessment. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1309–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.3629242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodenhuis S., Slebos R. J., Boot A. J., Evers S. G., Mooi W. J., Wagenaar S. S., van Bodegom P. C., Bos J. L. Incidence and possible clinical significance of K-ras oncogene activation in adenocarcinoma of the human lung. Cancer Res. 1988 Oct 15;48(20):5738–5741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodenhuis S., van de Wetering M. L., Mooi W. J., Evers S. G., van Zandwijk N., Bos J. L. Mutational activation of the K-ras oncogene. A possible pathogenetic factor in adenocarcinoma of the lung. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 8;317(15):929–935. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710083171504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan S. R., Newcomb E. W., Pellicer A. Neutron radiation can activate K-ras via a point mutation in codon 146 and induces a different spectrum of ras mutations than does gamma radiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):405–408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J. Identifying tumor suppressor genes in human colorectal cancer. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):12–13. doi: 10.1126/science.2403692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowers S. J., Glover P. L., Reynolds S. H., Boone L. R., Maronpot R. R., Anderson M. W. Activation of the K-ras protooncogene in lung tumors from rats and mice chronically exposed to tetranitromethane. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 15;47(12):3212–3219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Orita M., Shiraishi M., Hayashi K., Sekiya T. Detection of ras gene mutations in human lung cancers by single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis of polymerase chain reaction products. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):1037–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Oncogenes, antioncogenes, and the molecular bases of multistep carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1989 Jul 15;49(14):3713–3721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston A., Willey J. C., Modali R., Sugimura H., McDowell E. M., Resau J., Light B., Haugen A., Mann D. L., Trump B. F. Differential DNA sequence deletions from chromosomes 3, 11, 13, and 17 in squamous-cell carcinoma, large-cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma of the human lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5099–5103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynder E. L. Etiology of lung cancer. Reflections on two decades of research. Cancer. 1972 Nov;30(5):1332–1339. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197211)30:5<1332::aid-cncr2820300528>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You M., Candrian U., Maronpot R. R., Stoner G. D., Anderson M. W. Activation of the Ki-ras protooncogene in spontaneously occurring and chemically induced lung tumors of the strain A mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3070–3074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarbl H., Sukumar S., Arthur A. V., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. Direct mutagenesis of Ha-ras-1 oncogenes by N-nitroso-N-methylurea during initiation of mammary carcinogenesis in rats. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):382–385. doi: 10.1038/315382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


