Abstract
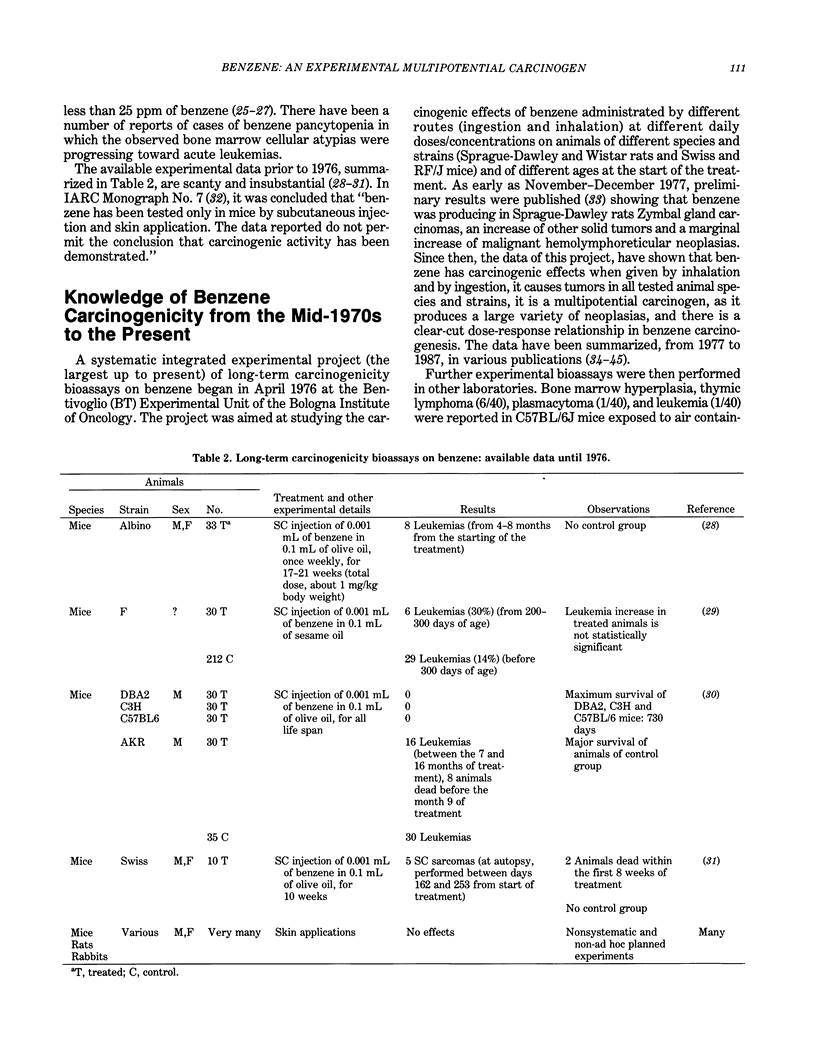
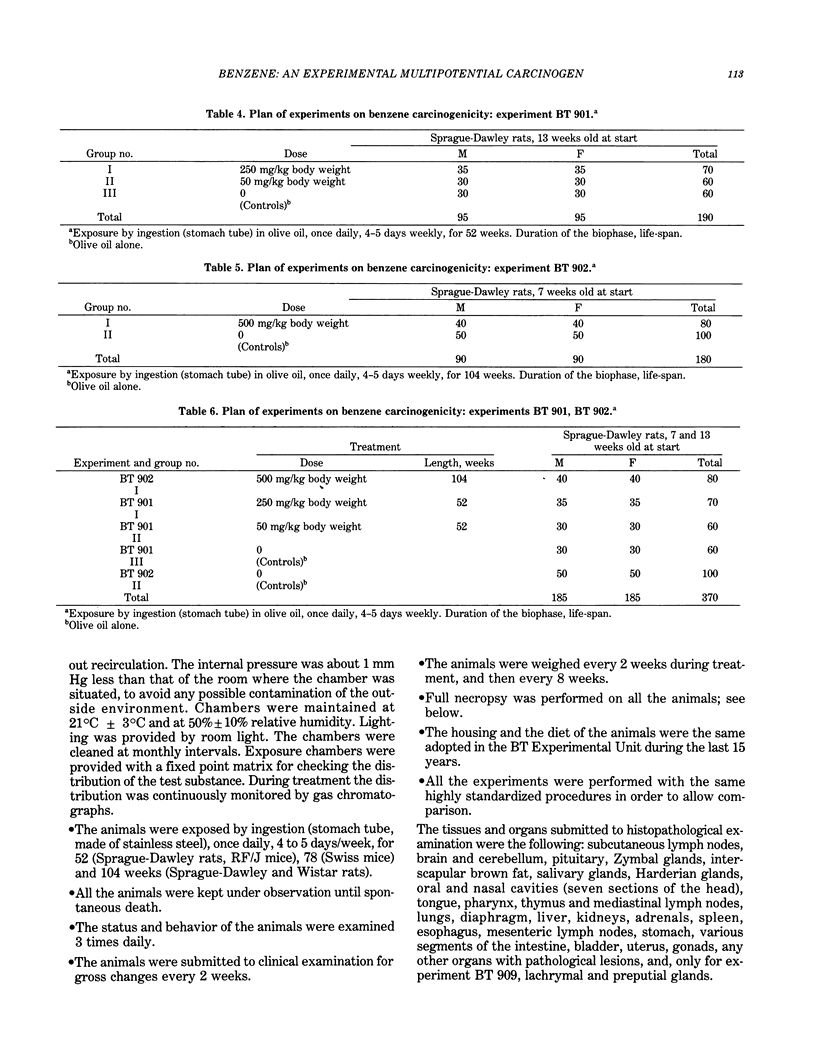
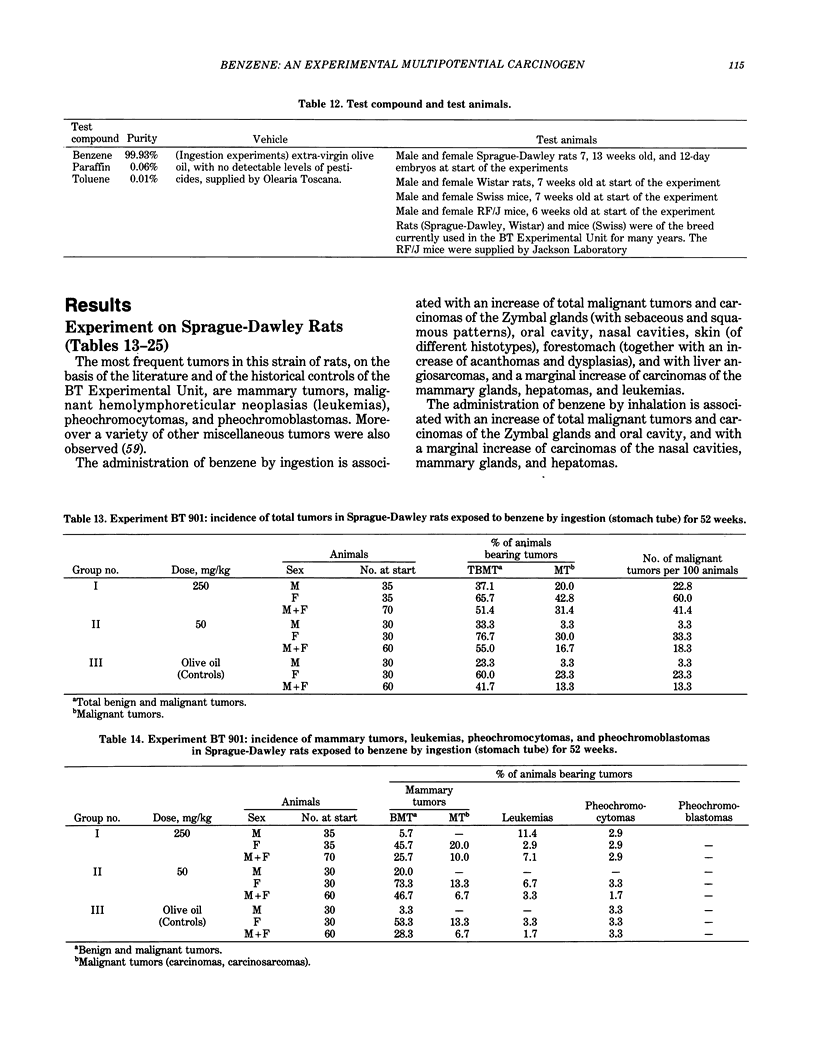
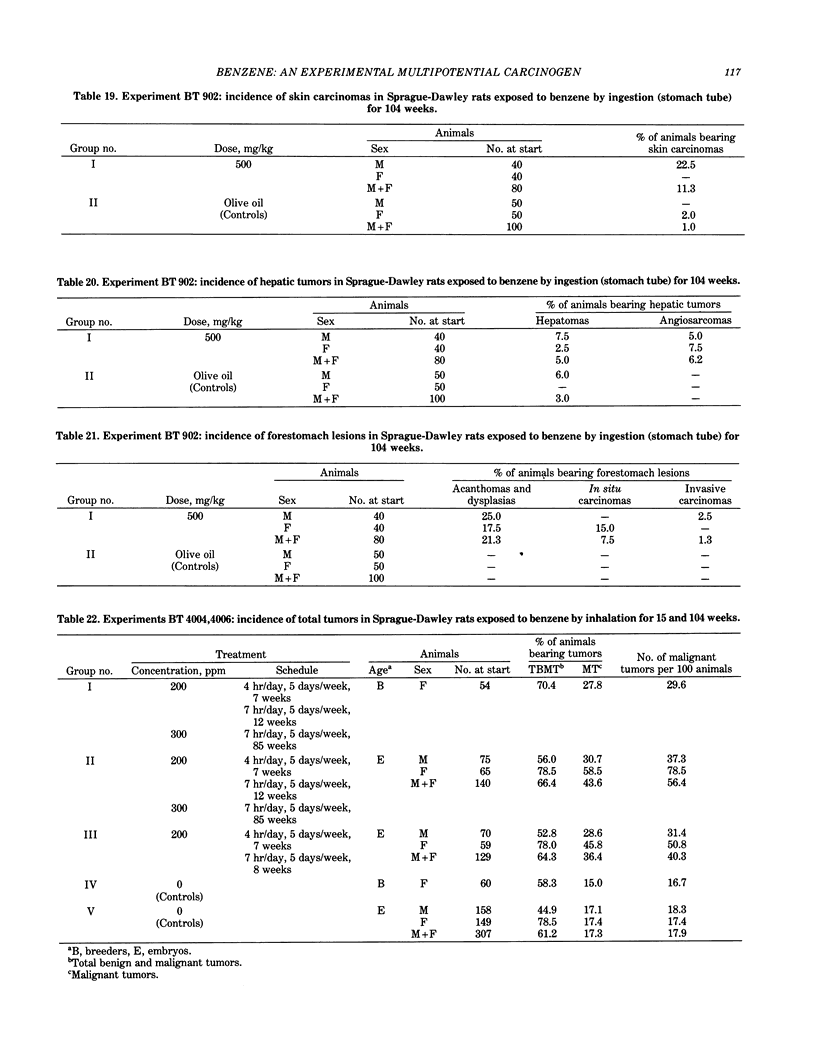
In 1976, a systematic and integrated project of long-term carcinogenicity bioassays began at the Bentivoglio Experimental Unit of the Bologna Institute of Oncology. The Bologna experiments proved for the first time that benzene is an experimental carcinogen. These experiments demonstrated that benzene is carcinogenic when administered by ingestion and by inhalation and that it cause tumors in the various tested animal models (Sprague-Dawley rats, Wistar rats, Swiss mice, and RF/J mice). They also showed that benzene is a multipotential carcinogen, as it produces a variety of neoplasias in one or more of the tested animal models, including Zymbal gland carcinomas, carcinomas of the oral cavity, nasal cavities, skin, forestomach, and mammary glands, as well as angiosarcomas of the liver, hemolymphoreticular neoplasias, tumors of the lung, and possibly hepatomas. The Bologna experiments also indicated a clear-cut dose-response relationship in benzene carcinogenesis. This report presents the up-to-date results of the Bologna project. The need for more experimental research aimed at assessing the carcinogenic effects of low doses of benzene, of chemical mixtures containing benzene, and of benzene substitutes is emphasized. Also recommended are more comprehensive epidemiological investigations, extended to all types of malignancies, with particular regard to lung carcinomas.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMIEL J. L. [Negative attempt at induction of leukemia in mice by benzene]. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1960 Feb;5:198–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy M., Dinçol K., Erdem S., Dinçol G. Acute leukemia due to chronic exposure to benzene. Am J Med. 1972 Feb;52(2):160–166. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy M., Erdem S., DinCol G. Leukemia in shoe-workers exposed chronically to benzene. Blood. 1974 Dec;44(6):837–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brief R. S., Lynch J., Bernath T., Scala R. A. Benzene in the workplace. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1980 Sep;41(9):616–623. doi: 10.1080/15298668091425392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronkite E. P., Bullis J., Inoue T., Drew R. T. Benzene inhalation produces leukemia in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 15;75(2):358–361. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(84)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decouflé P., Blattner W. A., Blair A. Mortality among chemical workers exposed to benzene and other agents. Environ Res. 1983 Feb;30(1):16–25. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(83)90161-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fori A., Pacifico E., Limonta A. Chromosome studies in workers exposed to benzene or toluene or both. Arch Environ Health. 1971 Mar;22(3):373–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forni A. M., Cappellini A., Pacifico E., Vigliani E. C. Chromosome changes and their evolution in subjects with past exposure to benzene. Arch Environ Health. 1971 Nov;23(5):385–391. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1971.10666024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard R., Prost G., Tolot F. Remarques sur l'indemnisation des leucémies et des aplasies benzéniques. (A propos de 48 cas. Arch Mal Prof. 1971 Sep;32(9):581–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard R., Revol L. La fréquence d'une exposition benzénique au cours des hémpathies graves. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1970 Jul-Aug;10(4):477–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard R., Rigaut P., Bertholon J., Tolot F., Bourret J. Les expositions benzéniques méconnues. Leur recherche systématique au cours des hémopathies graves. (Enquétets chez 200 hémopathiques hospitalisés) Arch Mal Prof. 1968 Dec;29(12):723–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard R., Tolot F., Bourret J. Emopatie maligne e benzolismo. Med Lav. 1971 Feb-Mar;62(2):71–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard R., Tolot F., Bourret J. Hydrocarbures benzéniques et hémopathies graves. Arch Mal Prof. 1970 Dec;31(12):625–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguel A., Cavigneaux A., Bernard J. Les leucémies benzéniques de la région parisienne entre 1950 et 1965 (etude de 50 observations) Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1967 Jul-Aug;7(4):465–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. D. Benzene toxicity: a critical evaluation: hematotoxicity in humans. J Toxicol Environ Health Suppl. 1977;2:69–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. D., Snyder C. A., Laskin S., Bromberg I., Albert R. E., Nelson N. Myelogenous leukemia in rodents inhaling benzene. Toxicol Lett. 1982 Oct;13(3-4):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(82)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRAKI K., IRINO S., MIYOSHI I. DEVELOPMENT OF SUBCUTANEOUS SARCOMAS IN SWISS MICE GIVEN REPEATED INJECTIONS OF BENZENE IN OLIVE OIL. Gan. 1963 Dec;54:427–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwich G., Schwanitz G. Chromosomenuntersuchungen nach chronischer Benzol-Exposition. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1972 Jan 14;97(2):45–49. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1107297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimaru T., Okada H., Tomiyasu T., Tsuchimoto T., Hoshino T., Ichimaru M. Occupational factors in the epidemiology of leukemia in Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Mar;93(3):157–165. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Conti B., Cotti G., Belpoggi F. Experimental studies on benzene carcinogenicity at the Bologna Institute of Oncology: current results and ongoing research. Am J Ind Med. 1985;7(5-6):415–446. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700070508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Conti B., Cotti G. Benzene: a multipotential carcinogen. Results of long-term bioassays performed at the Bologna Institute of Oncology. Am J Ind Med. 1983;4(5):589–630. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700040503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Conti B., Perino G., Di Maio V. Further evidence of benzene carcinogenicity. Results on Wistar rats and Swiss mice treated by ingestion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;534:412–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb30131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Conti B., Scarnato C. Squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity in Sprague-Dawley rats, following exposure to benzene by ingestion. First experimental demonstration. Med Lav. 1982 Jul-Aug;73(4):441–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Cotti G., Valgimigli L., Mandrioli A. Hepatocarcinomas in Sprague-Dawley rats, following exposure to benzene by inhalation. First experimental demonstration. Med Lav. 1982 Jul-Aug;73(4):446–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Cotti G., Valgimigli L., Mandrioli A. Zymbal gland carcinomas in rats following exposure to benzene by inhalation. Am J Ind Med. 1982;3(1):11–16. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700030104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltoni C., Scarnato C. First experimental demonstration of the carcinogenic effects of benzene; long-term bioassays on Sprague-Dawley rats by oral administration. Med Lav. 1979 Sep-Oct;70(5):352–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. G., Townsend J. C., Fishbeck W. A., Langner R. A. Mortality among individuals occupationally exposed to benzene. Arch Environ Health. 1978 Jan-Feb;33(1):3–10. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1978.10667299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinsky R. A., Smith A. B., Hornung R., Filloon T. G., Young R. J., Okun A. H., Landrigan P. J. Benzene and leukemia. An epidemiologic risk assessment. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 23;316(17):1044–1050. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704233161702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinsky R. A., Young R. J., Smith A. B. Leukemia in benzene workers. Am J Ind Med. 1981;2(3):217–245. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700020305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder C. A., Goldstein B. D., Sellakumar A. R., Bromberg I., Laskin S., Albert R. E. The inhalation toxicology of benzene: incidence of hematopoietic neoplasms and hematotoxicity in ARK/J and C57BL/6J mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1980 Jun 30;54(2):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(80)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIGLIANI E. C., SAITA G. BENZENE AND LEUKEMIA. N Engl J Med. 1964 Oct 22;271:872–876. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196410222711703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigliani E. C. Leukemia associated with benzene exposure. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;271:143–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb23103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


