Abstract
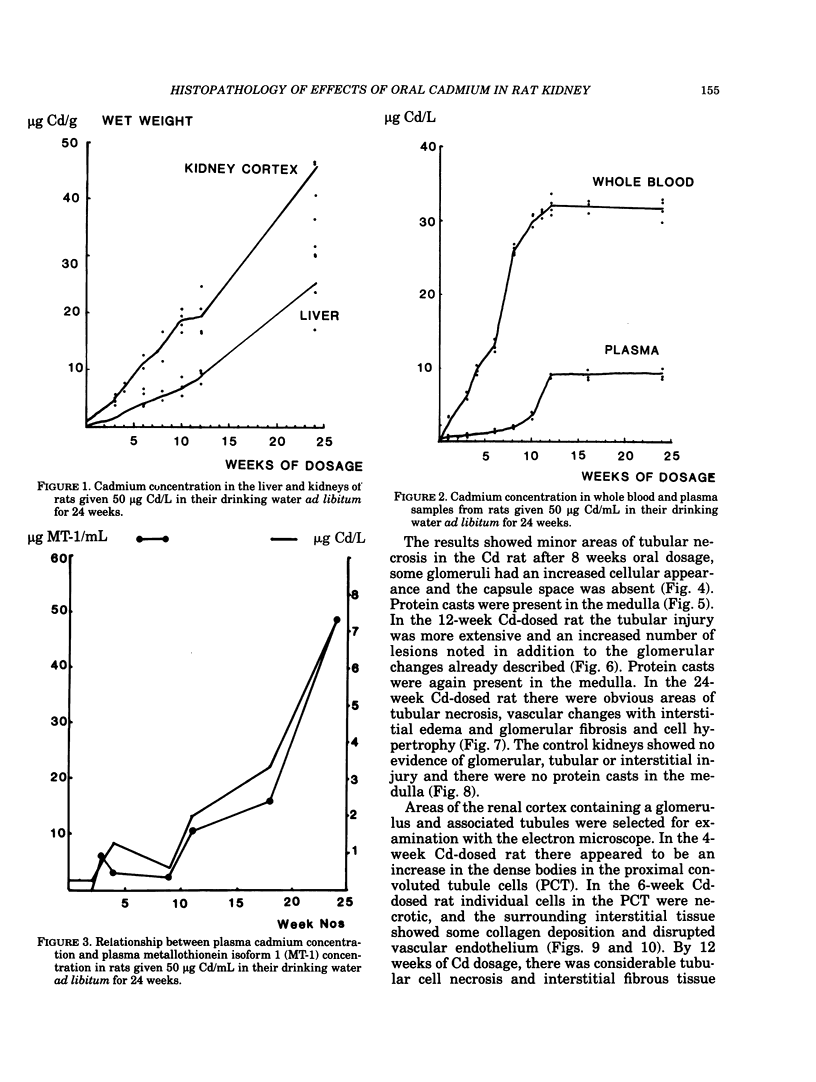
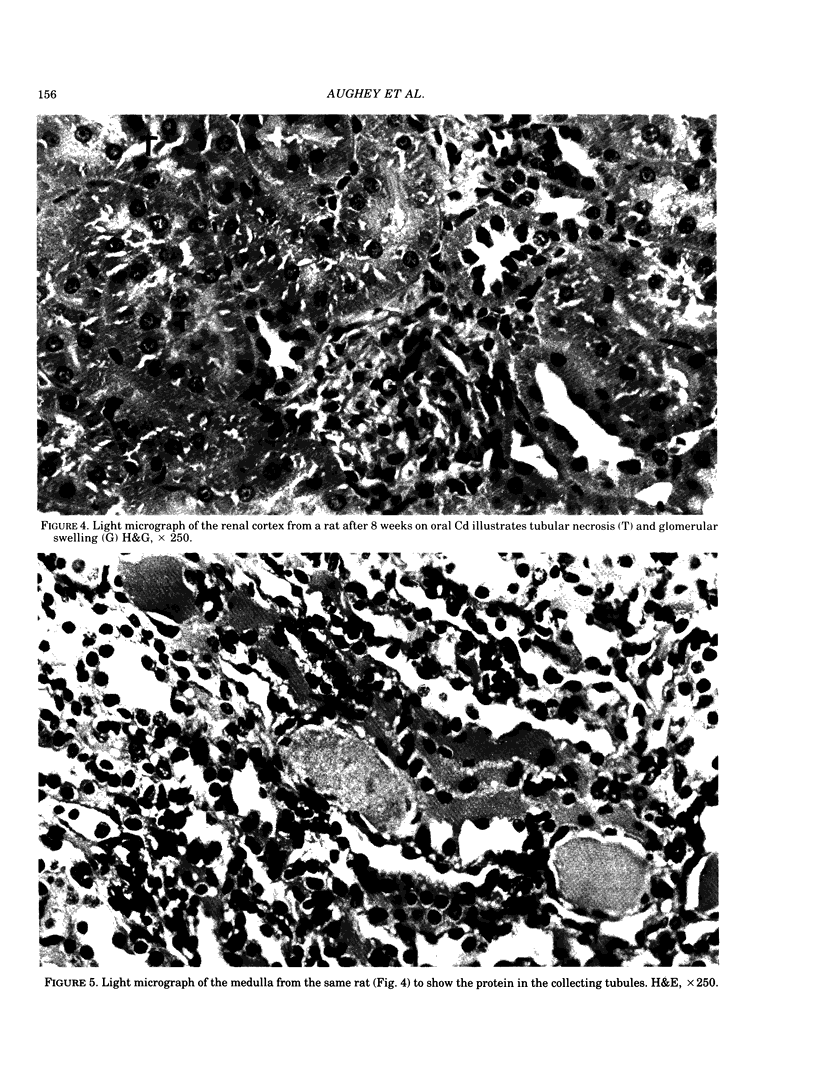
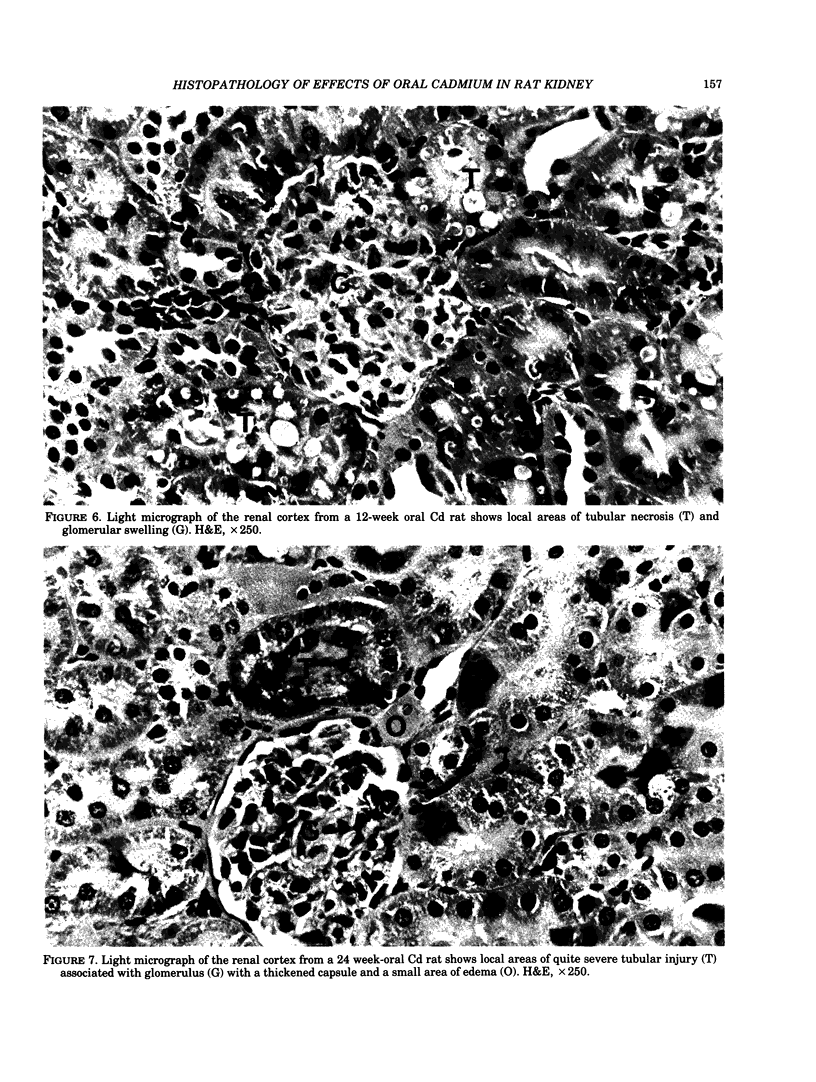
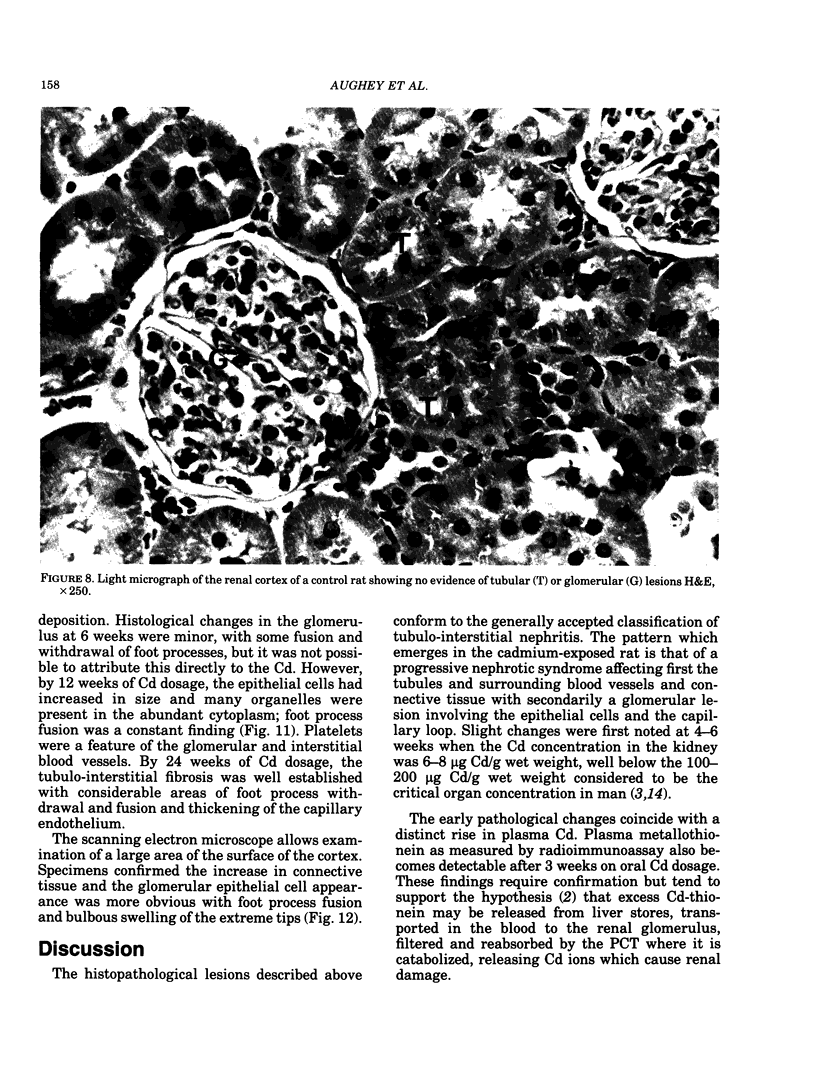
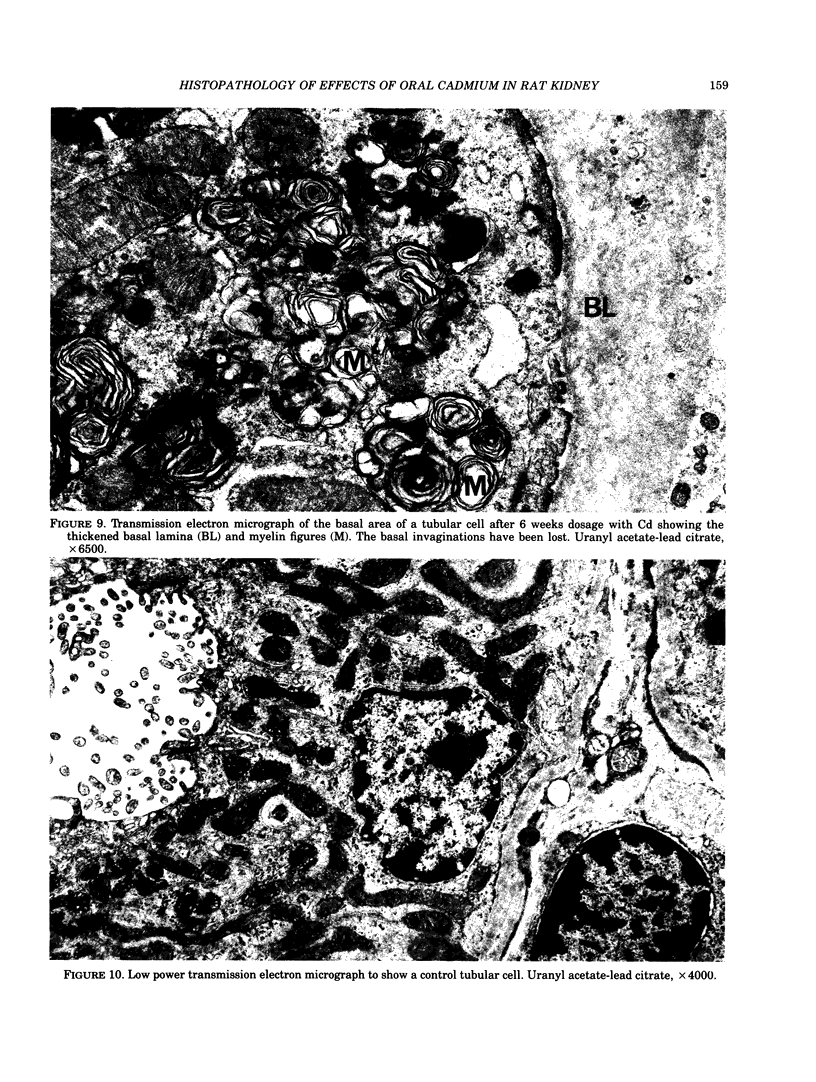
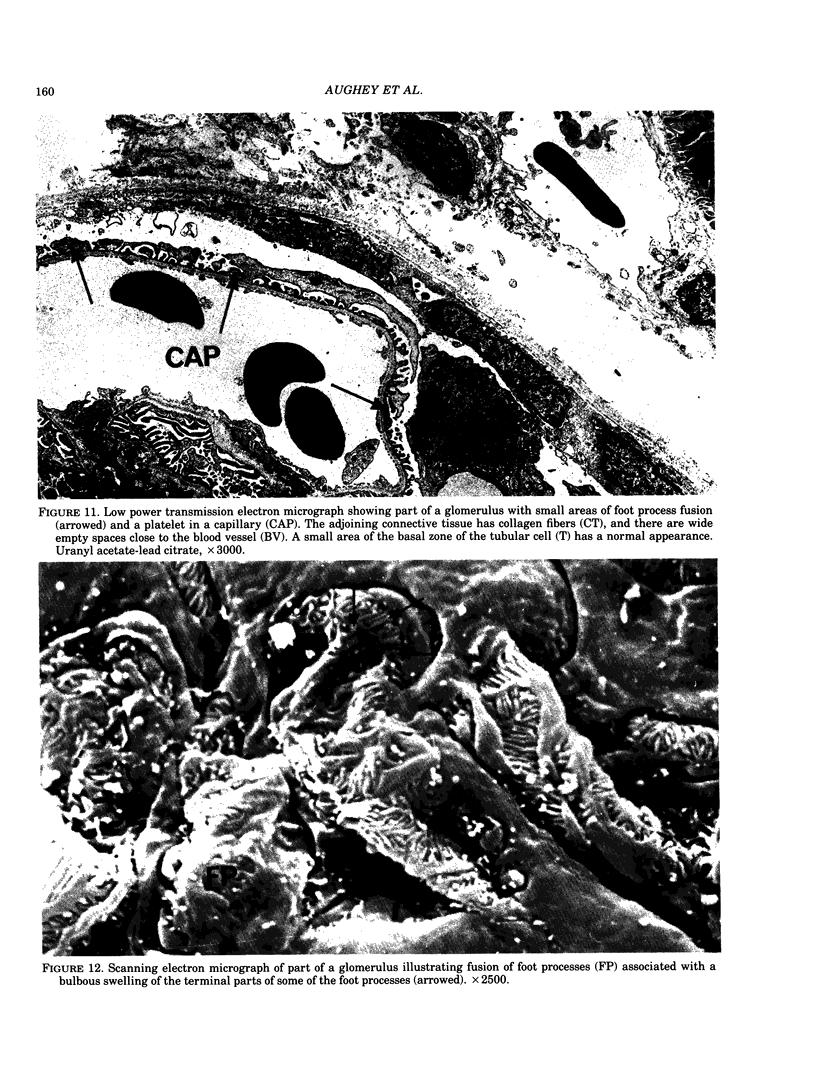
Adult male Wistar rats were given 50 ppm Cd in drinking water over a period of 1-24 weeks. The rats were killed and the cadmium concentration of whole blood, blood plasma red cells, liver and kidneys estimated. The plasma metallothionein concentration was measured by radioimmunoassay. Kidney samples were taken for light, transmission and scanning electron microscopic examination. The accumulation of cadmium in the tissues was shown by a linear increase with time, after exposure for 12 weeks. Plasma Cd concentrations showed a clear increase after 3 weeks and preliminary investigation suggests that most is present as Cd-thionein. Early pathological changes in the rat kidney were seen around the 4-6 week period which coincided with the distinct rise in plasma Cd. At 12 weeks, signs of tubular necrosis, interstitial fibrosis and glomerular epithelial cell hypertrophy were present in small areas of the cortex. By 24 weeks, the renal cortex showed clear evidence of tubulo-interstitial nephritis at a Cd concentration of 60 micrograms Cd/g wet weight.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard A., Lauwerys R., Gengoux P. Characterization of the proteinuria induced by prolonged oral administration of cadmium in female rats. Toxicology. 1981;20(4):345–357. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(81)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherian M. G., Goyer R. A., Delaquerriere-Richardson L. Cadmium-metallothionein-induced nephropathy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;38(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DECKER L. E., BYERRUM R. U., DECKER C. F., HOPPERT C. A., LANGHAM R. F. Chronic toxicity studies. I. Cadmium administered in drinking water to rats. AMA Arch Ind Health. 1958 Sep;18(3):228–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeser E., Lorke D. Semichronic oral toxicity of cadmium. I. Studies on rats. Toxicology. 1977 Apr;7(2):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(77)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel R. G., Hall M. L., Ottaway J. M., Fell G. S. Determination of cadmium in blood and urine by flame atomic-fluorescence spectrometry. Analyst. 1979 Jun;104(1239):491–504. doi: 10.1039/an9790400491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg M. Studies on metallothionein and cadmium. Environ Res. 1978 Jun;15(3):381–404. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(78)90120-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbioni E., Marafante E., Amantini L., Ubertalli L., Pietra R. Cadmium toxicity studies under long term-low level exposure (LLE) conditions. I. Metabolic patterns in rats exposed to present environmental dietary levels of Cd for two years. Sci Total Environ. 1978 Sep;10(2):131–161. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(78)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K. T., Takenaka S., Kubota K. Fate and comparative toxicity of metallothioneins with differing Cd/Zn ratios in rat kidney. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1979;8(1):85–95. doi: 10.1007/BF01055143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]