Abstract
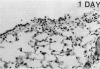
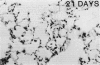
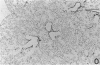
The assay of bronchoalveolar washings from acutely exposed animals has proven useful as a rapid screen for lung injury from inhaled airborne toxins. The screen is useful for choosing appropriate compounds and exposure levels for subsequent in-depth studies in which complete histopathologic evaluations will be made. An inflammatory response can be detected by the appearance of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and an increase in protein content of lung washings. The release of the cytoplasmic enzyme, lactate dehydrogenase, into the acellular portion of the lavage fluid serves as an indication of cell death or membrane damage. A large increase in some lysosomal enzymes has been found in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluids from animals chronically exposed to insoluble particles. Angiotensin-converting enzyme has been found to be elevated in bronchoalveolar washings from animals with endothelial cell damage in the pulmonary capillaries. The correlation of these cellular and biochemical alterations in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid with morphological indications of damage has served to validate this method of detecting acute lung injury. Further study is needed to validate indicators of developing chronic disease.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert S. M., Schwartz B. B., Lee S. D., Lewis T. R. Alveolar protein accumulation. A sensitive indicator of low level oxidant toxicity. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Jul;128(1):69–73. doi: 10.1001/archinte.128.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames B. N., Mccann J., Yamasaki E. Methods for detecting carcinogens and mutagens with the Salmonella/mammalian-microsome mutagenicity test. Mutat Res. 1975 Dec;31(6):347–364. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(75)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCKLEY R. D., BALCHUM O. J. ACUTE AND CHRONIC EXPOSURES TO NITROGEN DIOXIDE. EFFECTS ON OXYGEN CONSUMPTION AND ENZYME ACTIVITY ON GUINEA PIG TISSUES. Arch Environ Health. 1965 Feb;10:220–223. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1965.10663987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Band P., Feldstein M., Saccomanno G., Watson L., King G. Potentiation of cigarette smoking and radiation: evidence from a sputum cytology survey among uranium miners and controls. Cancer. 1980 Mar 15;45(6):1273–1277. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19800315)45:6<1273::aid-cncr2820450602>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck B. D., Brain J. D., Bohannon D. E. An in vivo hamster bioassay to assess the toxicity of particulates for the lungs. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1982 Oct;66(1):9–29. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(82)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck B. D., Brain J. D., Bohannon D. E. The pulmonary toxicity of an ash sample from the MT. St. Helens Volcano. Exp Lung Res. 1981 Nov;2(4):289–301. doi: 10.3109/01902148109052324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell D. Y., Haseman J. A., Spock A., McLennan G., Hook G. E. Plasma proteins of the bronchoalveolar surface of the lungs of smokers and nonsmokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jul;124(1):72–79. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell D. Y., Hook G. E. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: analysis of airway and alveolar proteins. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jun;119(6):979–990. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.6.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain J. D., Frank N. R. Recovery of free cells from rat lungs by repeated washings. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Jul;25(1):63–69. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.25.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow C. K., Tappel A. L. Activities of pentose shunt and glycolytic enzymes in lungs of ozone-exposed rats. Arch Environ Health. 1973 Apr;26(4):205–208. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1973.10666257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu E. H., Malling H. V. Mammalian cell genetics. II. Chemical induction of specific locus mutations in Chinese hamster cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1306–1312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chvapil M., Peng Y. M. Oxygen and lung fibrosis. Arch Environ Health. 1975 Nov;30(11):528–532. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1975.10666770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. A., Nellenbogen J., Trahan H. J. Pulmonary surfactant and evolution of the lungs. Science. 1970 Aug 7;169(3945):603–604. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3945.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. B., Batra G. K. Bronchoscopy and lung lavage induced bilateral pulmonary neutrophil influx and blood leukocytosis in dogs and monkeys. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Aug;122(2):239–247. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauber J. H., Rossman M. D., Daniele R. P. Pulmonary fibrosis: bronchoalveolar cell types and impaired function of alveolar macrophages in experimental silicosis. Environ Res. 1982 Feb;27(1):226–236. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(82)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeNicola D. B., Rebar A. H., Henderson R. F. Early damage indicators in the lung. V. Biochemical and cytological response to NO2 inhalation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981 Sep 15;60(2):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(91)90233-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiAugustine R. P. Lung concentric laminar organelle. Hydrolase activity and compositional analysis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):584–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew W. L., Finley T. N., Golde D. W. Diagnostic lavage and occult pulmonary hemorrhage in thrombocytopenic immunocompromised patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Aug;116(2):215–221. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey P. J., Utell M. J., Mayewski R. J., Wandtke J. D., Hyde R. W. Early diagnosis of bleomycin pulmonary toxicity using bronchoalveolar lavage in dogs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Jul;126(1):126–130. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.1.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J., Vassalli J. D., Reich E. Macrophage plasminogen activator: induction by asbestos is blocked by anti-inflammatory steroids. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1689–1694. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. A., Snider G. L., Palmer K. C. The evolution of biochemical damage in the rat lung after acute cadmium exposure. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Feb;113(2):121–130. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.2.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. F., Damon E. G., Henderson T. R. Early damage indicators in the the lung I. Lactate dehydrogenase activity in the airways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1978 May;44(2):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(78)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. F., Lowrey J. S. Effect of anesthetic agents on lavage fluid parameters used as indicators of pulmonary injury. Lab Anim Sci. 1983 Feb;33(1):60–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. F., Muggenburg B. A., Mauderly J. L., Tuttle W. A. Early damage indicators in the lung. II. Time sequence of protein accumulation and lipid loss in the airways of beagle dogs with beta irradiation of the lung. Radiat Res. 1978 Oct;76(1):145–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. F., Rebar A. H., Denicola D. B. Early damage indicators in the lungs. IV. Biochemical and cytologic response of the lung to lavage with metal salts. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;51(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. F., Rebar A. H., Pickrell J. A., Newton G. J. Early damage indicators in the lung. III. Biochemical and cytological response of the lung to inhaled metals salts. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;50(1):123–136. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90500-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Styles J. A. Activity of a macrophage factor in collagen formation by silica. Nature. 1967 Apr 29;214(5087):521–522. doi: 10.1038/214521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger M. A., Giri S. N., Patwell S., Zuckerman J. E., Gorin A., Parsons G. Effect of acute lung injury on angiotensin converting enzyme in serum, lung lavage, and effusate. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Feb;121(2):373–376. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook G. E., Bell D. Y., Gilmore L. B., Nadeau D., Reasor M. J., Talley F. A. Composition of bronchoalveolar lavage effluents from patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Lab Invest. 1978 Oct;39(4):342–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook G. E. Extracellular hydrolases of the lung. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):520–528. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hueter F. G., Fritzhand M. Oxidants and lung biochemistry. A brief review. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Jul;128(1):48–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Inflammatory and immune processes in the human lung in health and disease: evaluation by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am J Pathol. 1979 Oct;97(1):149–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston W. W., Frable W. J. The cytopathology of the respiratory tract. A review. Am J Pathol. 1976 Aug;84(2):372–424. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. A., Crystal R. G. Alveolitis: the key to the interstitial lung disorders. Thorax. 1982 Jan;37(1):1–10. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucich U., Rosenbloom J., Christner P., Kimbel P., Weinbaum G. Development of a hemagglutination assay to measure elastin fragments and antielastin antibodies. Chest. 1980 Feb;77(2 Suppl):278–279. doi: 10.1378/chest.77.2_supplement.278-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn C., 3rd Cytochemistry of pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1968 Nov;53(5):809–833. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kylstra J. A., Rausch D. C., Hall K. D., Spock A. Volume-controlled lung lavage in the treatment of asthma, bronchiectasis, and mucoviscidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 May;103(5):651–665. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.5.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence E. C., Martin R. R., Blaese R. M., Teague R. B., Awe R. J., Wilson R. K., Deaton W. J., Bloom K., Greenberg S. D., Stevens P. M. Increased bronchoalveolar IgG-secreting cells in interstitial lung diseases. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 22;302(21):1186–1188. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005223022106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYRVIK Q., LEAKE E. S., FARISS B. Studies on pulmonary alveolar macrophages from the normal rabbit: a technique to procure them in a high state of purity. J Immunol. 1961 Feb;86:128–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. J., Coalson J. J., Rogers R. M., Horton F. O., Manous L. E. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: the diagnosis by segmental lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 May;121(5):819–825. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.5.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauderly J. L. Bronchopulmonary lavage of small laboratory animals. Lab Anim Sci. 1977 Apr;27(2):255–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Moores S. R., Holmes A., Evans J. C., Evans N. H., Black A. The effect of quartz, administered by intratracheal instillation, on the rat lung. I. The cellular response. Environ Res. 1980 Jun;22(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(80)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggenburg B. A., Hahn F. F., Bowen J. A., Bice D. E. Flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy of chimpanzees. Lab Anim Sci. 1982 Oct;32(5):534–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggenburg B. A., Mauderly J. L., Halliwell W. H., Slauson D. O. Cardiopulmonary function and morphologic changes in beagle dogs after multiple lung lavages. Arch Environ Health. 1980 Mar-Apr;35(2):85–91. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1980.10667470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggenburg B. A., Mauderly J. L. Lung lavage using a single-lumen endotracheal tube. J Appl Physiol. 1975 May;38(5):922–926. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.38.5.922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggenburg B. A., Mauderly J. L., Pickrell J. A., Chiffelle T. L., Jones R. K., Luft U. C., McClellan R. O., Pfleger R. C. Pathophysiologic sequelae of bronchopulmonary lavage in the dog. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 Aug;106(2):219–232. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.106.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong T. M., De Serres F. J. Mutagenicity of chemical carcinogens in Neurospora crassa. Cancer Res. 1972 Sep;32(9):1890–1893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Orlowski J., Lesser M., Kilburn K. H. Proteolytic enzymes in bronchopulmonary lavage fluids: cathepsin B-like activity and prolyl endopeptidase. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Apr;97(4):467–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reasor M. J., Nadeau D., Hook G. E. Extracellular alkaline phosphatase in the airways of the rabbit lung. Lung. 1978;155(4):321–325. doi: 10.1007/BF02730706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Kazmierowski J. A., Roberts W. C., Frank M. M., Crystal R. G. Analysis of cellular and protein content of broncho-alveolar lavage fluid from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):165–175. doi: 10.1172/JCI108615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Newball H. H. Analysis of proteins and respiratory cells obtained from human lungs by bronchial lavage. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Oct;84(4):559–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossman M. D., Dauber J. H., Cardillo M. E., Daniele R. P. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: correlation of serum angiotensin-converting enzyme with blood and bronchoalveolar lymphocytes. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Mar;125(3):366–369. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.3.366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth C., Huchon G. J., Arnoux A., Stanislas-Leguern G., Marsac J. H., Chretien J. Bronchoalveolar cells in advanced pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jul;124(1):9–12. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A. Effect of pneumotoxicants on lactate dehydrogenase activity in airways of rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981 Jan;57(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(81)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R., Mattsby I., Snella M. C. Airway immune response after exposure to inhaled endotoxin. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1980 Jul-Aug;16(4):501–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R., Sjöstrand M., Bergström R. Free lung cell response after combined exposure to cigarette smoke and industrial dusts. Toxicology. 1979 Mar-Apr;12(3):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(79)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccomanno G., Saunders R. P., Archer V. E., Auerbach O., Kuschner M., Beckler P. A. Cancer of the lung: the cytology of sputum prior to the development of carcinoma. Acta Cytol. 1965 Nov-Dec;9(6):413–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahu S., DiAugustine R. P., Lynn W. S. Lipids found in pulmonary lavage of patients with alveolar proteinosis and in rabbit lung lamellar organelles. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jul;114(1):177–185. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahu S., Lynn W. S. Characterization of a high-molecular-weight glycoprotein isolated from the pulmonary secretions of patients with alveolar proteinosis. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):153–158. doi: 10.1042/bj1770153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahu S., Lynn W. S. Lipid composition of airway secretions from patients with asthma and patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Feb;115(2):233–239. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneeberger E. E. Structural basis for some permeability properties of the air--blood barrier. Fed Proc. 1978 Sep;37(11):2471–2478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Shasby S. S., Bowman C. M., Fox R. B., Harada R. M., Tate R. M., Repine J. E. Angiotensin converting enzyme concentrations in the lung lavage of normal rabbits and rabbits treated with nitrogen mustard exposed to hyperoxia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Aug;124(2):202–203. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.2.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skopek T. R., Liber H. L., Krolewski J. J., Thilly W. G. Quantitative forward mutation assay in Salmonella typhimurium using 8-azaguanine resistance as a genetic marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):410–414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. J. Bronchoalveolar lavage today. Chest. 1981 Sep;80(3):251–252. doi: 10.1378/chest.80.3.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobels F. H. The advantages of drosophila for mutation studies. Mutat Res. 1974 Aug;26(4):277–284. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(74)80025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl W. R. Scaling of respiratory variables in mammals. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Mar;22(3):453–460. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.3.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strumpf I. J., Bacher J. D., Gadek J. E., Morin M. L., Crystal R. G. Flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy of the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). Lab Anim Sci. 1979 Dec;29(6):785–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strumpf I. J., Feld M. K., Cornelius M. J., Keogh B. A., Crystal R. G. Safety of fiberoptic bronchoalveolar lavage in evaluation of interstitial lung disease. Chest. 1981 Sep;80(3):268–271. doi: 10.1378/chest.80.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORPE B. D., MARCUS S. PHAGOCYTOSIS AND INTRACELLULAR FATE OF PASTEURELLA TULARENSIS. II. IN VITRO STUDIES WITH RABBIT ALVEOLAR AND GUINEA PIG ALVEOLAR AND PERITONEAL MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES. J Immunol. 1964 Oct;93:558–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tierney D. F. Lactate metabolism in rat lung tissue. Arch Intern Med. 1971 May;127(5):858–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tierney D. F., Yang J., Ayers L. Enzymatic activity in rat lungs. Some changes with exposure to 1 ATM oxygen. Chest. 1975 Feb;67(2 Suppl):40S–42S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tierney D., Ayers L., Herzog S., Yang J. Pentose pathway and production of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. A mechanism that may protect lungs from oxidants. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Dec;108(6):1348–1351. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.6.1348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle W. C., Westerberg S. C. Alpha-1 globulin trypsin inhibitor in canine surfactant protein. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 May;146(1):232–235. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. Secretory function of mononuclear phagocytes: a review. Am J Pathol. 1976 May;83(2):396–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valeyre D., Saumon G., Bladier D., Amouroux J., Pré J., Battesti J. P., Georges R. The relationships between noninvasive explorations in pulmonary sarcoidosis of recent origin, as shown in bronchoalveolar lavage, serum, and pulmonary function tests. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Jul;126(1):41–45. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijeyaratnam G. S., Corrin B. Pulmonary histiocytosis simulating desquamative interstitial pneumonia in rats receiving oral iprindole. J Pathol. 1972 Oct;108(2):105–113. doi: 10.1002/path.1711080203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. D., Gardner D. E., Aranyi C., Coffin D. L. Metal toxicity for rabbit alveolar macrophages in vitro. Environ Res. 1975 Feb;9(1):32–47. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(75)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger S. E., Kelman J. A., Elson N. A., Young R. C., Jr, Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Crystal R. G. Bronchoalveolar lavage in interstitial lung disease. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Oct;89(4):459–466. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Dukor P., Zurier R. B. Effect of cyclic AMP on release of lysosomal enzymes from phagocytes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 2;231(22):131–135. doi: 10.1038/newbio231131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witsch I. H. Proliferation of type II alveolar cells: a review of common responses in toxic lung injury. Toxicology. 1976 Mar;5(3):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(76)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witschi H. Environmental agents altering lung biochemistry. Fed Proc. 1977 Apr;36(5):1631–1634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]