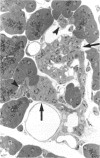
Abstract
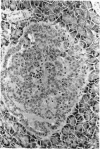
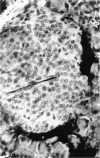
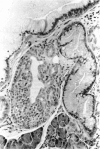
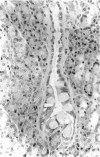
There is strong evidence that induced pancreatic adenomas and carcinomas derive from ductal and ductular cells in the pancreas. We base our beliefs on our knowledge of the embryology and histology of the pancreas in Syrian golden hamsters, along with the sequential alterations that occur during exocrine pancreatic tumor formation. This concept also has been supported by much experimental evidence, including autoradiographic, immunologic and in vitro studies. We also present other viewpoints on the origin of pancreatic cancer histogenesis and outline certain areas of disagreement. We report the development of acinar cell lesions under certain experimental dietary conditions in hamsters (the lesions resemble those commonly seen in the rat pancreatic tumor model) and the nature of these lesions.
Full text
PDF
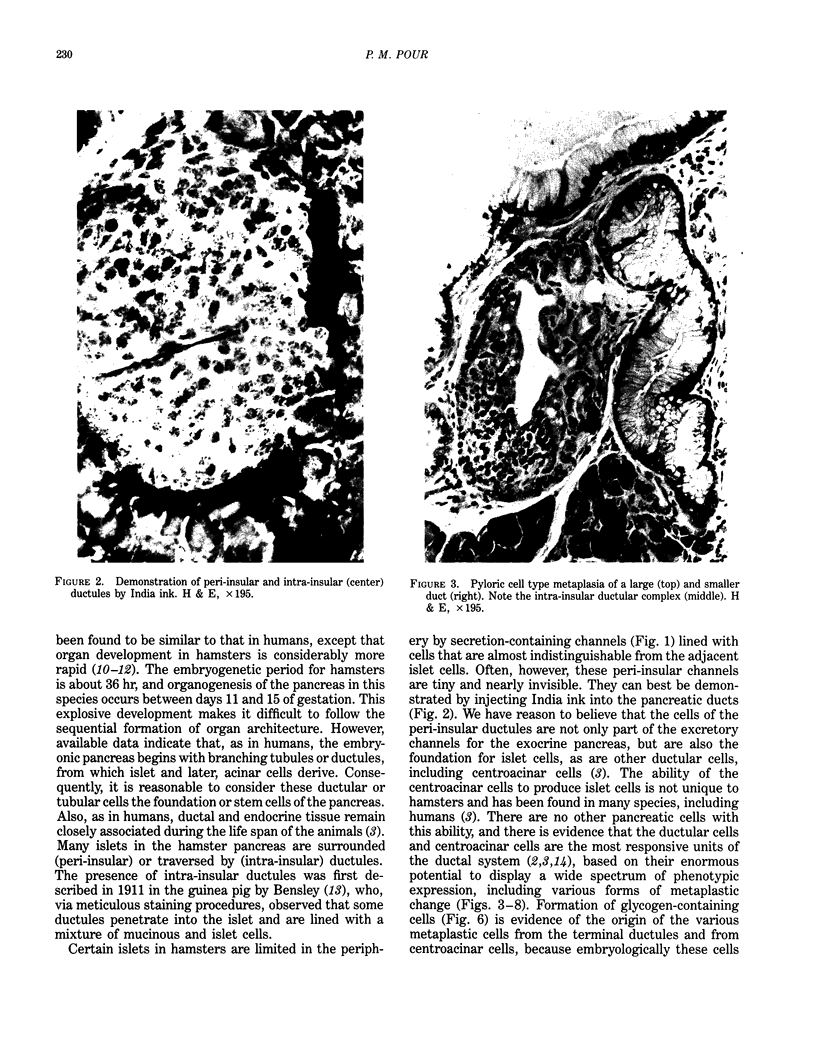
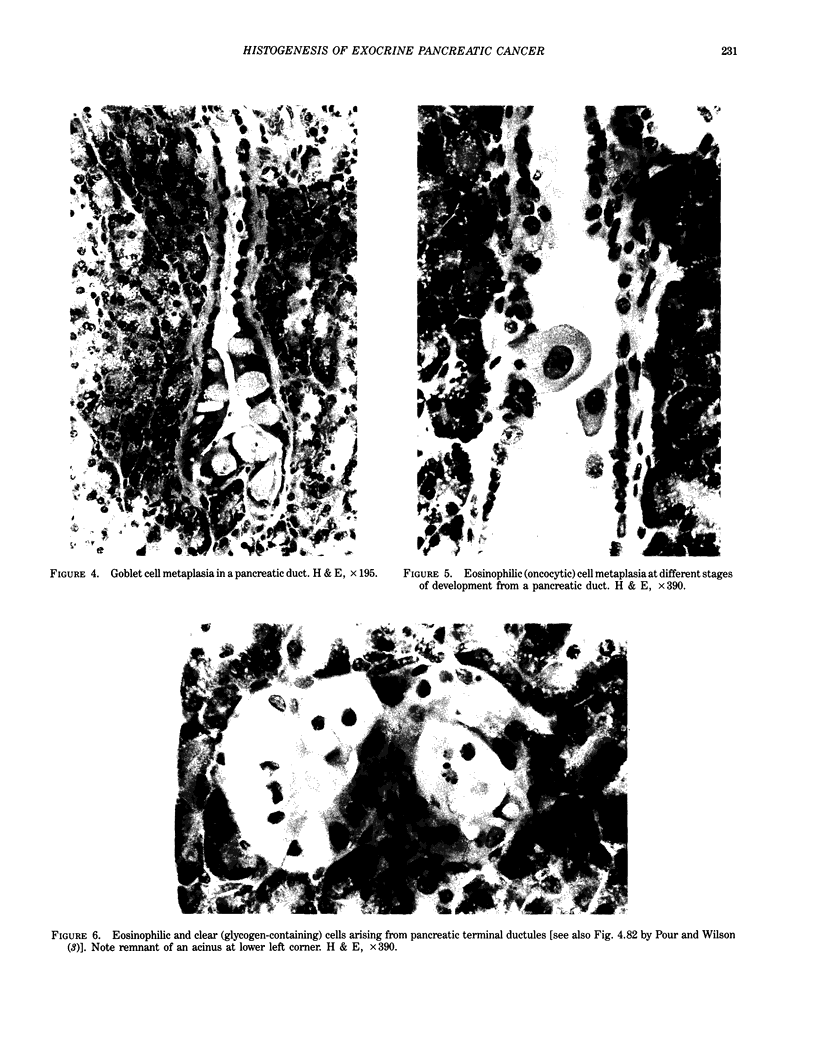
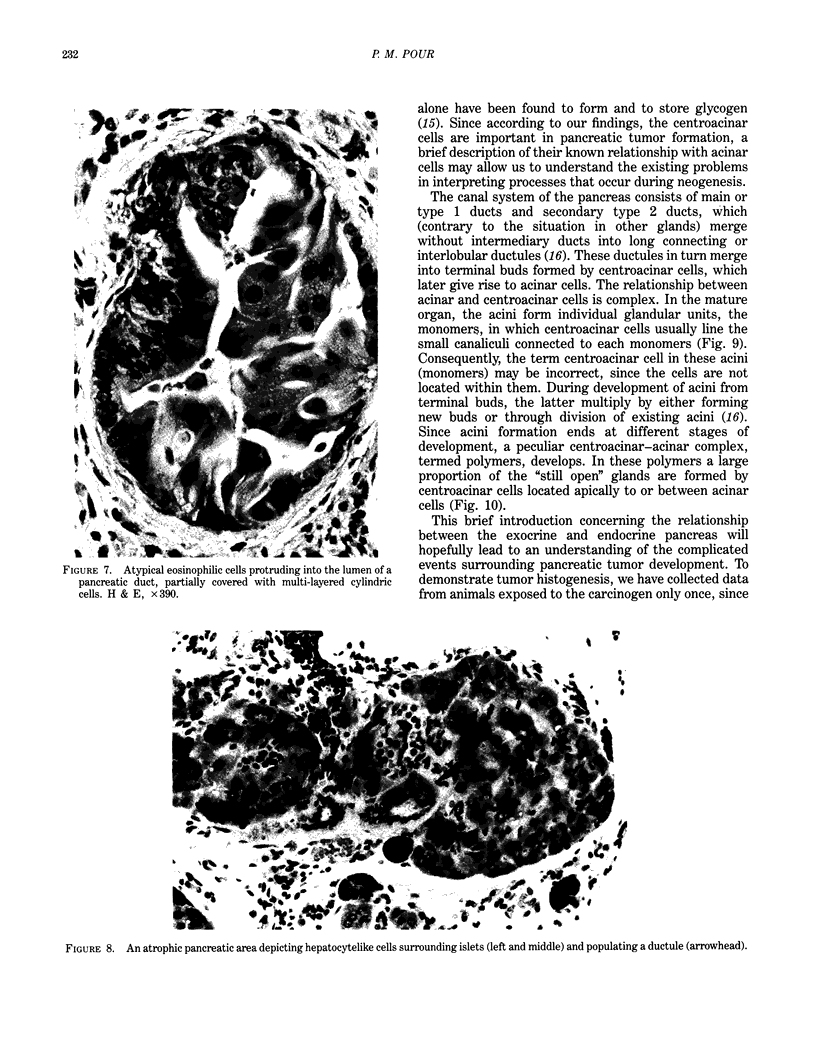



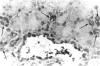
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birt D. F., Salmasi S., Pour P. M. Enhancement of experimental pancreatic cancer in Syrian golden hamsters by dietary fat. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Dec;67(6):1327–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman D. E. Cells of origin of pancreatic cancer: experimental animal tumors related to human pancreas. Cancer. 1981 Mar 15;47(6 Suppl):1528–1534. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810315)47:6+<1528::aid-cncr2820471415>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantenys D., Portha B., Dutrillaux M. C., Hollande E., Rozé C., Picon L. Histogenesis of the endocrine pancreas in newborn rats after destruction by streptozotocin. An immunocytochemical study. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1981;35(2):109–122. doi: 10.1007/BF02889153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux M. C., Portha B., Rozé C., Hollande E. Ultrastructural study of pancreatic B cell regeneration in newborn rats after destruction by streptozotocin. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1982;39(2):173–185. doi: 10.1007/BF02892846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eusebi V., Capella C., Bondi A., Sessa F., Vezzadini P., Mancini A. M. Endocrine-paracrine cells in pancreatic exocrine carcinomas. Histopathology. 1981 Nov;5(6):599–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1981.tb01827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaks B., Moore M. A., Flaks A. Ultrastructural analysis of pancreatic carcinogenesis. III. Multifocal cystic lesions induced by N-nitroso-bis(2-hydroxypropyl)amine in the hamster exocrine pancreas. Carcinogenesis. 1980 Aug;1(8):693–706. doi: 10.1093/carcin/1.8.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaks B., Moore M. A., Flaks A. Ultrastructural analysis of pancreatic carcinogenesis. VI. Early changes in hamster acinar cells induced by N-nitroso-bis(2-hydroxypropyl)amine. Carcinogenesis. 1982;3(9):1063–1070. doi: 10.1093/carcin/3.9.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Like A. A., Orci L. Embryogenesis of the human pancreatic islets: a light and electron microscopic study. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):511–534. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. A., Takahashi M., Ito N., Bannasch P. Early lesions during pancreatic carcinogenesis induced in Syrian hamster by DHPN or DOPN. I. Histologic, histochemical and radioautographic findings. Carcinogenesis. 1983;4(4):431–437. doi: 10.1093/carcin/4.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. A., Takahashi M., Ito N., Bannasch P. Early lesions during pancreatic carcinogenesis induced in the Syrian hamster by DHPN or DOPN. II. Ultrastructural findings. Carcinogenesis. 1983;4(4):439–448. doi: 10.1093/carcin/4.4.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oates P. S., Morgan R. G. Pancreatic growth and cell turnover in the rat fed raw soya flour. Am J Pathol. 1982 Aug;108(2):217–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogrowsky D., Fawcett J., Althoff J., Wilson R. B., Pour P. Structure of the pancreas in Syrian hamsters. Scanning electron-microscopic observations. Acta Anat (Basel) 1980;107(2):121–128. doi: 10.1159/000145236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pour P. M., Patil K. Modification of pancreatic carcinogenesis in the hamster model. X. Effect of streptozotocin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Nov;71(5):1059–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pour P. M., Reber H. A., Stepan K. Modification of pancreatic carcinogenesis in the hamster model. XII. Dose-related effect of ethanol. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Nov;71(5):1085–1087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pour P. M., Runge R. G., Birt D., Gingell R., Lawson T., Nagel D., Wallcave L., Salmasi S. Z. Current knowledge of pancreatic carcinogenesis in the hamster and its relevance to the human disease. Cancer. 1981 Mar 15;47(6 Suppl):1573–1589. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810315)47:6+<1573::aid-cncr2820471420>3.0.co;2-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pour P., Mohr U., Cardesa A., Althoff J., Krüger F. W. Pancreatic neoplasms in an animal model: morphological, biological, and comparative studies. Cancer. 1975 Aug;36(2):379–389. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197508)36:2<379::aid-cncr2820360213>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J. D., Yuh S. L., Petrelli M., Jaffe R. Ductuloinsular tumors of the pancreas: a light, electron microscopic and immunohistochemical study. Cancer. 1982 Mar 1;49(5):908–915. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19820301)49:5<908::aid-cncr2820490514>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runge R. G., Pour P. Blood group specificity of pancreatic tumor mucin. Cancer Lett. 1980 Oct;10(4):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(80)90053-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runge R., Takahashi M., Pour P. Pancreatic ductulitis in Syrian golden hamsters bearing homologous transplantable pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Cancer Lett. 1978 Oct;5(4):225–229. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(78)80044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpelli D. G., Rao M. S., Subbarao V. Augmentation of carcinogenesis by N-nitrosobis(2-oxopropyl)amine administered during S phase of the cell cycle in regenerating hamster pancreas. Cancer Res. 1983 Feb;43(2):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlosnagle D. C., Campbell W. G., Jr The papillary and solid neoplasm of the pancreas: a report of two cases with electron microscopy, one containing neurosecretory granules. Cancer. 1981 Jun 1;47(11):2603–2610. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810601)47:11<2603::aid-cncr2820471115>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidenheim K. M., Hinchey W. W., Campbell W. G., Jr Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in adults with islet-cell hyperplasia and degranulation of exocrine cells of the pancreas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jan;79(1):14–24. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/79.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]