Abstract
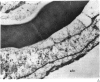
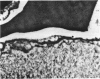
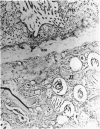
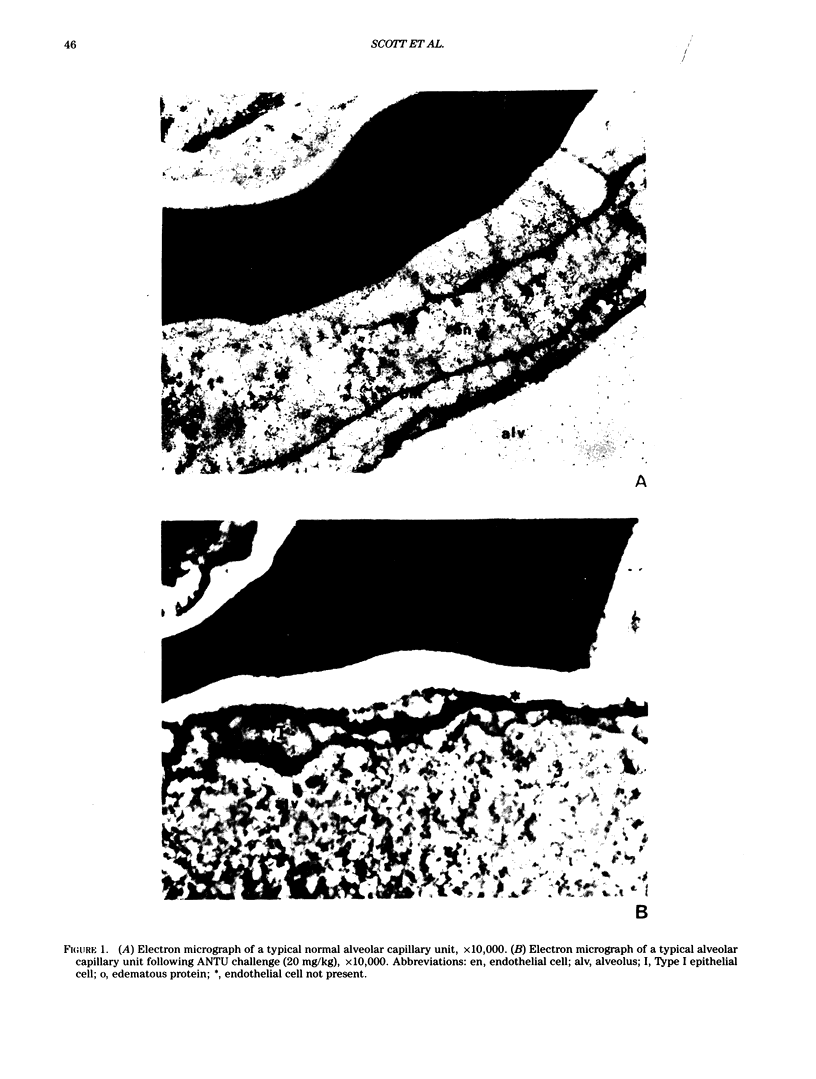
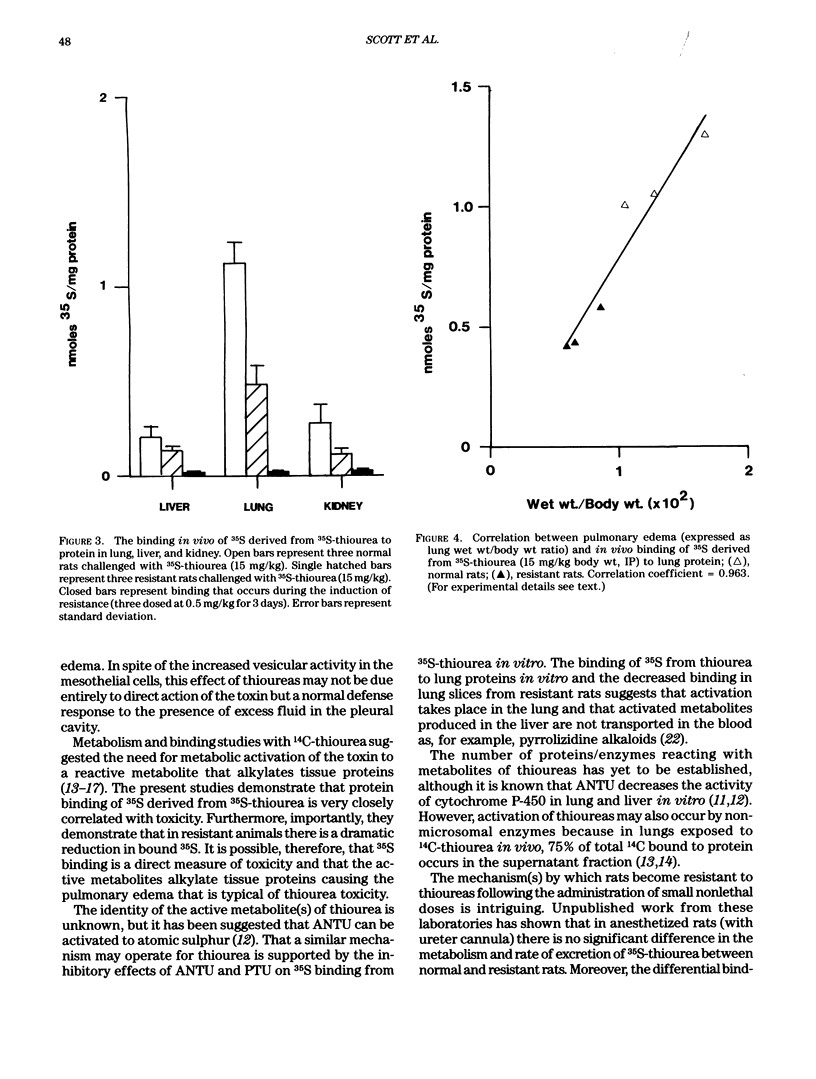
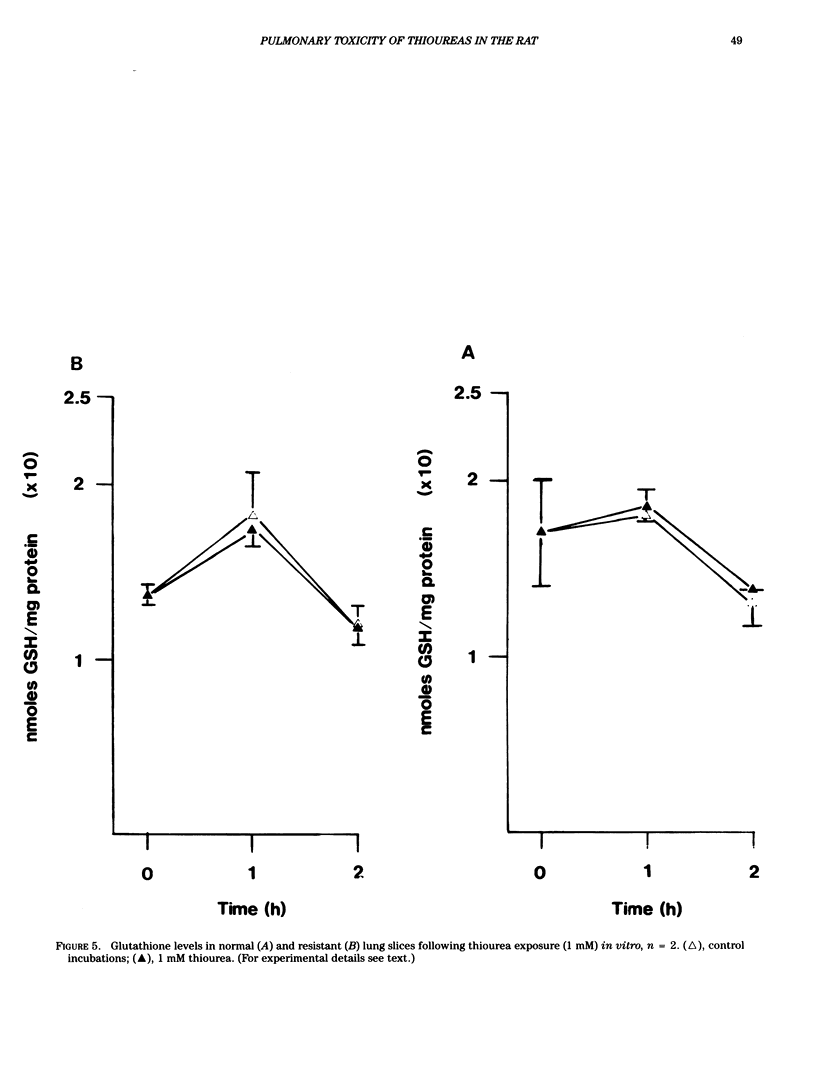
Administration of alpha-naphthylthiourea (ANTU) to rats causes damage to pulmonary endothelial cells and possibly mesothelial lining cells that together may account for the massive pleural effusion characteristic of thiourea toxicity. Using 35S-thiourea as a model compound, the extent of binding of 35S to lung proteins correlated well with the extent of edema, suggesting that the extent of binding of thiourea metabolites is a measure of lung toxicity. ANTU and phenylthiourea (PTU) compete for 35S binding to lung slices, suggesting that these toxins may act in a similar way. Binding of 35S in lung slices from resistant rats is much less than in controls, and resistance cannot be explained by differences in either whole body metabolism or redistribution of thiourea in vivo. Lung glutathione levels (in vitro and in vivo) in normal and resistant rats following thiourea administration were essentially the same. However, at doses of thiourea that cause pleural effusion, there was an increase in total lung glutathione.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Block E. R., Schoen F. J. Effect of alpha naphthylthiourea on uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine from the pulmonary circulation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jan;123(1):69–73. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd M. R., Neal R. A. Studies on the mechanism of toxicity and of development of tolerance to the pulmonary toxin, alpha-naphthylthiourea (ANTU). Drug Metab Dispos. 1976 Jul-Aug;4(4):314–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn V. H., Lyle J. A fluorometric assay for glutathione. Anal Biochem. 1966 Mar;14(3):434–440. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90286-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. L., Hurley J. V. Alpha-naphthyl-thiourea-induced pulmonary oedema in the rat: a topographical and electron-microscope study. J Pathol. 1972 Jan;106(1):25–35. doi: 10.1002/path.1711060103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri S. N., Combs A. B. Sulfur-containing compounds and tolerance in the prevention of certain metabolic effects of phenylthiourea. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1970 May;16(3):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(70)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond T. G., Mobbs M. Lung oedema--microscopic detection. J Appl Toxicol. 1984 Aug;4(4):219–221. doi: 10.1002/jat.2550040411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger M. A., Giri S. N. 14C-Thiourea binding in the rat lung. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;26(3):609–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger M. A., Giri S. N., Alley M., Budd E. R., Hwang F. Tissue distribution and binding of radioactivity from 14C-thiourea in the rat. Proc West Pharmacol Soc. 1975;18:351–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger M. A., Giri S. N., Alley M., Budd E. R., Hwang F. Tissue distribution and binding of radioactivity from 14C-thiourea in the rat. Drug Metab Dispos. 1974 Nov-Dec;2(6):521–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger M. A., Giri S. N., Budd E. A pharmacodynamic study of (14C)thiourea toxicity in mature, immature, tolerant, and nontolerant rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 Sep;37(3):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger M. A., Giri S. N., Hwang F. Binding of radioactivity from (14C)thiourea to rat lung protein. Drug Metab Dispos. 1976 Mar-Apr;4(2):119–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger M. A., Giri S. N., Patwell S., Zuckerman J. E., Gorin A., Parsons G. Effect of acute lung injury on angiotensin converting enzyme in serum, lung lavage, and effusate. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Feb;121(2):373–376. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrer J. P., Kacew S. Systematically applied chemicals that damage lung tissue. Toxicology. 1985 Jun 28;35(4):251–293. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(85)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Arnau T., Neal R. A. Metabolism of alpha-naphthylthiourea by rat liver and rat lung microsomes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1980 Mar 30;53(1):164–173. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(80)90393-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. R., Moore M., Chrzanowski R., Cieplinski W. The effect of alphanapthylthiourea (ANTU)-induced acute injury on lung binding of antibody to angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE). Adv Exp Med Biol. 1986;198(Pt A):503–512. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5143-6_67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Miller J., Reid L. Pulmonary oedema induced by ANTU, or by high or low oxygen concentrations in rat--an electron microscopic study. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Aug;53(4):347–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. F., Makarski J. S., Rounds S. Studies on the mechanism of decreased angiotensin I conversion in rat lungs injured with alpha-naphthylthiourea. Exp Lung Res. 1985;8(4):243–259. doi: 10.3109/01902148509087807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]