Abstract
Paraquat, a quaternary ammonium bipyridyl herbicide, produces degenerative lesions in the lung after systemic administration to man and animals. The pulmonary toxicity of paraquat resembles in several ways the toxicity of several other lung toxins, including oxygen, nitrofurantoin and bleomycin. Although a definitive mechanism of toxicity of paraquat has not been delineated, a cyclic single electron reduction/oxidation of the parent molecule is a critical mechanistic event. The redox cycling of paraquat has two potentially important consequences relevant to the development of toxicity: generation of "activated oxygen" (e.g., superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical) which is highly reactive to cellular macromolecules; and/or oxidation of reducing equivalents (e.g., NADPH, reduced glutathione) necessary for normal cell function. Paraquat-induced pulmonary toxicity, therefore, is a potentially useful model for evaluation of oxidant mechanisms of toxicity. Furthermore, characterization of the consequences of intracellular redox cycling of xenobiotics will no doubt provide basic information regarding the role of this phenomena in the development of chemical toxicity.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H., Cote M. G., Witschi H. Lung injury induced by butylated hydroxytoluene: cytodynamic and biochemical studies in mice. Lab Invest. 1977 Jan;36(1):26–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. The pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am J Pathol. 1974 Nov;77(2):185–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H., Wyatt J. P. Oxygen poisoning in mice. Ultrastructural and surfactant studies during exposure and recovery. Arch Pathol. 1970 Nov;90(5):463–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autor A. P. Reduction of paraquat toxicity by superoxide dismutase. Life Sci. 1974 Apr 1;14(7):1309–1319. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90439-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin R. C., Pasi A., MacGregor J. T., Hine C. H. The rates kof radical formation from dipyridylium herbicides paraquat, diquat, and morfamquat in homogenates of rat lung, kidney, and liver: an inhibitory effect of carbon monoxide. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1975 May;32(2):298–304. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(75)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett D. J., Fisher A. B. Alterations of glucose metabolism during perfusion of rat lung with paraquat. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jun;234(6):E653–E659. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.6.E653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block E. R., Fisher A. B. Hyperoxia and lung serotonin clearance: a new observation. Chest. 1977 Feb;71(2 Suppl):289–291. doi: 10.1378/chest.71.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigelius R., Lenzen R., Sies H. Increase in hepatic mixed disulphide and glutathione disulphide levels elicited by paraquat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Apr 15;31(8):1637–1641. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90393-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk R. F., Lawrence R. A., Lane J. M. Liver necrosis and lipid peroxidation in the rat as the result of paraquat and diquat administration. Effect of selenium deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1024–1031. doi: 10.1172/JCI109754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
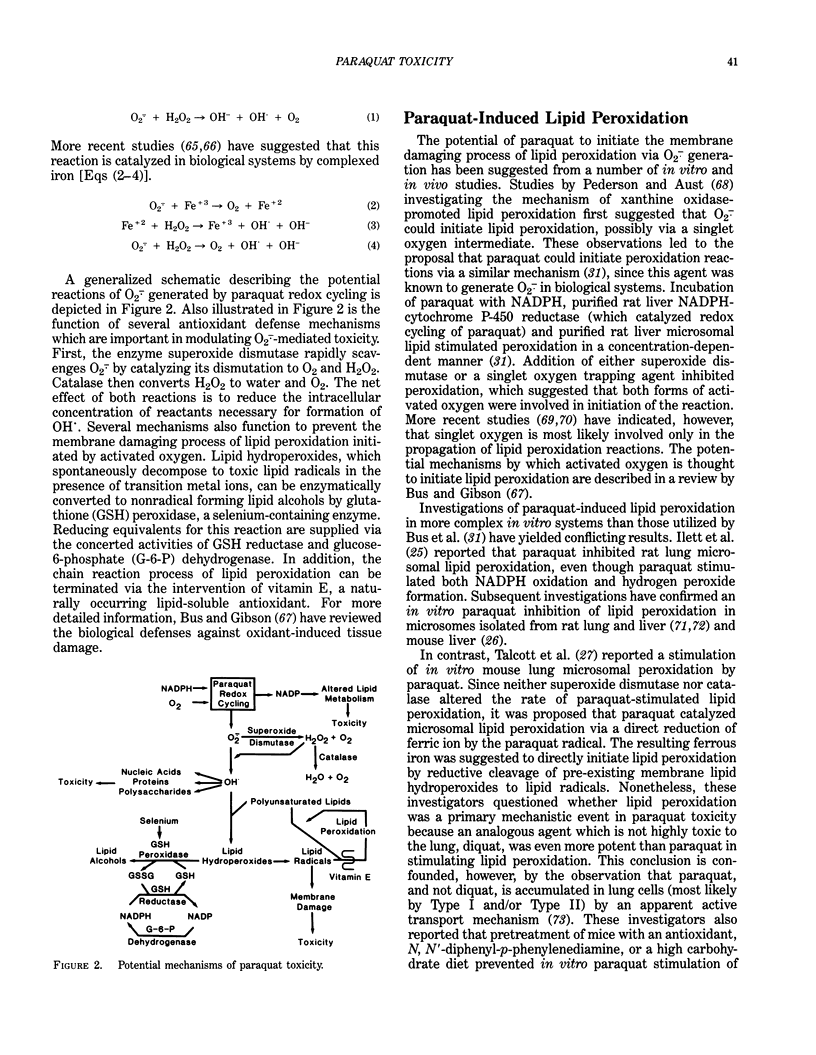
- Bus J. S., Aust S. D., Gibson J. E. Lipid peroxidation: a possible mechanism for paraquat toxicity. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1975 May;11(1):31–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bus J. S., Aust S. D., Gibson J. E. Superoxide- and singlet oxygen-catalyzed lipid peroxidation as a possible mechanism for paraquat (methyl viologen) toxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jun 4;58(3):749–755. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80481-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bus J. S., Cagen S. Z., Olgaard M., Gibson J. E. A mechanism of paraquat toxicity in mice and rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;35(3):501–513. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bus J. S., Gibson J. E. Postnatal toxicity of chronically administered paraquat in mice and interactions with oxygen and bromobenzene. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;33(3):461–470. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(75)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler C., 2nd, Kleinerman J. Paraquat in the rabbit. Br J Ind Med. 1971 Jan;28(1):67–71. doi: 10.1136/oem.28.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cagen S. Z., Gibson J. E. Liver damage following paraquat in selenium-deficient and diethyl maleate-pretreated mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 May;40(2):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(77)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow C. K., Tappel A. L. An enzymatic protective mechanism against lipid peroxidation damage to lungs of ozone-exposed rats. Lipids. 1972 Aug;7(8):518–524. doi: 10.1007/BF02533017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. G., McElligott T. F., Hurst E. W. The toxicity of paraquat. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Apr;23(2):126–132. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.2.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., Tierney D. F. Superoxide dismutase and pulmonary oxygen toxicity. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jun;226(6):1401–1407. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.6.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneke S. M., Fanburg B. L. Normobaric oxygen toxicity of the lung. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 10;303(2):76–86. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007103030204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Luzio N. R. Antioxidants, lipid peroxidation and chemical-induced liver injury. Fed Proc. 1973 Aug;32(8):1875–1881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge A. D. The mode of action of the bipyridylium herbicides, paraquat and diquat. Endeavour. 1971 Sep;30(111):130–135. doi: 10.1016/0160-9327(71)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douze J. M., Van Heijst A. N. The paraquat intoxication--oxygen a real poison. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1977;41 (Suppl 2):241–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrington J. A., Ebert M., Land E. J., Fletcher K. Bipyridylium quaternary salts and related compounds. V. Pulse radiolysis studies of the reaction of paraquat radical with oxygen. Implications for the mode of action of bipyridyl herbicides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 26;314(3):372–381. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher H. K., Clements J. A., Tierney D. F., Wright R. R. Pulmonary effects of paraquat in the first day after injection. Am J Physiol. 1975 Apr;228(4):1217–1223. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.4.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher H. K., Clements J. A., Wright R. R. Enhancement of oxygen toxicity by the herbicide paraquat. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Feb;107(2):246–252. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.2.246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher H. K. Paraquat is not bacteriostatic under anaerobic conditions. Life Sci. 1976 Aug 1;19(3):421–425. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Massaro D. Oxygen toxicity. Am J Med. 1980 Jul;69(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90509-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage J. C. The action of paraquat and diquat on the respiration of liver cell fractions. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):757–761. doi: 10.1042/bj1090757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri S. N., Krishna G. A. The effect of paraquat on guanylate cyclase activity in relation to morphological changes of guinea pig lungs. Lung. 1980;157(3):127–134. doi: 10.1007/BF02713609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. B., Lyons S. A., Last J. A. Paraquat-induced changes in the rate of collagen biosynthesis by rat lung explants. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Dec;92(6):1033–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFSTEN P. E., HUNTER F. E., Jr, GEBICKI J. M., WEINSTEIN J. Formation of "lipid peroxide" under conditions which lead to swelling and lysis of rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 4;7:276–280. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER F. E., Jr, GEBICKI J. M., HOFFSTEN P. E., WEINSTEIN J., SCOTT A. Swelling and lysis of rat liver mitochondria induced by ferrous ions. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:828–835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. O., Castle J. R., Swenson E. W., Block A. J. Lobar lavage: therapeutic benefit in pulmonary alveolar filling disorders. Chest. 1974 Jun;65(6):655–659. doi: 10.1378/chest.65.6.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Fridovich I. Intracellular production of superoxide radical and of hydrogen peroxide by redox active compounds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Sep;196(2):385–395. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90289-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Fridovich I. Paraquat and Escherichia coli. Mechanism of production of extracellular superoxide radical. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10846–10852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Fridovich I. Regulation of the synthesis of superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli. Induction by methyl viologen. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7667–7672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide radical and the oxygen enhancement of the toxicity of paraquat in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8143–8148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger M. A., Chvapil M. Effect of paraquat on rat lung prolyl hydroxylase. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1977 Jan;16(1):159–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M. Z., Bhatnagar R. S. Involvement of superoxide in the paraquat-induced enhancement of lung collagen synthesis in organ culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90944-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilett K. F., Stripp B., Menard R. H., Reid W. D., Gillette J. R. Studies on the mechanism of the lung toxicity of paraquat: comparison of tissue distribution and some biochemical parameters in rats and rabbits. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1974 May;28(2):216–226. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(74)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapanci Y., Weibel E. R., Kaplan H. P., Robinson F. R. Pathogenesis and reversibility of the pulmonary lesions of oxygen toxicity in monkeys. II. Ultrastructural and morphometric studies. Lab Invest. 1969 Jan;20(1):101–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeling P. L., Smith L. L., Aldridge W. N. The formation of mixed disulphides in rat lung following paraquat administration. Correlation with changes in intermediary metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 27;716(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrer J. P., Haschek W. M., Witschi H. The influence of hyperoxia on the acute toxicity of paraquat and diquat. Drug Chem Toxicol. 1979;2(4):397–408. doi: 10.3109/01480547909016033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbrough R. D., Gaines T. B. Toxicity of paraquat to rats and its effect on rat lungs. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;17(3):679–690. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(70)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbrough R. D., Linder R. E. The ultrastructure of the paraquat lung lesion in the rat. Environ Res. 1973 Sep;6(3):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(73)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. M., Lai E. K., McCay P. B. Singlet oxygen production associated with enzyme-catalyzed lipid peroxidation in liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6496–6502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbrust D. J., Mavis R. D. The effect of paraquat on microsomal lipid peroxidation in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1980 Apr;53(2):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(80)90433-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger R. I., Lee P. W., Black A., Fukuto T. R. Inhibition of microsomal aldrin epoxidation by diquat and several related bipyridylium compounds. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1973 Jan;9(1):1–3. doi: 10.1007/BF01856762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengfelder E., Elstner E. F. Determination of the superoxide dismutating activity of D-penicillamine copper. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Jun;359(6):751–757. doi: 10.1515/bchm.1978.359.1.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Day E. D., Jr Superoxide-dependent production of hydroxyl radical catalyzed by iron-EDTA complex. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 1;86(1):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra H. P., Fridovich I. The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3170–3175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery M. R. Interaction of paraquat with the pulmonary microsomal fatty acid desaturase system. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;36(3):543–554. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery M. R. Paraquat toxicity and pulmonary superoxide dismutase: an enzymic deficiency of lung microsomes. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1977 Jan;16(1):155–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omaye S. T., Reddy K. A., Cross C. E. Enhanced lung toxicity of paraquat in selenium-deficient rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1978 Feb;43(2):237–247. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(78)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T. C., Aust S. D. The role of superoxide and singlet oxygen in lipid peroxidation promoted by xanthine oxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 8;52(3):1071–1078. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T. C., Buege J. A., Aust S. D. Microsomal electron transport. The role of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-cytochrome c reductase in liver microsomal lipid peroxidation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7134–7141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popenoe D. Effects of paraquat aerosol on mouse lung. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1979 Jul;103(7):331–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffin T. A., Simon L. M., Douglas W. H., Theodore J., Robin E. D. The effects of variable O2 tension and of exogenous superoxide dismutase on type II pneumocytes exposed to paraquat. Lab Invest. 1980 Feb;42(2):205–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy K. A., Litov R. E., Omaye S. T. Effect of pretreatment with antiinflammatory agents on paraquat toxicity in the rat. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1977 May;17(1):87–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes M. L., Zavala D. C., Brown D. Hypoxic protection in paraquat poisoning. Lab Invest. 1976 Nov;35(5):496–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigo A., Stevanato R., Finazzi-Agro A., Rotilio G. An attempt to evaluate the rate of the Haber-Weiss reaction by using OH radical scavengers. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 1;80(1):130–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80422-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B., Grossmann G., Ivemark B. The alveolar lining layer in experimental paraquat poisoning. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1976 Jan;84(1):40–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. S., Smith L. L., Wyatt I. Evidence for energy-dependent accumulation of paraquat into rat lung. Nature. 1974 Nov 22;252(5481):314–315. doi: 10.1038/252314b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. S., Smith L. L., Wyatt I. The relevance of pentose phosphate pathway stimulation in rat lung to the mechanism of paraquat toxicity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Aug 1;25(15):1763–1767. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90412-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. E., Block E. R., Chang R. Y. Paraquat-induced DNA damage in mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 28;91(4):1302–1308. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasame H. A., Boyd M. R. Superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production and NADPH oxidation stimulated by nitrofurantoin in lung microsomes: possible implications for toxicity. Life Sci. 1979 Mar 19;24(12):1091–1096. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu H., Talcott R. E., Rice S. A., Wei E. T. Lipid peroxidation and paraquat toxicity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979;28(2):327–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90523-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. S., Jackett P. S., Carroll M. E., Lowrie D. B. Superoxide independence of paraquat toxicity in Escherichia coli. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 Aug;37(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90090-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P., Heath D., Kay J. M. The pathogenesis and structure of paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. J Pathol. 1974 Oct;114(2):57–67. doi: 10.1002/path.1711140202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P., Heath D. Paraquat. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol. 1976 Oct;4(4):411–445. doi: 10.1080/10408447609164020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P., Heath D. The ultrastructure and time sequence of the early stages of paraquat lung in rats. J Pathol. 1974 Dec;114(4):177–184. doi: 10.1002/path.1711140402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen C., Muliawan H., Kappus H. Lack of in vivo lipid peroxidation in experimental paraquat poisoning. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;310(3):241–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00499917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen C., Netter K. J. On the mechanism of paraquat action on microsomal oxygen reduction and its relation to lipid peroxidation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 15;47(3):593–602. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90529-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. J., Freeman G., Evans M. J. Early response of lungs to low levels of nitrogen dioxide. Light and electron microscopy. Arch Environ Health. 1972 Mar;24(3):160–179. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1972.10666066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. J., Sloan M. F., Evans M. J., Freeman G. Alveolar type 1 cell response to exposure to 0.5 PPM O3 for short periods. Exp Mol Pathol. 1974 Feb;20(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(74)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svingen B. A., O'Neal F. O., Aust S. D. The role of superoxide and singlet oxygen in lipid peroxidation. Photochem Photobiol. 1978 Oct-Nov;28(4-5):803–809. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1978.tb07022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. I., Purchase I. F., Smith L. L. Pulmonary ultrastructure after oral and intravenous dosage of paraquat to rats. J Pathol. 1977 Apr;121(4):233–241. doi: 10.1002/path.1711210407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talcott R. E., Shu H., Wei E. T. Dissociation of microsomal oxygen reduction and lipid peroxidation with the electron acceptors, paraquat and menadione. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 1;28(5):665–671. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. D., Patrick R. S. Collagen prolyl hydroxylase levels in experimental paraquat poisoning. Br J Exp Pathol. 1978 Jun;59(3):288–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N. A convenient electrochemical preparation of reduced methyl viologen and a kinetic study of the reaction with oxygen using an anaerobic stopped-flow apparatus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 26;333(3):487–496. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90133-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trush M. A., Mimnaugh E. G., Ginsburg E., Gram T. E. Studies on the in vitro interaction of mitomycin C, nitrofurantoin and paraquat with pulmonary microsomes. Stimulation of reactive oxygen-dependent lipid peroxidation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Mar 1;31(5):805–814. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90467-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijeyaratnam G. S., Corrin B. Experimental paraquat poisoning: a histological and electron-optical study of the changes in the lung. J Pathol. 1971 Feb;103(2):123–129. doi: 10.1002/path.1711030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witschi H., Côte M. G. Primary pulmonary responses to toxic agents. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol. 1977 May;5(1):23–66. doi: 10.3109/10408447709101341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witschi H., Kacew S., Hirai K. I., Côté M. G. In vivo oxidation of reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate by paraquat and diquat in rat lung. Chem Biol Interact. 1977 Nov;19(2):143–160. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(77)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman R. J., Dodge A. D. Mechanism of paraquat action: inhibition of the herbicidal effect by a copper chelate with superoxide dismutating activity. Z Naturforsch C. 1979 Nov;34(11):1033–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


