Abstract
The lung is a primary target of cell injury in patients receiving cytotoxic drugs, and in many cases the reaction is severe enough to produce diffuse pulmonary fibrosis. Although many different agents may damage the lung, the patterns of cellular injury and repair are relatively constant. Using bleomycin toxicity as an example, it has been shown that, after IV injection, the selective site of lung injury is the vascular endothelium; this is followed by the accumulation of interstitial edema and later by necrosis of Type I epithelial cells. In normal repair, rapid proliferation of Type II cells, followed by differentiation to Type I, restores the epithelial surface without fibrosis. However, after bleomycin, Type II cell proliferation is frequently followed by abnormal differentiation to a metaplastic form of epithelium. Fibroblast proliferation accompanies this abnormal epithelial response which is related either to selective retention of bleomycin by epithelial cells or to the toxic effects of administering more drug at the time of Type II cell division. It is concluded that diffuse interstitial fibrosis results from prolonged disturbance of the normal epithelial-mesenchymal interrelationships at the alveolar wall. Disruption of the fibroblastic control system by extensive epithelial necrosis or by delayed or inappropriate repair may be the key factor in instigating fibroblast proliferation and subsequent deposition of collagen. This mechanism may account for the development of diffuse fibrosis or fibrosing alveolitis in response to a variety of pulmonary toxins.
Full text
PDF




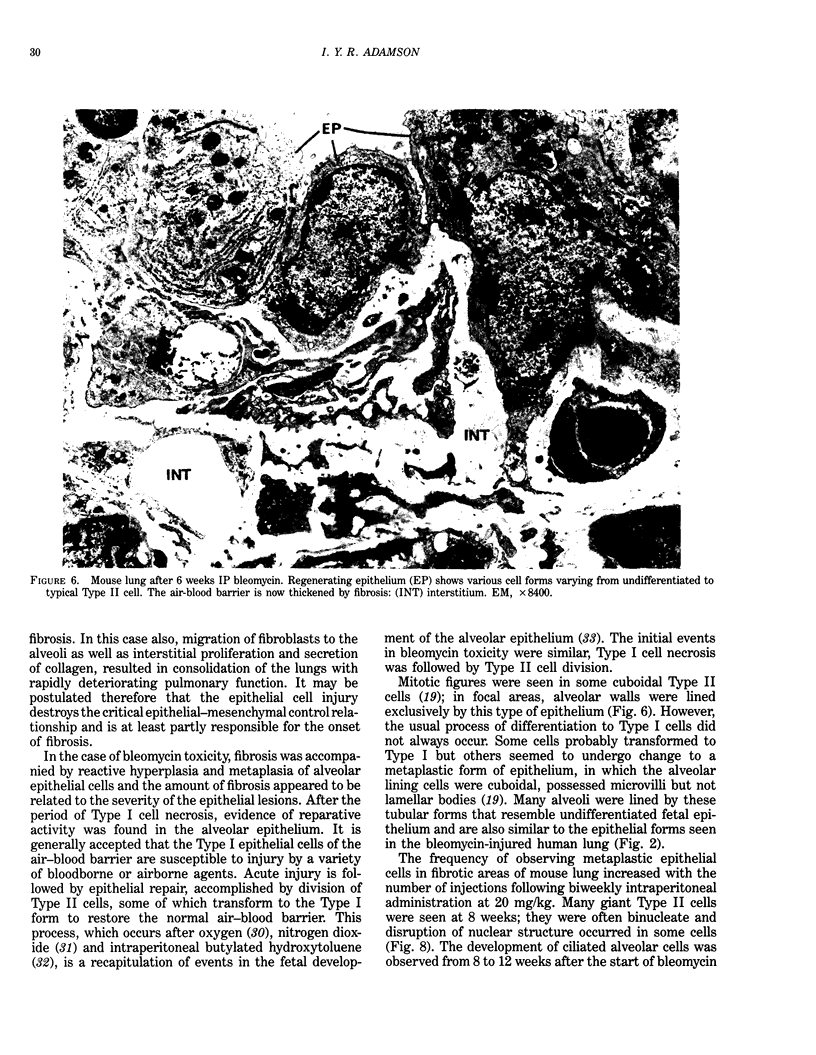


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. Bleomycin-induced injury and metaplasia of alveolar type 2 cells. Relationship of cellular responses to drug presence in the lung. Am J Pathol. 1979 Aug;96(2):531–544. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H., Cote M. G., Witschi H. Lung injury induced by butylated hydroxytoluene: cytodynamic and biochemical studies in mice. Lab Invest. 1977 Jan;36(1):26–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. Derivation of type 1 epithelium from type 2 cells in the developing rat lung. Lab Invest. 1975 Jun;32(6):736–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. Origin of ciliated alveolar epithelial cells in bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am J Pathol. 1977 Jun;87(3):569–580. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. The pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am J Pathol. 1974 Nov;77(2):185–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. The type 2 cell as progenitor of alveolar epithelial regeneration. A cytodynamic study in mice after exposure to oxygen. Lab Invest. 1974 Jan;30(1):35–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson Y. I., Bowden D. H. Pulmonary injury and repair. Organ culture studies of murine lung after oxygen. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Dec;100(12):640–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs S. S., Sartiano G. P., DeMezza A. Minimal bone marrow damage in mice given bleomycin. Cancer Res. 1974 Aug;34(8):1938–1942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden D. H., Adamson I. Y. Endothelial regeneration as a marker of the differential vascular responses in oxygen-induced pulmonary edema. Lab Invest. 1974 Mar;30(3):350–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo A. Importance of experimental data for the improvement of the therapeutical effect of bleomycin. Prog Biochem Pharmacol. 1976;11:2–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen O. P. The effect of bleomycin on rapidly proliferating epidermis. A comparative investigation using micro-flow fluorometry, H3Tdr incorporation and a stathmokinetic method (colcemid). Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1975 Dec 19;19(4):337–348. doi: 10.1007/BF02889377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codling B. W., Chakera T. M. Pulmonary fibrosis following therapy with Melphalan for multiple myeloma. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Aug;25(8):668–673. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.8.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dlugi A. M., Robie K. M., Mitchell M. S. Failure of bleomycin to affect humoral or cell-mediated immunity in the mouse. Cancer Res. 1974 Oct;34(10):2504–2507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Cabral L. J., Stephens R. J., Freeman G. Renewal of alveolar epithelium in the rat following exposure to NO2. Am J Pathol. 1973 Feb;70(2):175–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman A. P., Pietra G. G. Handling of bioactive materials by the lung (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Oct 24;291(17):884–889. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197410242911706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman R. W., Baker J. R., Thompson G. R., Schaeppi U. H., Illievski V. R., Cooney D. A., Davis R. D. Bleomycin-induced interstitial pneumonia in dogs. Thorax. 1971 Nov;26(6):675–682. doi: 10.1136/thx.26.6.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto J. Radioautographic studies on the intracellular distribution of bleomycin-14C in mouse tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1974 Nov;34(11):2969–2974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould V. E., Tosco R., Wheelis R. F., Gould N. S., Kapanci Y. Oxygen pneumonitis in man. Ultrastructural observations on the development of alveolar lesions. Lab Invest. 1972 May;26(5):499–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hittelman W. N., Rao P. N. Bleomycin-induced damage in prematurely condensed chromosomes and its relationship to cell cycle progression in CHO cells. Cancer Res. 1974 Dec;34(12):3433–3439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal Z. M., Kohn K. W., Ewig R. A., Fornace A. J., Jr Single-strand scission and repair of DNA in mammalian cells by bleomycin. Cancer Res. 1976 Oct;36(10):3834–3838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel K. S., Brashear R. E., Sharma H. M., Yum M. N., Glover J. L. Pulmonary fibrosis and nitrofurantoin. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Aug;108(2):353–356. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen P. H., Clausen O. P., Iversen U. M., Rohrbach R. Some effects of bleomycin on the proliferation, maturation time and protein synthesis of hairless mouse epidermis. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1976 Jan;9(1):77–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1976.tb01255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kistler G. S., Caldwell P. R., Weibel E. R. Development of fine structural damage to alveolar and capillary lining cells in oxygen-poisoned rat lungs. J Cell Biol. 1967 Mar;32(3):605–628. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.3.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. T., Auger L. T., Saunders G. F., Haidle C. W. Effect of bleomycin on the synthesis and function of RNA. Cancer Res. 1977 May;37(5):1345–1348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson S., Cronberg S., Denneberg T., Ohlsson N. M. Pulmonary reaction to nitrofurantoin. Scand J Respir Dis. 1973;54(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehane D. E., Hurd E., Lane M. The effects of bleomycin on immunocompetence in man. Cancer Res. 1975 Oct;35(10):2724–2728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lown J. W., Sim S. K. The mechanism of the bleomycin-induced cleavage of DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 22;77(4):1150–1157. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark G. J., Lehimgar-Zadeh A., Ragsdale B. D. Cyclophosphamide pneumonitis. Thorax. 1978 Feb;33(1):89–93. doi: 10.1136/thx.33.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullough B., Collins J. F., Johanson W. G., Jr, Grover F. L. Bleomycin-induced diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis in baboons. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):79–88. doi: 10.1172/JCI108928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onuma T., Holland J. F., Masuda H., Waligunda J. A., Goldberg G. A. Microbiological assay of bleomycin: inactivation, tissue distribution, and clearance. Cancer. 1974 May;33(5):1230–1238. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197405)33:5<1230::aid-cncr2820330507>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orwoll E. S., Kiessling P. J., Patterson J. R. Interstitial pneumonia from mitomycin. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Sep;89(3):352–355. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-3-352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka K., Murota S. I., Mori Y. Stimulatory effect of bleomycin on the synthesis of acidic glycosaminoglycans in cultured fibroblasts derived from rat carrageenin granuloma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 24;444(2):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90379-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudders R. A., Hensley G. T. Bleomycin pulmonary toxicity. Chest. 1973 Apr;63(4):627–628. doi: 10.1378/chest.63.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M. L., Johnson D. E., Holoye P. Y., Lanzotti V. J. Large-dose bleomycin therapy and pulmonary toxicity. A possible role of prior radiotherapy. JAMA. 1976 Mar 15;235(11):1117–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scadding J. G., Hinson K. F. Diffuse fibrosing alveolitis (diffuse interstitial fibrosis of the lungs). Correlation of histology at biopsy with prognosis. Thorax. 1967 Jul;22(4):291–304. doi: 10.1136/thx.22.4.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P., Heath D., Kay J. M. The pathogenesis and structure of paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. J Pathol. 1974 Oct;114(2):57–67. doi: 10.1002/path.1711140202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider G. L., Hayes J. A., Korthy A. L. Chronic interstitial pulmonary fibrosis produced in hamsters by endotracheal bleomycin: pathology and stereology. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jun;117(6):1099–1108. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.6.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sostman H. D., Matthay R. A., Putman C. E. Cytotoxic drug-induced lung disease. Am J Med. 1977 Apr;62(4):608–615. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starcher B. C., Kuhn C., Overton J. E. Increased elastin and collagen content in the lungs of hamsters receiving an intratracheal injection of bleomycin. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Feb;117(2):299–305. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szapiel S. V., Elson N. A., Fulmer J. D., Hunninghake G. W., Crystal R. G. Bleomycin-induced interstitial pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Oct;120(4):893–899. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.4.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrall R. S., McCormick J. R., Jack R. M., McReynolds R. A., Ward P. A. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in the rat: inhibition by indomethacin. Am J Pathol. 1979 Apr;95(1):117–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toner P. G., Vetters J. M., Spilg W. G., Harland W. A. Fine structure of the lung lesion in a case of paraquat poisoning. J Pathol. 1970 Nov;102(3):182–185. doi: 10.1002/path.1711020311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H. Chemistry and mechanism of action of bleomycin. Fed Proc. 1974 Nov;33(11):2296–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Ishizuka M., Maeda K., Takeuchi T. Studies on bleomycin. Cancer. 1967 May;20(5):891–895. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(1967)20:5<891::aid-cncr2820200550>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Ishizuki M., Hori S., Chimura H., Takeuchi T. The distribution of 3H-bleomycin in mouse tissue. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Nov;21(11):638–642. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Takeuchi T., Hori S., Sawa T., Ishizuka M. Studies on the mechanism of antitumor effect of bleomycin of squamous cell carcinoma. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Jul;25(7):409–420. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijeyaratnam G. S., Corrin B. Experimental paraquat poisoning: a histological and electron-optical study of the changes in the lung. J Pathol. 1971 Feb;103(2):123–129. doi: 10.1002/path.1711030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuzumi G., Hyo Y., Hoshiya T., Yasuzumi F. Effects of bleomycin on human tongue carcinoma cells as revealed by electron microscopy. Cancer Res. 1976 Oct;36(10):3574–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]