Abstract
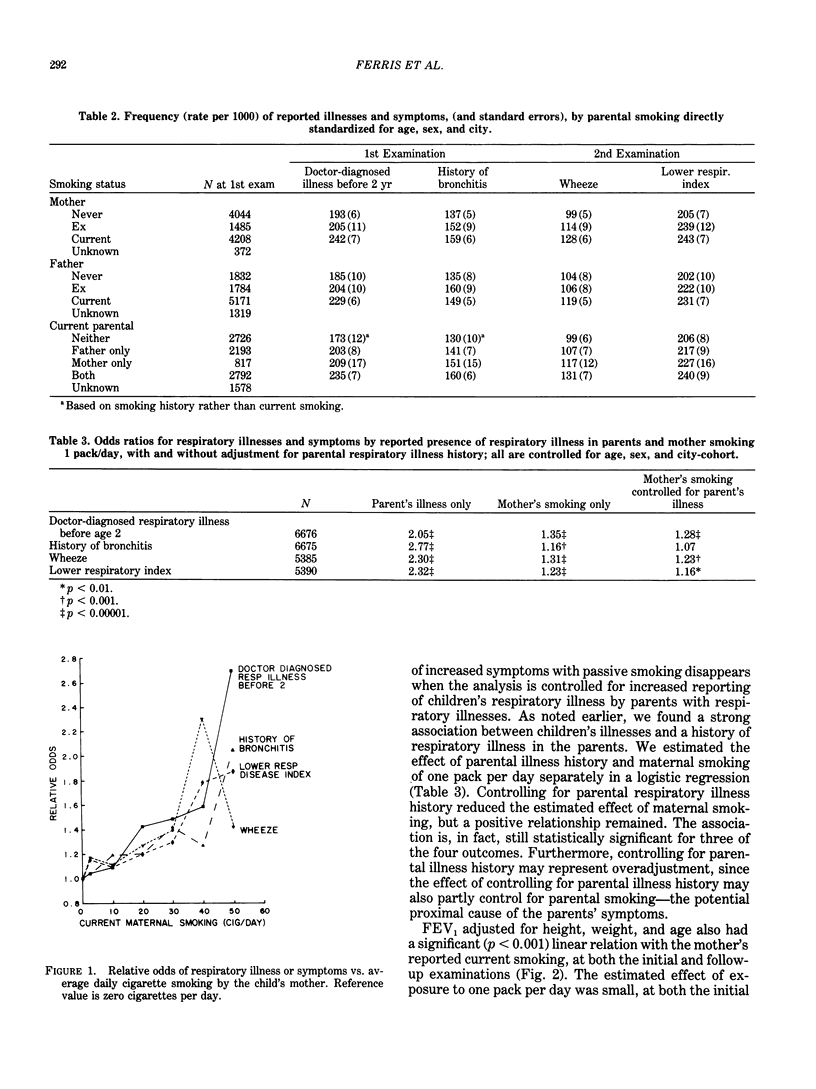
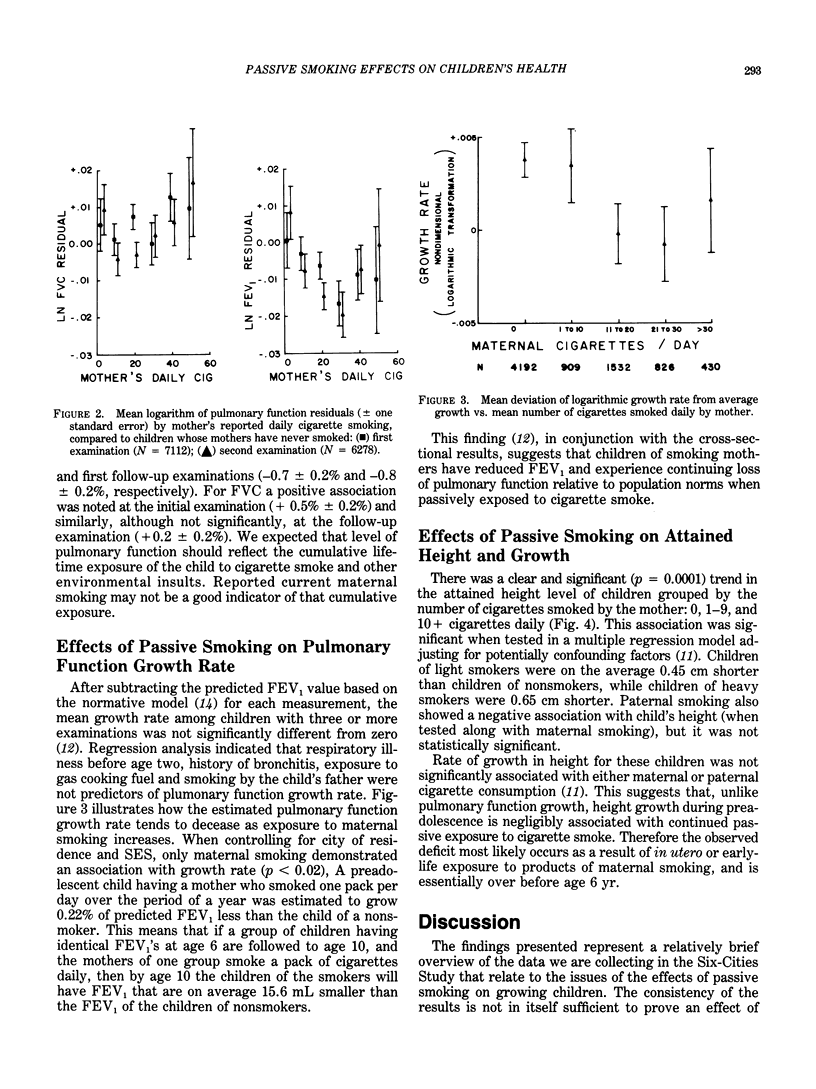
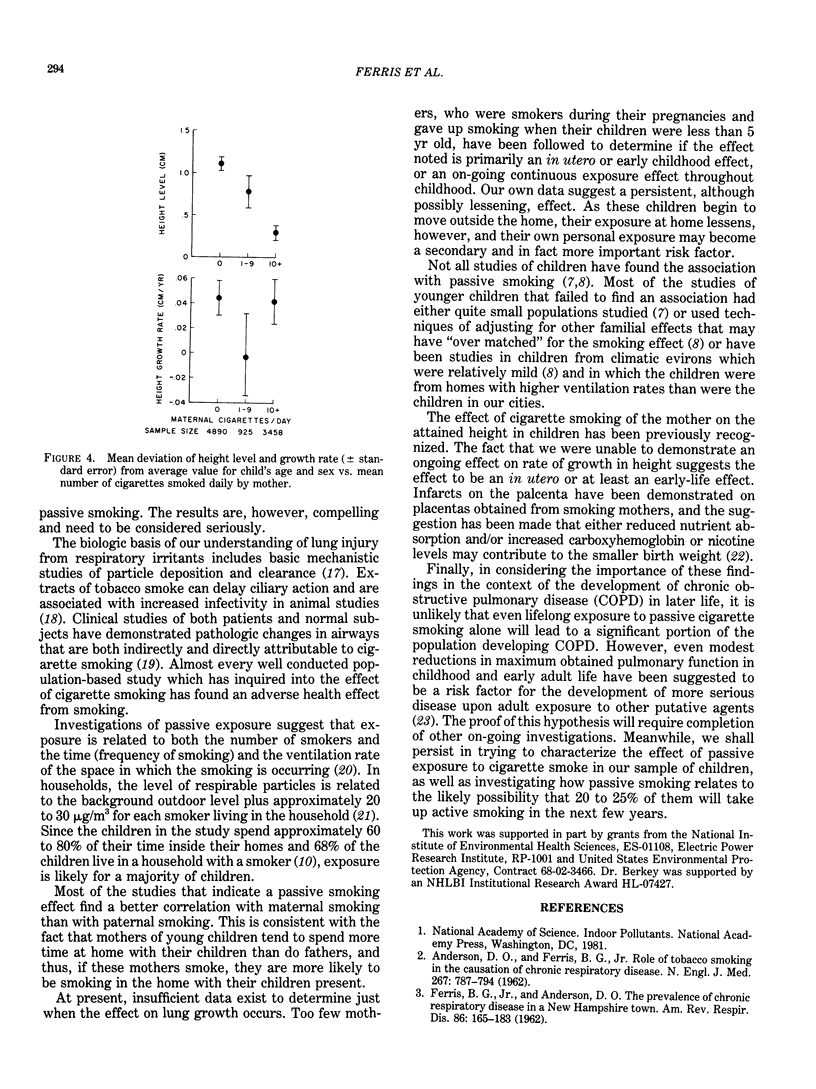
Analysis of data on the effects of passive smoking obtained in preadolescent children from the Harvard Six-Cities Study demonstrates an exposure-response relationship between the number of smokers in the household and the reporting rates for doctor-diagnosed respiratory illness before age 2, history of bronchitis, wheeze most days and nights apart from colds, and a composite of symptoms defined as the lower respiratory index. Similarly, when only the amount currently smoked by the mother was used, the data indicated a relatively uniform increase in each of the reported diseases and symptoms. FEV1 was lower in children with smoking mothers compared to children of nonsmoking mothers. Rate of increases in FEV1 after adjusting for normal growth was significantly smaller in children of smoking mothers and was related also to amount smoked. Notably the effect on level of FVC was not seen and this finding, consistent in several studies, remains unexplained. Although children of smoking mothers were shorter on the average than children of nonsmoking mothers, no on-going passive smoking effect on height growth can be ascertained. All these differences are small and their medical significance remains to be defined.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON D. O., FERRIS B. G., Jr Role of tobacco smoking in the causation of chronic respiratory disease. N Engl J Med. 1962 Oct 18;267:787–794. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196210182671601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abel E. L. Smoking during pregnancy: a review of effects on growth and development of offspring. Hum Biol. 1980 Dec;52(4):593–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert R. E., Lippmann M., Briscoe W. The characteristics of bronchial clearance in humans and the effects of cigarette smoking. Arch Environ Health. 1969 May;18(5):738–755. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1969.10665482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkey C. S., Ware J. H., Speizer F. E., Ferris B. G., Jr Passive smoking and height growth of preadolescent children. Int J Epidemiol. 1984 Dec;13(4):454–458. doi: 10.1093/ije/13.4.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockery D. W., Berkey C. S., Ware J. H., Speizer F. E., Ferris B. G., Jr Distribution of forced vital capacity and forced expiratory volume in one second in children 6 to 11 years of age. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Sep;128(3):405–412. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.3.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRIS B. G., Jr, ANDERSON D. O. The prevalence of chronic respiratory disease in a New Hampshire town. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1962 Aug;86:165–177. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1962.86.2.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris B. G., Jr, Speizer F. E., Spengler J. D., Dockery D., Bishop Y. M., Wolfson M., Humble C. Effects of sulfur oxides and respirable particles on human health. Methodology and demography of populations in study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Oct;120(4):767–779. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.4.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M., Carolin D. The depressant effect of cigarette smoke on the in vitro antibacterial activity of alveolar macrophages. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 23;276(8):421–427. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702232760801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz M. D., Burrows B. Respiratory symptoms related to smoking habits of family adults. Chest. 1976 Jan;69(1):48–50. doi: 10.1378/chest.69.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeder S. R., Corkhill R., Irwig L. M., Holland W. W., Colley J. R. Influence of family factors on the incidence of lower respiratory illness during the first year of life. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1976 Dec;30(4):203–212. doi: 10.1136/jech.30.4.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samet J. M., Tager I. B., Speizer F. E. The relationship between respiratory illness in childhood and chronic air-flow obstruction in adulthood. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Apr;127(4):508–523. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.4.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling R. S., Letai A. D., Hui S. L., Beck G. J., Schoenberg J. B., Bouhuys A. Lung function, respiratory disease, and smoking in families. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Oct;106(4):274–283. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THURLBECK W. M., ANGUS G. E., PARE J. P. Mucous gland hypertrophy in chronic bronchitis, and its occurrence in smokers. Br J Dis Chest. 1963 Apr;57:73–78. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(63)80017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager I. B., Weiss S. T., Rosner B., Speizer F. E. Effect of parental cigarette smoking on the pulmonary function of children. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 Jul;110(1):15–26. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J. H., Dockery D. W., Spiro A., 3rd, Speizer F. E., Ferris B. G., Jr Passive smoking, gas cooking, and respiratory health of children living in six cities. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Mar;129(3):366–374. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.3.366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


