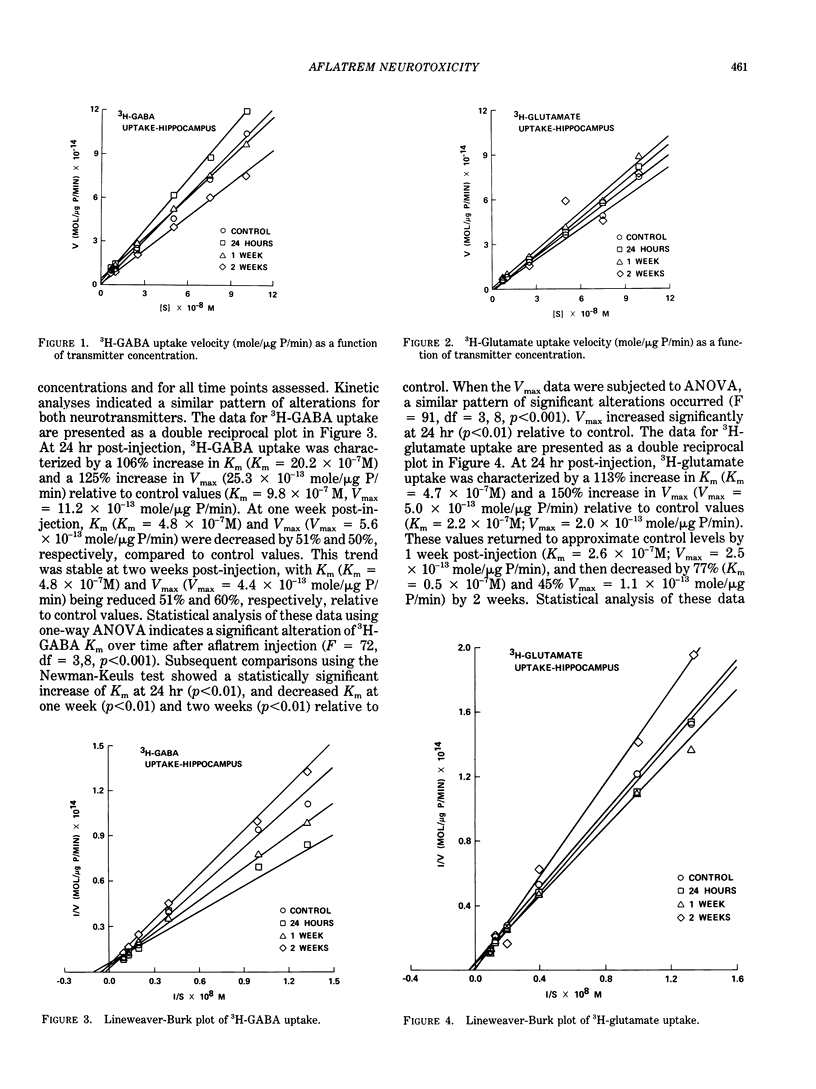
Abstract
Tremorgenic mycotoxins induce neurologic symptoms ranging from mental confusion to tremors, seizures and death, and are apparently the only class of mycotoxins with significant central nervous system activity. Tremorgens have been implicated in a number of neurologic diseases of cattle collectively known as staggers syndromes, and pose significant agricultural and health problems for both cattle and humans. Although the effects of tremorgens are thought to result from transient perturbations of amino acid neurotransmitter release mechanisms, there is reason to believe that acute exposures to toxins with such synaptic effects may result in degeneration of neuronal fiber processes. To test this hypothesis, rats were given a single tremorgenic (3 mg/kg, IP) dose of aflatrem, and kinetics of amino acid neurotransmitter uptake was assessed in isolated hippocampal nerve terminals at 1 day, 1 week, and 2 weeks after injection. Results indicate a decrease in the capacity of the GABA and glutamate uptake systems, which was interpreted as a loss of nerve terminals. The affinity constants suggest a decrease in release of these transmitters as well. In addition to its transient influence on transmitter release, a single low dose of aflatrem is able to induce degeneration of neuronal processes in hippocampal neurotransmitter systems and therefore represents a long-term health threat.
Full text
PDF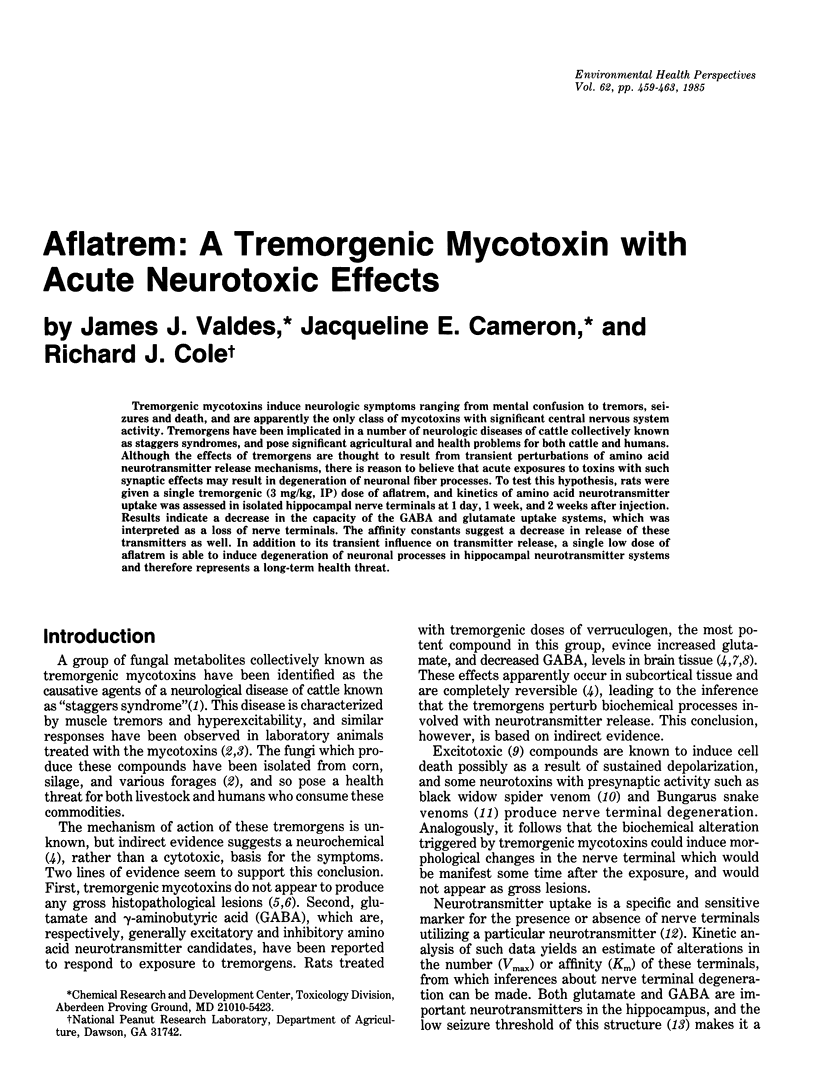



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe T., Alemá S., Miledi R. Isolation and characterization of presynaptically acting neurotoxins from the venom of Bungarus snakes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cysewski S. J., Baetz A. L., Pier A. C. Penitrem A intoxication of calves: blood chemical and pathologic changes. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Jan;36(1):53–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer R. S., Swartzwelder H. S., Eccles C. U., Annau Z. Hippocampal afterdischarges and their post-ictal sequelae in rats: a potential tool for assessment of CNS neurotoxicity. Neurobehav Toxicol. 1979 Spring;1(1):5–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotujac L., Stern P. Pharmacological examination of verruculogen induced tremor. Acta Med Iugosl. 1974;28(3):223–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J. Neurotransmitter uptake: a tool in identifying neurotransmitter-specific pathways. Life Sci. 1973 Dec 16;13(12):1623–1634. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(73)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle P. G., Mortimer P. H., White E. P. Mycotoxic tremorgens of Claviceps paspali and Penicillium cyclopium: a comparative study of effects on sheep and cattle in relation to natural staggers syndromes. Res Vet Sci. 1978 Jan;24(1):49–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris P. J., Smith C. C., De Belleroche J., Bradford H. F., Mantle P. G., Thomas A. J., Penny R. H. Actions of tremorgenic fungal toxins on neurotransmitter release. J Neurochem. 1980 Jan;34(1):33–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb04618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney J. W., Rhee V., Ho O. L. Kainic acid: a powerful neurotoxic analogue of glutamate. Brain Res. 1974 Sep 13;77(3):507–512. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90640-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penny R. H., O'Sullivan B. M., Mantle P. G., Shaw B. I. Clinical studies on tremorgenic mycotoxicoses in sheep. Vet Rec. 1979 Oct 27;105(17):392–393. doi: 10.1136/vr.105.17.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. W., Bradford H. F., Mantle P. G. Actions of a tremorgenic mycotoxin on amino acid transmitter release in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Sep 1;31(17):2807–2810. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell F. E. Venom Poisoning. Ration Drug Ther. 1971 Aug;5(8):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON B. J., WILSON C. H. TOXIN FROM ASPERGILLUS FLAVUS: PRODUCTION ON FOOD MATERIALS OF A SUBSTANCE CAUSING TREMORS IN MICE. Science. 1964 Apr 10;144(3615):177–178. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3615.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


