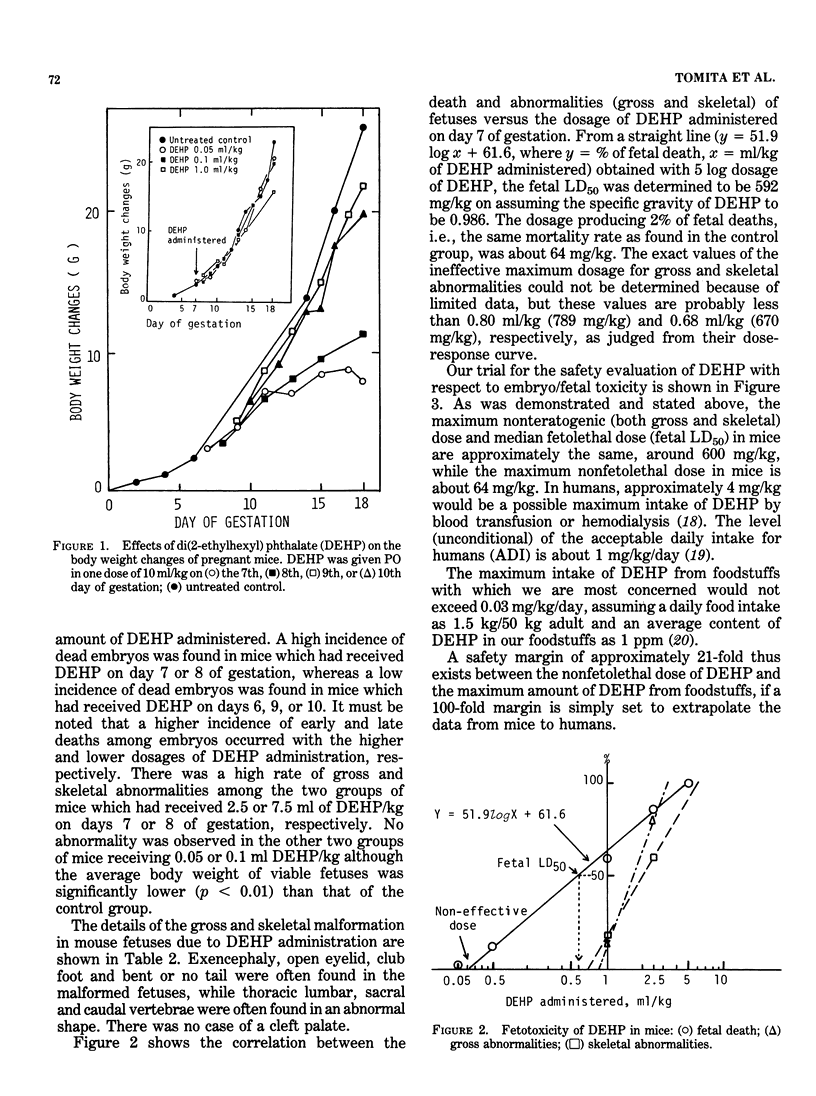
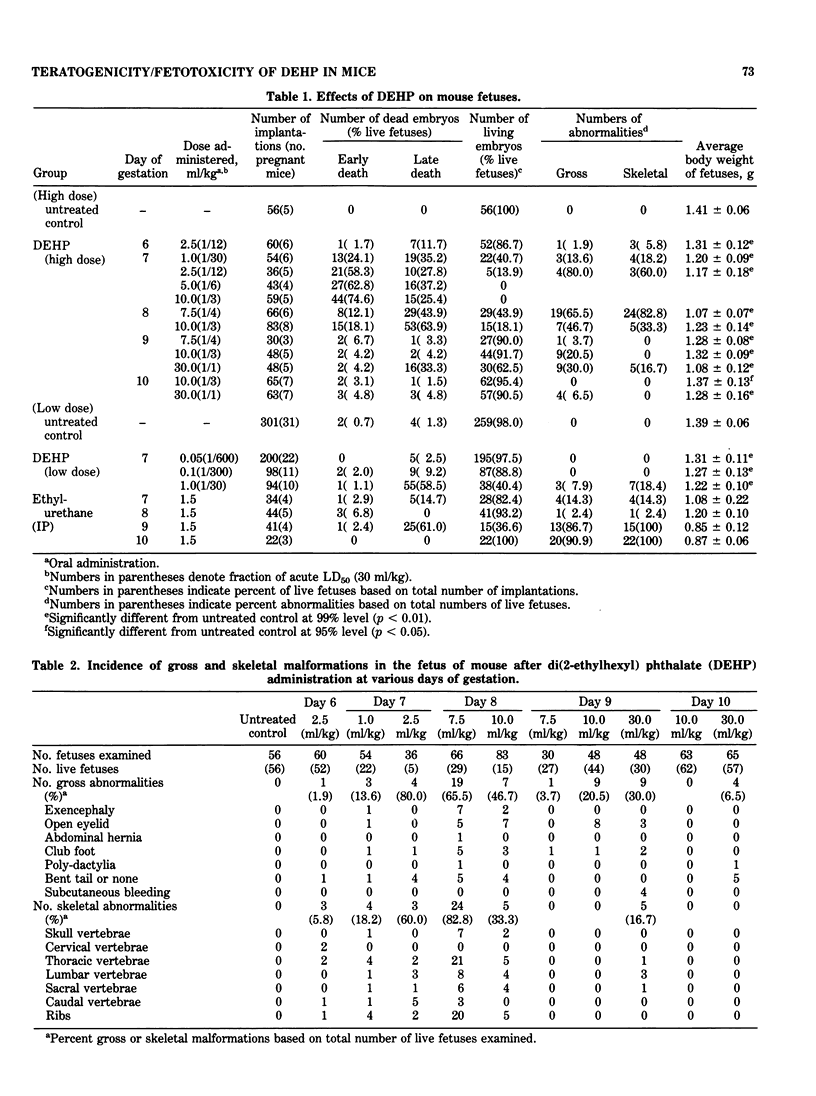
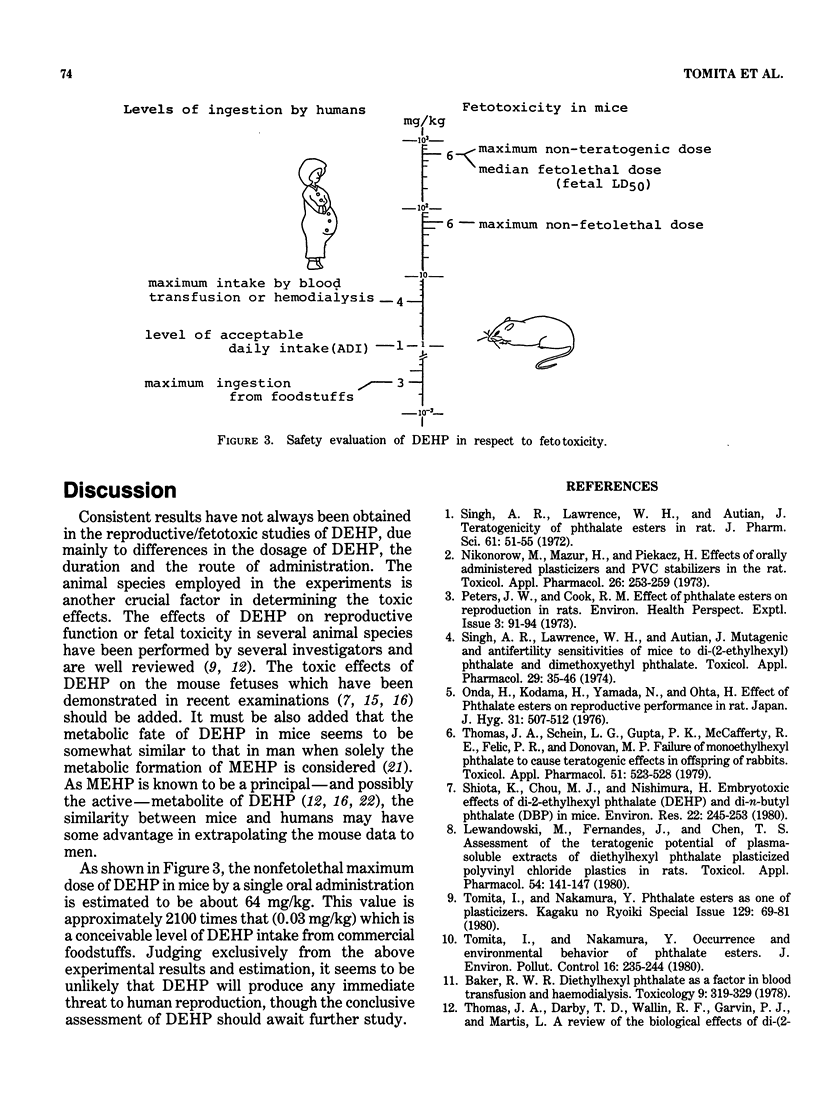
Abstract
The embryonic/fetotoxic effects of DEHP on pregnant mice (ddY-Slc female x CBA male) were studied. DEHP was administered orally in dosages of 0.05 ml/kg to 30.0 mg/kg on day 6, 7, 8, 9 or 10 of gestation. A single administration of DEHP over 0.1 ml/kg (1/300 of LD50) on day 7 of gestation decreased the numbers and the body weight of living fetuses, whereas no significant changes in the numbers of living fetuses (with no gross and skeletal abnormalities) were observed compared with those of the control group, when 0.05 ml/kg (1/600 of LD50) of DEHP was administered. The fetotoxicity (fetal death) was dose dependent. The LD50 and the nonfetolethal maximum dosage of DEHP in its single, oral administration was 592 mg/kg and 64 mg/kg, respectively. The latter value is much higher than an estimated DEHP intake from commercial foodstuffs in men, which is approximately 0.03 mg/kg/day.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albro P. W., Hass J. R., Peck C. C., Odam D. G., Corbett J. T., Bailey F. J., Blatt H. E., Barrett B. B. Identification of the metabolites of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in urine from the African green monkey. Drug Metab Dispos. 1981 May-Jun;9(3):223–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. W. Diethylhexyl phthalate as a factor in blood transfusion and haemodialysis. Toxicology. 1978 Apr;9(4):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(78)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. W. Toxicity and metabolism of phthalate esters. Clin Toxicol. 1978;13(2):257–268. doi: 10.3109/15563657808988236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger R. J., Rubin R. J. Migration of a phthalate ester plasticizer from polyvinyl chloride blood bags into stored human blood and its localization in human tissues. N Engl J Med. 1972 Nov 30;287(22):1114–1118. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197211302872203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence W. H. Phthalate esters: the question of safety. Clin Toxicol. 1978;13(1):89–139. doi: 10.3109/15563657808988230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowski M., Fernandes J., Chen T. S. Assessment of the teratogenic potential of plasma-soluble extracts of diethylhexyl phthalate plasticized polyvinyl chloride plastics in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1980 Jun 15;54(1):141–147. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(80)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCOLLISTER D. D. TOXICOLOGICAL RESEARCH APPROPRIATE TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF A PLASTIC PACKAGE FOR FOOD. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1964 Apr;2:23–29. doi: 10.1016/s0015-6264(64)80003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikonorow M., Mazur H., Piekacz H. Effect of orally administered plasticizers and polyvinyl chloride stabilizers in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1973 Oct;26(2):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(73)90259-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onda H., Kodama H., Yamada N., Ota H. [Effect of phthalate ester on reproductive performance in rat (author's transl)]. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 1976 Oct;31(4):507–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. W., Cook R. M. Effect of phthalate esters on reproduction in rats. Environ Health Perspect. 1973 Jan;3:91–94. doi: 10.1289/ehp.730391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiota K., Chou M. J., Nishimura H. Embryotoxic effects of di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) and di-n-buty phthalate (DBP) in mice. Environ Res. 1980 Jun;22(1):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(80)90136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. R., Lawrence W. H., Autian J. Mutagenic and antifertility sensitivities of mice to di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) and dimethoxyethyl phthalate (DMEP). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1974 Jul;29(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(74)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. R., Lawrence W. H., Autian J. Teratogenicity of phthalate esters in rats. J Pharm Sci. 1972 Jan;61(1):51–55. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600610107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Darby T. D., Wallin R. F., Garvin P. J., Martis L. A review of the biological effects of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;45(1):1–27. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(78)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Schein L. G., Gupta P. K., McCafferty R. E., Felice P. R., Donovan M. P. Failure of monoethylhexyl phthalate to cause teratogenic effects in offspring of rabbits. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;51(3):523–528. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90377-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita I., Nakamura Y., Yagi Y. Phthalic acid esters in various foodstuffs and biological materials. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 1977 Sep;1(2):275–287. doi: 10.1016/0147-6513(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vessman J., Rietz G. Formation of mono(ethylhexyl)phthalate from di(ethylhexyl)phthalate in human plasma stored in PVC bags and its presence in fractionated plasma proteins. Vox Sang. 1978 Jul-Aug;35(1-2):75–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1978.tb02903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi Y., Nakamura Y., Tomita I., Tsuchikawa K., Shimoi N. Teratogenic potential of di- and mono-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate in mice. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1980 Sep;4(2-3):533–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


