Abstract
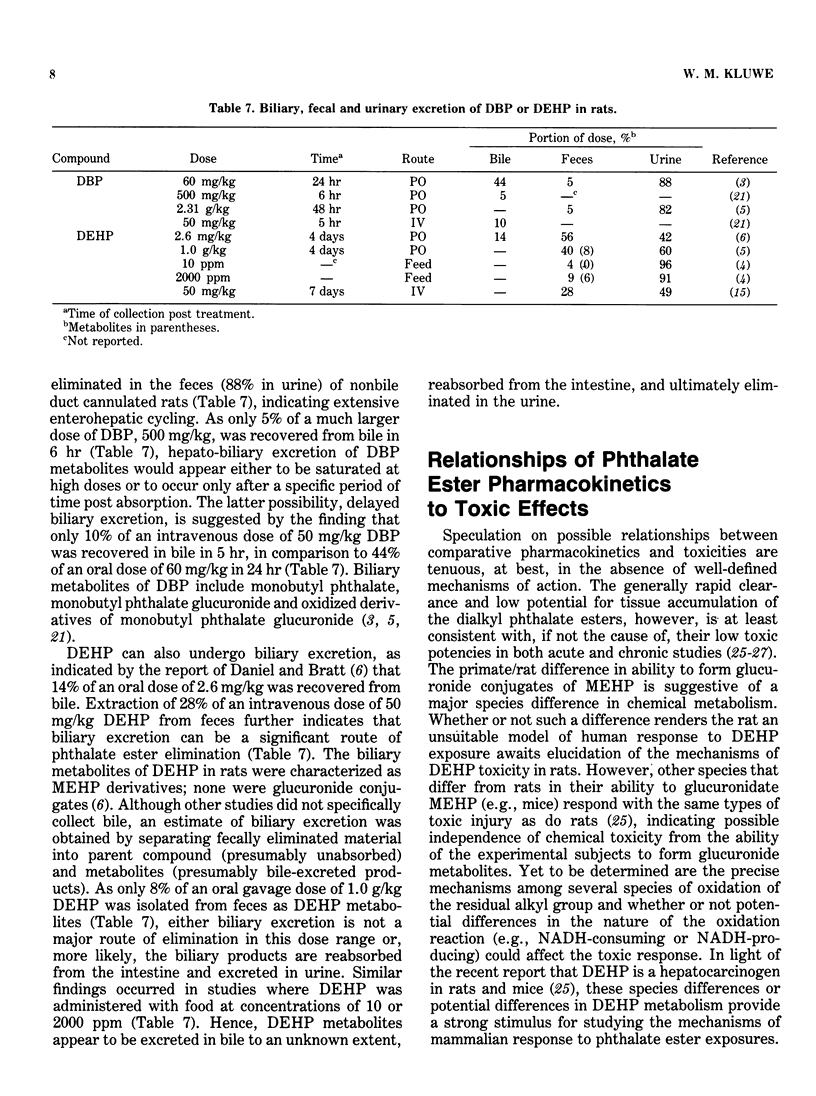
Phthalic acid esters, or phthalate esters, are generally well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration. Hydrolysis to the corresponding monoester metabolite, with release of an alcoholic substituent, largely occurs prior to intestinal absorption of the longer-chain alkyl derivatives such as di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP). Phthalate esters are widely distributed in the body, with the liver being the major, initial repository organ. Clearance from the body is rapid and there is only a slight cumulative potential. Short-chain dialkyl phthalates, such as dimethyl phthalate, can be excreted in an unchanged form or following complete hydrolysis to phthalic acid. Longer-chain compounds such as DEHP, however, are converted principally to polar derivatives of the monoesters by oxidative metabolism prior to excretion. A marked species difference in DEHP metabolism exists: primates (man, monkey, some rodent species) glucuronidate DEHP at the carboxylate moiety following hydrolysis of a single ester linkage, whereas rats appear to be unable to glucuronidate the monoester metabolite and oxidize the residual alkyl chain instead to various ketone and carboxylate derivatives. The major route of phthalate ester elimination from the body is urinary excretion. Certain phthalate esters are excreted in the bile but undergo enterohepatic circulation. The relationships of phthalate ester pharmacokinetics to their toxicological actions are unknown at the present time, largely due to a lack of elucidated mechanisms of toxic action.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albro P. W., Corbett J. T. Distribution of di- and mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in human plasma. Transfusion. 1978 Nov-Dec;18(6):750–755. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1978.18679077962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albro P. W., Corbett J. T., Schroeder J. L., Jordan S., Matthews H. B. Pharmacokinetics, interactions with macromolecules and species differences in metabolism of DEHP. Environ Health Perspect. 1982 Nov;45:19–25. doi: 10.1289/ehp.824519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albro P. W., Hass J. R., Peck C. C., Odam D. G., Corbett J. T., Bailey F. J., Blatt H. E., Barrett B. B. Identification of the metabolites of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in urine from the African green monkey. Drug Metab Dispos. 1981 May-Jun;9(3):223–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albro P. W., Moore B. Identification of the metabolites of simple phthalate diesters in rat urine. J Chromatogr. 1974 Jul 17;94(0):209–218. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)92368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albro P. W., Thomas R. O. Enzymatic hydrolysis of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate by lipases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 21;306(3):380–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albro P. W., Thomas R., Fishbein L. Metabolism of diethylhexyl phthalate by rats. Isolation and characterization of the urinary metabolites. J Chromatogr. 1973 Feb 28;76(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96915-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autian J. Toxicity and health threats of phthalate esters: review of the literature. Environ Health Perspect. 1973 Jun;4:3–26. doi: 10.1289/ehp.73043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter J. E., Roll D. B., Petersen R. V. The in vitro hydrolysis of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate by rat tissues. Drug Metab Dispos. 1974 Jul-Aug;2(4):341–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu I., Villeneuve D. C., Secours V., Franklin C., Rock G., Viau A. Metabolism and tissue distribution of mono-2-ethylhexyl phthalate in the rat. Drug Metab Dispos. 1978 Mar-Apr;6(2):146–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. W., Bratt H. The absorption, metabolism and tissue distribution of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate in rats. Toxicology. 1974 Mar;2(1):51–65. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(74)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda G. J., Sapienza P. P., Couvillion J. L., Farber T. M., Smith C. P., Inskeep P. B., Marks E. M., Cerra F. E., van Loon E. J. Distribution and excretion of two phthalate esters in rats, dogs and miniature pigs. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1978 Oct;16(5):409–413. doi: 10.1016/s0015-6264(78)80257-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. S., Kevy S. V., Grand R. J. Effects of a plasticizer leached from polyvinyl chloride on the subhuman primate: a consequence of chronic transfusion therapy. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 May;89(5):1066–1079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneshima H., Yamaguchi T., Okui T., Naitoh M. Studies on the effects of phthalate esters on the biological system (part 2)--in vitro metabolism and biliary excretion of phthalate esters in rats. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1978 Apr;19(4):502–509. doi: 10.1007/BF01685833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake B. G., Brantom P. G., Gangolli S. D., Butterworth K. R., Grasso P. Studies on the effects of orally administered Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in the ferret. Toxicology. 1976 Nov-Dec;6(3):341–356. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(76)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock G., Secours V. E., Franklin C. A., Chu I., Villeneuve D. C. The accumulation of mono-2-ethylhexylphthalate (MEHP) during storage of whole blood and plasma. Transfusion. 1978 Sep-Oct;18(5):553–558. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1978.18579036383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland I. R., Cottrell R. C., Phillips J. C. Hydrolysis of phthalate esters by the gastro-intestinal contents of the rat. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1977 Feb;15(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/s0015-6264(77)80257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland I. R. Metabolism of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate by the contents of the alimentary tract of the rat. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1974 Jun;12(3):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0015-6264(74)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. R., Lawrence W. H., Autian J. Maternal-fetal transfer of 14C-di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate and 14C-diethyl phthalate in rats. J Pharm Sci. 1975 Aug;64(8):1347–1350. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600640819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Adachi T., Takahashi T., Yamaha T. Biochemical studies on phthalic esters I. Elimination, distribution and metabolism of di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate in rats. Toxicology. 1975 May;4(2):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(75)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Matsumoto A., Yamaha T. Biochemical studies on phthalic esters. III. Metabolism of dibutyl phthalate (DBP) in animals. Toxicology. 1978 Feb;9(1-2):109–123. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(78)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. T., Blanchfield B. J. Retention, excretion and metabolism of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate administered orally to the rat. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1974 Apr;11(4):371–378. doi: 10.1007/BF01684945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. T., Blanchfield B. J. Retention, excretion and metabolism of phthalic acid administered orally to the rat. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1974 Jul;12(1):109–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01713035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. T., Blanchfield B. J. The retention, distribution, excretion, and metabolism of dibutyl phthalate-7-14 C in the rat. J Agric Food Chem. 1975 Sep-Oct;23(5):854–858. doi: 10.1021/jf60201a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



