Abstract
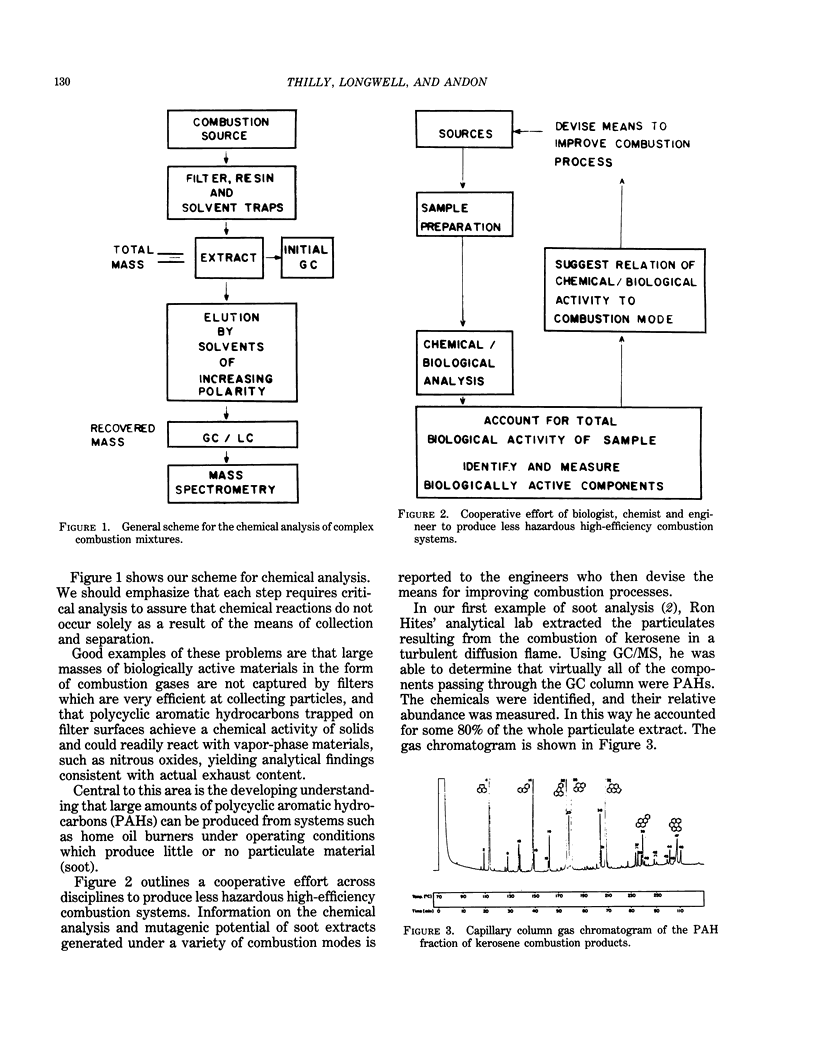
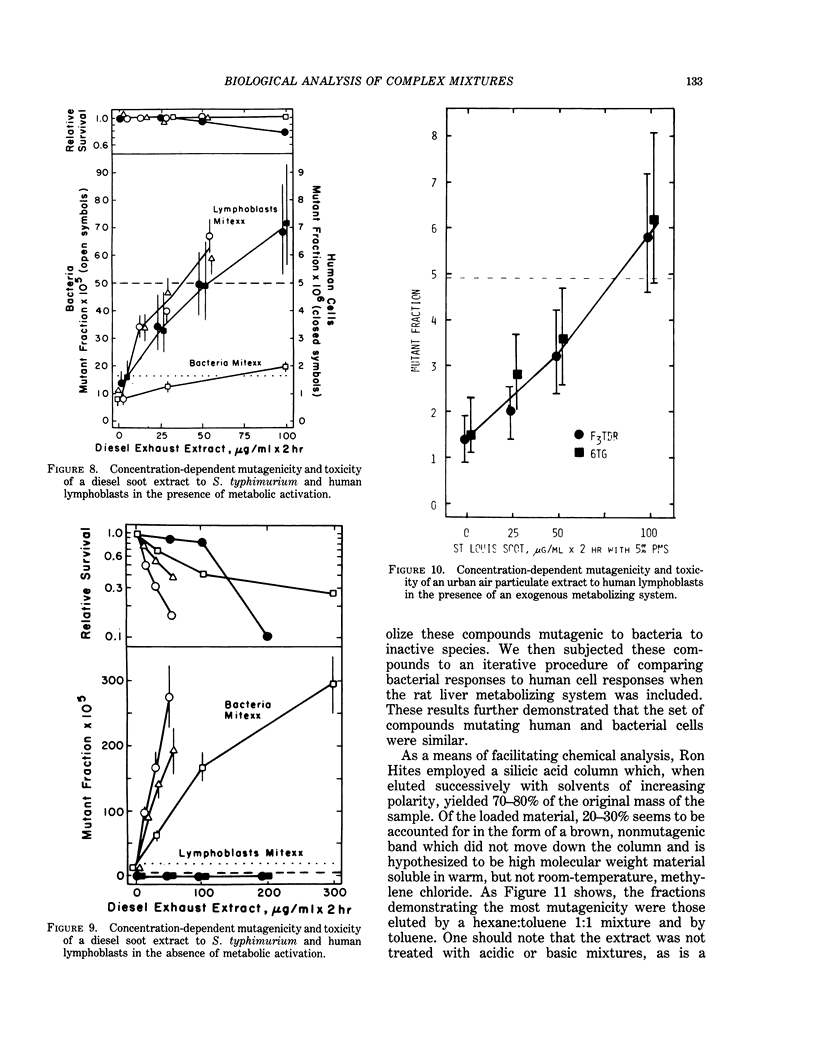
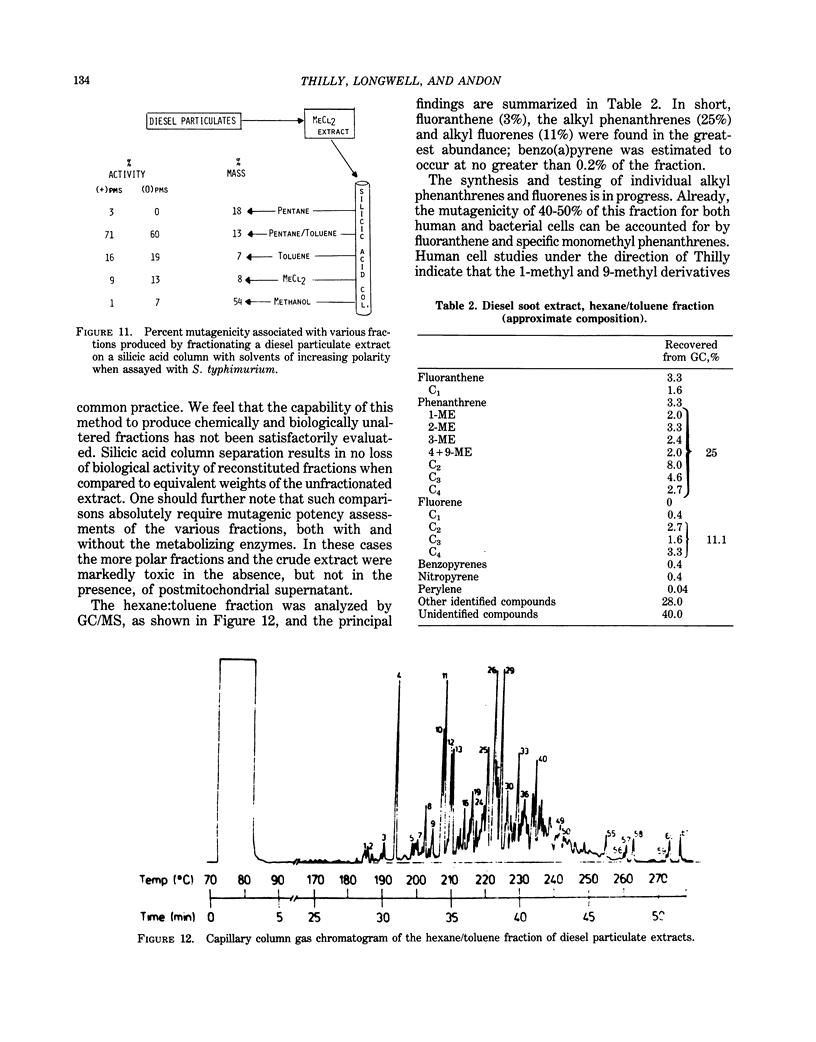
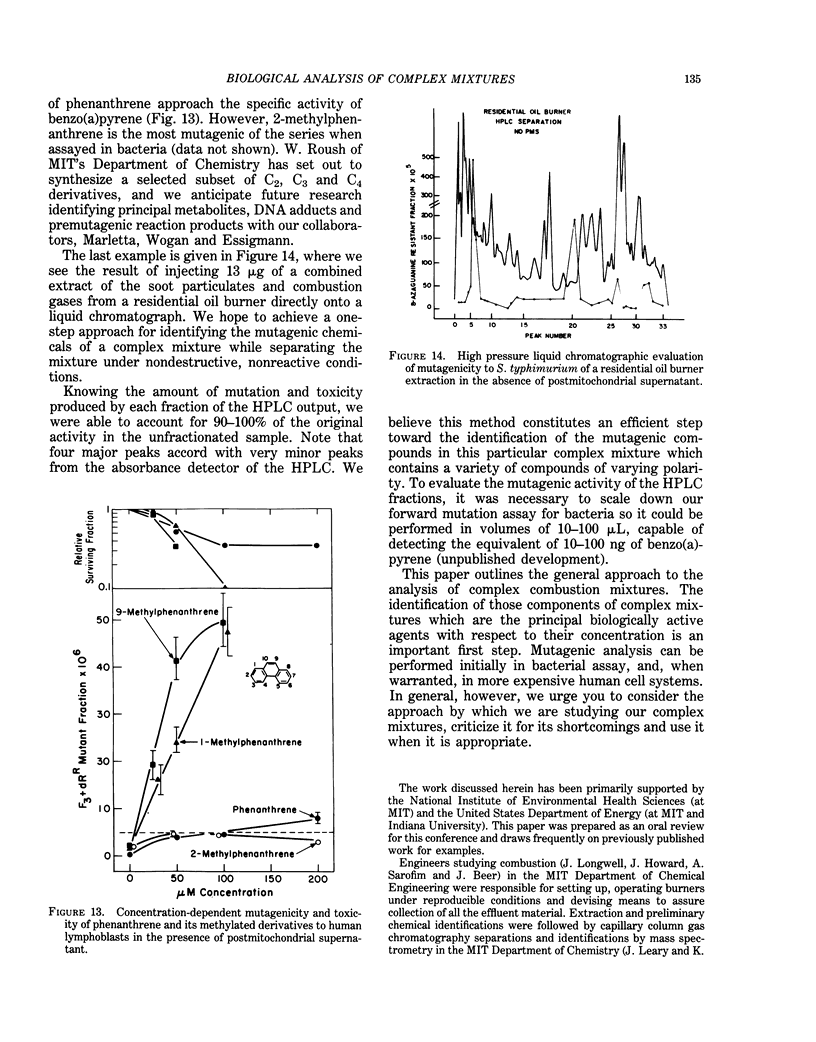
The study of potential health effects of combustion effluents involves identifying the substances present and estimating the probable health hazards of each. Unfortunately, this second step cannot be done by using present techniques. Approximations of health hazards by bacterial and human cell assays are being used to set priorities for further biological studies and to suggest needs for modifications of combustion systems. The assumptions underlying this approximation are discussed, and several examples of combustion effluents are reviewed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kaden D. A., Hites R. A., Thilly W. G. Mutagenicity of soot and associated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to Salmonella typhimurium. Cancer Res. 1979 Oct;39(10):4152–4159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skopek T. R., Liber H. L., Kaden D. A., Hites R. A., Thilly W. G. Mutation of human cells by kerosene soot. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Aug;63(2):309–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skopek T. R., Liber H. L., Kaden D. A., Thilly W. G. Relative sensitivities of forward and reverse mutation assays in Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4465–4469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skopek T. R., Liber H. L., Krolewski J. J., Thilly W. G. Quantitative forward mutation assay in Salmonella typhimurium using 8-azaguanine resistance as a genetic marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):410–414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


