Abstract
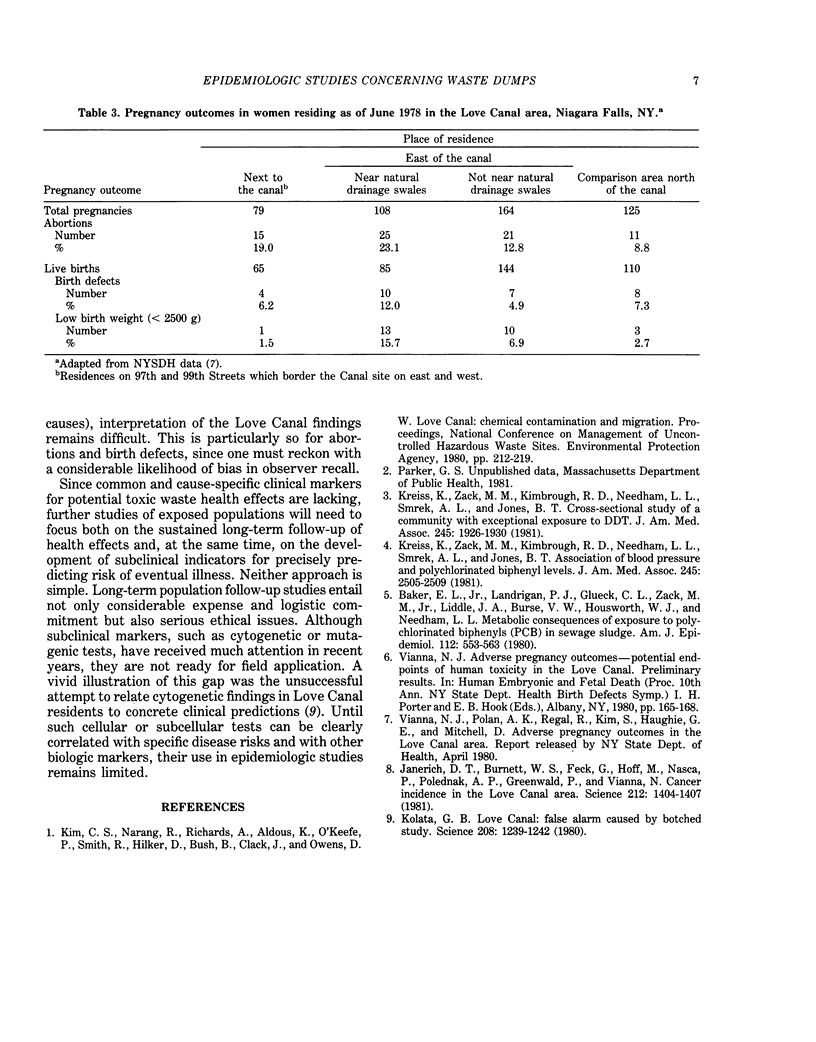
Epidemiologic studies are required for assessing health risks related to toxic waste exposure. Since the settings in which such studies must be performed are extremely diverse, epidemiologic approaches must be versatile. For any particular study, three fundamental requirements are to assess what toxic materials are present, understand how human exposure may occur, and objectively measure possible biologic effects. In assessing links between exposure and disease, epidemiologists must be particularly aware of: expected disease frequencies in relation to the size of populations studied, implications of long or varied disease latencies for study design and competing causes of disease and associated confounding variables. These concepts are illustrated by discussion of epidemiologic studies related to the Love Canal toxic waste dump site in Niagara Falls, NY.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker E. L., Jr, Landrigan P. J., Glueck C. J., Zack M. M., Jr, Liddle J. A., Burse V. W., Housworth W. J., Needham L. L. Metabolic consequences of exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) in sewage sludge. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Oct;112(4):553–563. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janerich D. T., Burnett W. S., Feck G., Hoff M., Nasca P., Polednak A. P., Greenwald P., Vianna N. Cancer incidence in the Love Canal area. Science. 1981 Jun 19;212(4501):1404–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.7233229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolata G. B. Love Canal: false alarm caused by botched study. Science. 1980 Jun 13;208(4449):1239–1242. doi: 10.1126/science.7375934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss K., Zack M. M., Kimbrough R. D., Needham L. L., Smrek A. L., Jones B. T. Association of blood pressure and polychlorinated biphenyl levels. JAMA. 1981 Jun 26;245(24):2505–2509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss K., Zack M. M., Kimbrough R. D., Needham L. L., Smrek A. L., Jones B. T. Cross-sectional study of a community with exceptional exposure to DDT. JAMA. 1981 May 15;245(19):1926–1930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


