Abstract
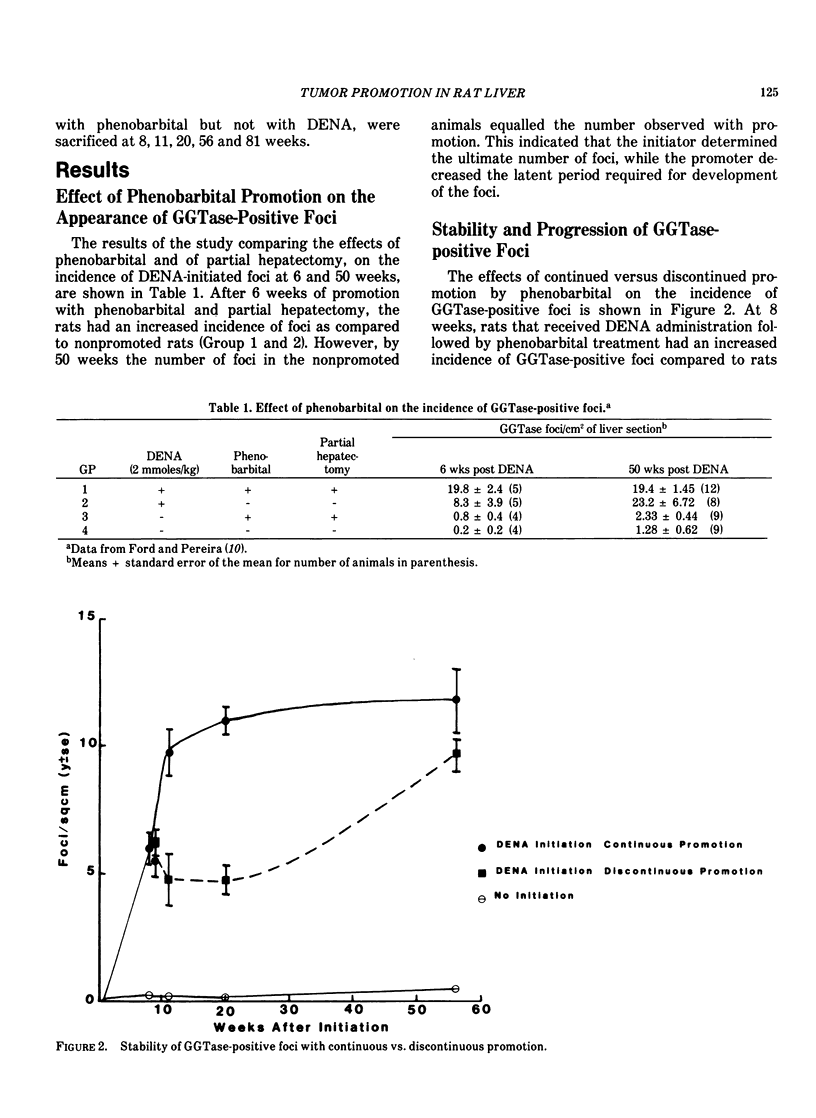
An initiation/promotion bioassay for chemical carcinogens and tumor promoters has been developed in rat liver using presumed preneoplastic lesions, foci of gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (GGTase)-positive hepatocytes, as the endpoint. To evaluate the tumor-promoting activity of phenobarbital, rats were administered diethylnitrosamine (DENA), 2.0 mmole/kg, followed by 500 ppm phenobarbital in their drinking water. After 6 weeks of phenobarbital promotion, the rats had an increased incidence of foci as compared to nonphenobarbital-treated rats. By 50 weeks, the number of foci in the nonpromoted animals equaled the number observed with promotion. The stability and progression of GGTase-positive foci was determined in rats that received a 2/3 partial hepatectomy, followed 24 hours later by DENA administration (0.3 mmole/kg). The rats then received 500 ppm phenobarbital in the drinking water for 7 weeks. After 7 weeks, half of the rats were continued on phenobarbital and the other half were removed from phenobarbital treatment. The number of foci observed in rats continued on phenobarbital treatment leveled off after 10 weeks of promotion, while in rats taken off phenobarbital it did not regress but increased at a slower rate, and, by 56 weeks, approached the number observed in rats subjected to continuous promotion. At 56 weeks, the size of foci was larger after continuous promotion. At 81 weeks, all 6 (100%) of the rats on continuous promotion had liver tumors, while only 3 of 6 (50%) of the rats removed from promotion had tumors. Promotion by phenobarbital stimulated the growth and decreased the time required for the appearance of GGTase-positive foci and liver tumors.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Farber E. Carcinogenesis--cellular evolution as a unifying thread: Presidential address. Cancer Res. 1973 Nov;33(11):2537–2550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber E. Hyperplastic areas, hyperplastic nodules, and hyperbasophilic areas as putative precursor lesions. Cancer Res. 1976 Jul;36(7 Pt 2):2532–2533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber E. The sequential analysis of liver cancer induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 6;605(2):149–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford J. O., Pereira M. A. Short-term in vivo initiation/promotion bioassay for hepatocarcinogens. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1980 Nov;4(5-6):39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb S., Pugh T. D. Enzyme histochemical phenotypes in primary hepatocellular carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1981 Jun;41(6):2092–2095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota N., Williams G. M. The sensitivity and heterogeneity of histochemical markers for altered foci involved in liver carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1979 May;95(2):317–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa T., Imai F., Sato K. Re-elevation of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity in periportal hepatocytes of rats with age. Gan. 1980 Jun;71(3):362–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa T., Pitot H. C., Miller E. C., Miller J. A. Promotion by dietary phenobarbital of hepatocarcinogenesis by 2-methyl-N,N-dimethyl-4-aminoazobenzene in the rat. Cancer Res. 1979 Jan;39(1):112–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa T., Sugano H. Enhancing effect of phenobarbital on the development of enzyme-altered islands and hepatocellular carcinomas initiated by 3'-methyl-4-(dimethylamino) azobenzene or diethylnitrosamine. Gan. 1978 Oct;69(5):679–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki Y., Furukawa K., Sawada N., Gotoh M. Dose-dependent enhancing effect of phenobarbital on hepatocarcinogenesis initiated by diethylnitrosamine in the rat. Gan. 1981 Feb;72(1):170–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizumi M. Effect of phenobarbital, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, and polychlorinated biphenyls on diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Gan. 1979 Dec;70(6):835–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizumi M. Enhancement of diethylnitrosamine hepatocarcinogenesis in rats by exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls or phenobarbital. Cancer Lett. 1976 Sep;2(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(76)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa K., Solt D. B., Farber E. Phenotypic diversity as an early property of putative preneoplastic hepatocyte populations in liver carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1980 Mar;40(3):725–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peraino C., Fry R. J., Staffeldt E., Christopher J. P. Comparative enhancing effects of phenobarbital, amobarbital, diphenylhydantoin, and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane on 2-acetylaminofluorene-induced hepatic tumorigenesis in the rat. Cancer Res. 1975 Oct;35(10):2884–2890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peraino C., Fry R. J., Staffeldt E. Effects of varying the onset and duration of exposure to phenobarbital on its enhancement of 2-acetylaminofluorene-induced hepatic tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 1977 Oct;37(10):3623–3627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peraino C., Fry R. J., Staffeldt E., Kisieleski W. E. Effects of varying the exposure to phenobarbital on its enhancement of 2-acetylaminofluorene-induced hepatic tumorigenesis in the rat. Cancer Res. 1973 Nov;33(11):2701–2705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. A., Herren S. L., Britt A. L. Effect of dibutylnitrosamine and saccharin on glutamyl transpeptidase-positive foci and liver cancer. Environ Health Perspect. 1983 Apr;50:169–176. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8350169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. A., Herren S. L., Britt A. L., Khoury M. M. Promotion by polychlorinated biphenyls of enzyme-altered foci in rat liver. Cancer Lett. 1982 Feb;15(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(82)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. A., Herren S. L., Britt A. L., Khoury M. M. Sex difference in enhancement of GGTase-positive foci by hexachlorobenzene and lindane in rat liver. Cancer Lett. 1982 Jan;15(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(82)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. A., Savage R. E., Jr, Herren S. L., Guion C. W. Comparison of enhancement of GGTase-positive foci and induction of ornithine decarboxylase in rat liver by barbiturates. Carcinogenesis. 1982;3(2):147–150. doi: 10.1093/carcin/3.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitot H. C., Barsness L., Goldsworthy T., Kitagawa T. Biochemical characterisation of stages of hepatocarcinogenesis after a single dose of diethylnitrosamine. Nature. 1978 Feb 2;271(5644):456–458. doi: 10.1038/271456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitot H. C., Goldsworthy T., Campbell H. A., Poland A. Quantitative evaluation of the promotion by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin of hepatocarcinogenesis from diethylnitrosamine. Cancer Res. 1980 Oct;40(10):3616–3620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitot H. C., Sirica A. E. The stages of initiation and promotion in hepatocarcinogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 6;605(2):191–215. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitot H. C. The natural history of neoplasia. Newer insights into an old problem. Am J Pathol. 1977 Nov;89(2):402–411. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston B. D., Van Miller J. P., Moore R. W., Allen J. R. Promoting effects of polychlorinated biphenyls (Aroclor 1254) and polychlorinated dibenzofuran-free Aroclor 1254 on diethylnitrosamine-induced tumorigenesis in the rat. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Mar;66(3):509–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh T. D., Goldfarb S. Quantitative histochemical and autoradiographic studies of hepatocarcinogenesis in rats fed 2-acetylaminofluorene followed by phenobarbital. Cancer Res. 1978 Dec;38(12):4450–4457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutenburg A. M., Kim H., Fischbein J. W., Hanker J. S., Wasserkrug H. L., Seligman A. M. Histochemical and ultrastructural demonstration of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 Aug;17(8):517–526. doi: 10.1177/17.8.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer E., Emmelot P. Foci of altered liver cells induced by a single dose of diethylnitrosamine and partial hepatectomy: their contribution to hepatocarcinogenesis in the rat. Eur J Cancer. 1975 Mar;11(3):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(75)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer E., Emmelot P. Kinetics of induction and growth of precancerous liver-cell foci, and liver tumour formation by diethylnitrosamine in the rat. Eur J Cancer. 1975 Oct;11(10):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(75)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer E., Hoffmann M., Emmelot P., Friedrich-Freksa M. Quantitative study on foci of altered liver cells induced in the rat by a single dose of diethylnitrosamine and partial hepatectomy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Jul;49(1):93–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatematsu M., Shirai T., Tsuda H., Miyata Y., Shinohara Y., Ito N. Rapid production of hyperplastic liver nodules in rats treated with carcinogenic chemicals: a new approach for an in vivo short-term screening test for hepatocarcinogens. Gan. 1977 Aug;68(4):499–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatematsu M., Takano T., Hasegawa R., Imaida K., Nakanowatari J., Ito N. A sequential quantitative study of the reversibility or irreversibility of liver hyperplastic nodules in rats exposed to hepatocarcinogens. Gan. 1980 Dec;71(6):843–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda H., Lee G., Farber E. Induction of resistant hepatocytes as a new principle for a possible short-term in vivo test for carcinogens. Cancer Res. 1980 Apr;40(4):1157–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yager J. D., Jr, Yager R. Oral contraceptive steroids as promoters of hepatocarcinogenesis in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Cancer Res. 1980 Oct;40(10):3680–3685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



