Abstract
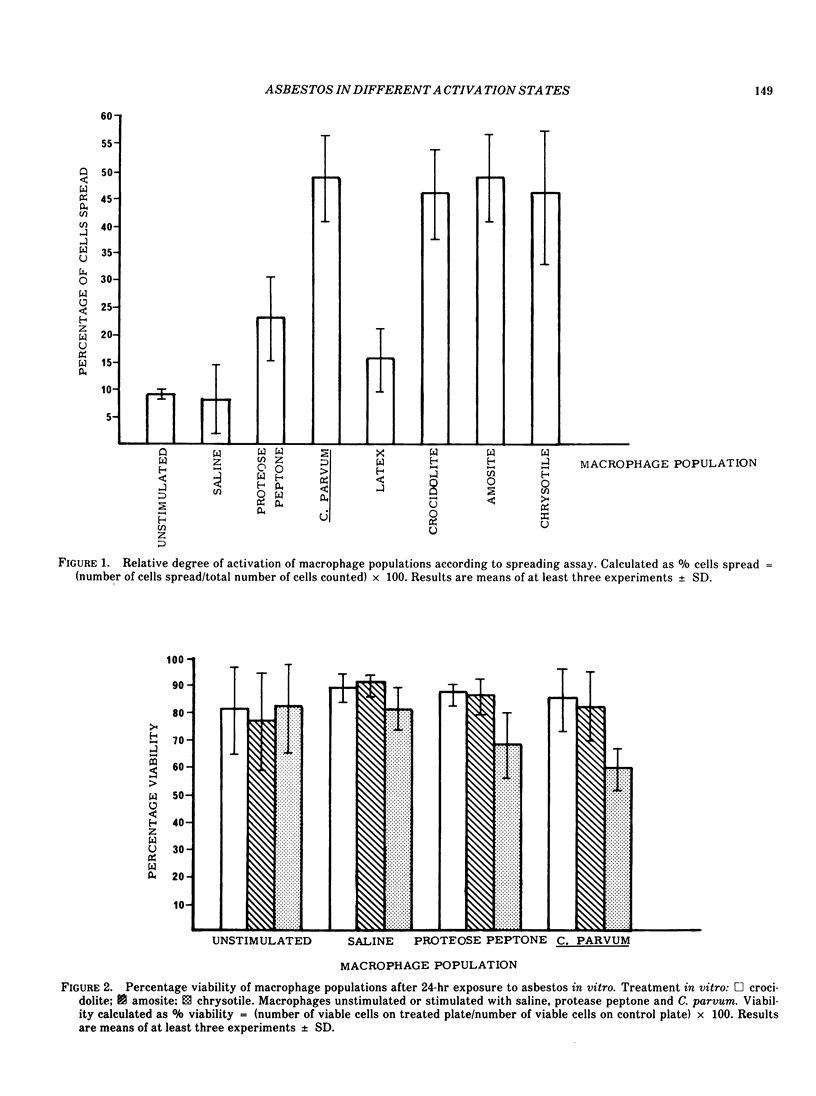
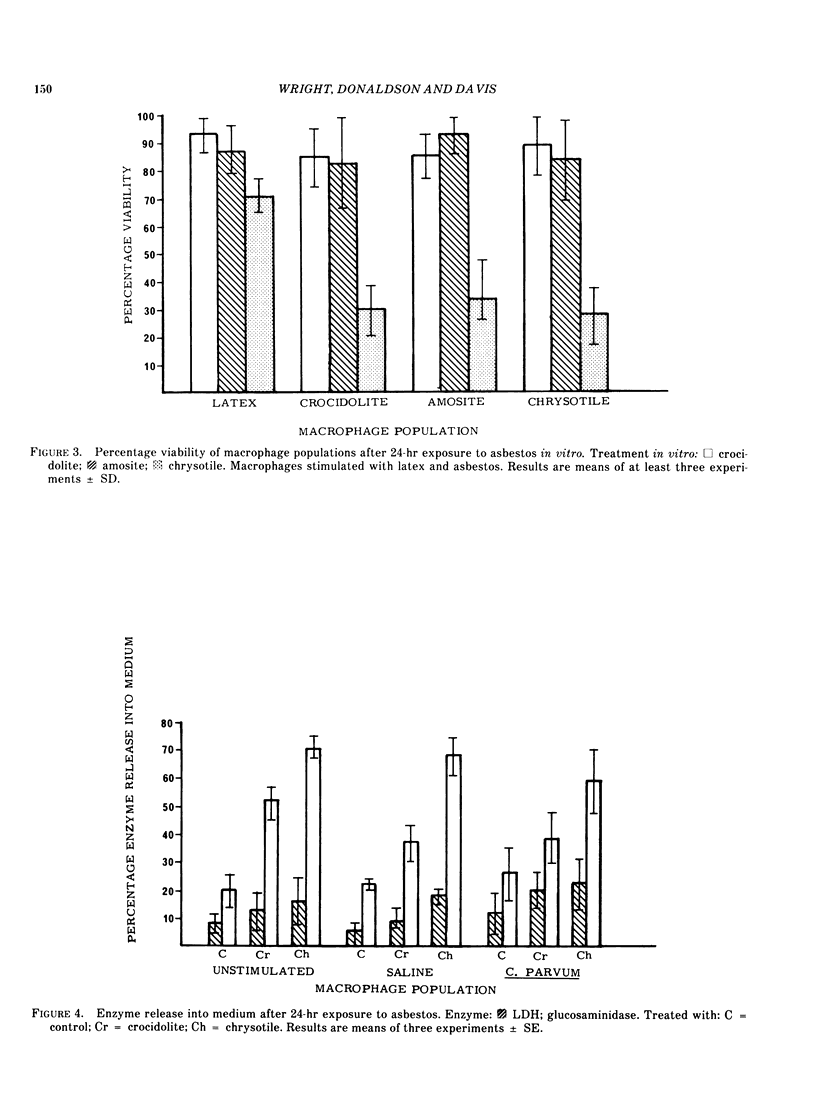
The in vitro effects due to phagocytosis of asbestos by mouse peritoneal macrophages in various stages of activation have been compared. The amphiboles proved relatively inert; chrysotile, however, expressed a greater degree of cytotoxicity toward those populations of macrophages induced in vivo with asbestos, than toward any of the other populations of cells. These results are compared with data concerning the enzyme release from the different populations of macrophages following phagocytosis of asbestos. The results indicate that those macrophages that have been exposed to a prior stimulation of either amphibole or serpentine asbestos in vivo are particularly sensitive to exposure to a second dose of a toxic fiber.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bey E., Harington J. S. Cytotoxic effects of some mineral dusts on Syrian hamster peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1971 May 1;133(5):1149–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.5.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Allison A. C., Ackerman J., Butterfield A., Williams S. Asbestos induces selective release of lysosomal enzymes from mononuclear phagocytes. Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):423–425. doi: 10.1038/251423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson K., Davis J. M., James K. Characteristics of peritoneal macrophages induced by asbestos injection. Environ Res. 1982 Dec;29(2):414–424. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(82)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAM R. G. An improved nutrient solution for diploid Chinese hamster and human cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Feb;29:515–526. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(63)80014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. A. Macrophage stimulation and the inflammatory response to asbestos. Environ Health Perspect. 1980 Feb;34:69–74. doi: 10.1289/ehp.803469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurand M. C., Bignon J., Gaudichet A., Magne L., Oblin A. Biological effects of chrysotile after SO2 sorption. II. Effects on alveolar macrophages and red blood cells. Environ Res. 1978 Oct;17(2):216–227. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(78)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdins J. K., Kühner A. L., David J. R., Karnovsky M. L. Alteration of some functional and metabolic characteristics of resident mouse peritoneal macrophages by lymphocyte mediators. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):746–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loose L. D., Astry C. L., Megirian R. Dose-dependent macrophage stimulation by Corynebacterium parvum. J Immunopharmacol. 1980;2(3):349–365. doi: 10.3109/08923978009046466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee M. P., Myrvik Q. N. Phagocytosis-induced injury of normal and activated alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):910–915. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.910-915.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. Alterations in the surface-related phenomena of alveolar macrophages following inhalation of crocidolite asbestos and quartz dusts: an overview. Environ Res. 1979 Oct;20(1):162–182. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(79)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLLEN J. W., HEYWORTH R., WALKER P. G. Studies on glucosaminidase. 3. Testicular N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase and N-acetyl-beta-galactosaminidase. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:111–116. doi: 10.1042/bj0780111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Dukor P., Zurier R. B. Effect of cyclic AMP on release of lysosomal enzymes from phagocytes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 2;231(22):131–135. doi: 10.1038/newbio231131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Remington J. S. Cell-mediated immunity and its role in resistance to infection. West J Med. 1977 Jan;126(1):14–31. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


