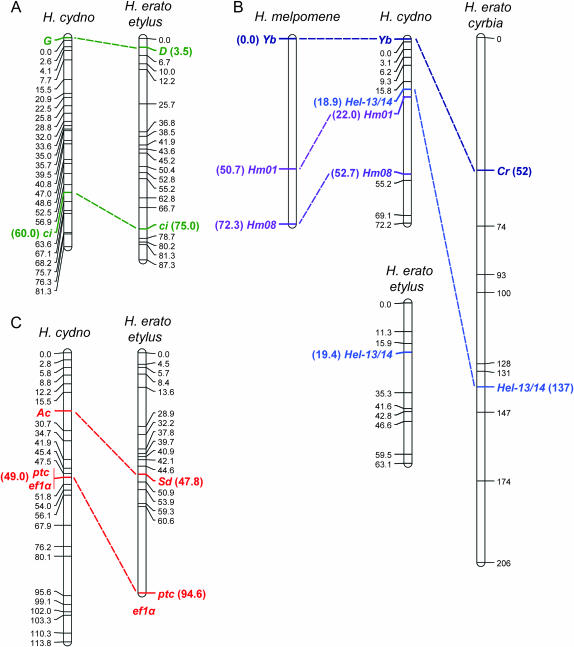
Figure 2.—
Comparative genetic mapping of mimicry genes in Heliconius. (A) H. cydno color-patterning gene G and H. erato D are both syntenic with anchor locus ci. (B) H. cydno color-patterning gene Yb and H. erato Cr are both syntenic with anchor locus Hel-13/14. The H. erato cyrbia linkage group containing Hel-13/14 (Tobler et al. 2005) is substantially longer than that of H. erato etylus (Kapan et al. 2006), suggesting that distances may be artificially inflated in the former. H. cydno Yb is also syntenic with microsatellite loci Hm01 and Hm08, which are linked to Yb in crosses between races of sister species H. melpomene (Jiggins et al. 2005; Joron et al. 2006). (C) H. cydno color-patterning gene Ac and H. erato Sd are both syntenic with anchor loci ptc and ef1α. Although ef1α is syntenic with ptc and Sd in H. erato etylus, its exact position is unknown (Kapan et al. 2006). H. erato maps were estimated using backcross or F2 broods derived from crosses between H. himera and either H. erato cyrbia (for the linkage group with Cr) as described in Tobler et al. (2005) or H. erato etylus (for linkage groups with D and Sd) as described in Kapan et al. (2006). The H. melpomene Yb linkage group was mapped using F2 broods derived from crosses between H. m. cythera and H. m. melpomene as described in Jiggins et al. (2005) and Joron et al. (2006). For H. cydno, we used segregation data from 33 H. pachinus (female) × H. cydno (male) F1 hybrids (pseudotestcross design) to map amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) loci, microsatellite loci, and single-copy nuclear loci that were heterozygous in the H. cydno male parent (Kronforst et al. 2006). We typed ci, Hel-13/14, Hm01, and Hm08 using PCR product length variation and ptc and eflα using single-nucleotide polymorphisms. We then scored 65 F2 offspring for allelic variation at color-patterning loci and a subset of the mapped markers and used these data to locate the positions of color-patterning loci G, Yb, and Ac. Completely linked AFLP loci in opposite phases were used to score each F2 individual as marker present (homozygous or heterozygous for the H. cydno allele) or marker absent (homozygous for the H. pachinus allele) while AFLP loci without a linked marker in the opposite phase were scored as marker present or missing data. Using likelihood we assigned each H. cydno color-patterning locus to the interval with the highest probability, but we did not estimate approximate positions within intervals. We also used likelihood to estimate placement support limits (∼95% confidence intervals) for each of the loci in both studies (Kapan et al. 2006). Mapping was performed with Joinmap 3.0 (Van Ooijen and Voorrips 2001) and Mapmaker/Exp 3.0 (Lincoln et al. 1993) using the Haldane mapping function and maps were drawn with MapChart 2.1 (Voorrips 2002). Markers are labeled with their position, in centimorgans, and homologous loci are highlighted.