Abstract
The relationship of agonist efficacy to the rate of G protein-coupled receptor signaling desensitization is controversial.
Expressing inwardly rectifying potassium channels (GIRKs) in Xenopus oocytes, we have devised a signaling assay that clearly identifies CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonists with low intrinsic efficacy.
In this assay, the synthetic CB1 agonists, AM411, AM782, AM1902, AM2233 and WIN55,212-2 and the endogenous cannabinoid, 2-arachidonoyl ester, were full agonists.
The synthetic CB1 agonist AM356 (methanandamide), the endogenous cannabinoids, anandamide and 2-arachidonoyl ether, and the phytocannabinoid, Δ9THC, were partial agonists.
The rate of desensitization of CB1 was independent of agonist efficacy. WIN55,212-2, AM782, AM1902, AM2233, and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol ester all desensitized quickly, with desensitization rates varying from 14% min−1 to 10% min−1. AM356, AM411, anandamide, and Δ9THC all desensitized considerably slower, at a rate of 5% min−1.
Despite high potency and efficacy, AM411 desensitized as slowly as anandamide and Δ9THC.
CB1 agonist efficacy and rate of desensitization are not necessarily related.
Keywords: Cannabinoid, Xenopus, desensitization, efficacy, potassium channel
Introduction
When cannabis, its active constituents, or other compounds that produce the classic psychoactive effects associated with cannabis (loosely termed, cannabinoids) are given chronically, tolerance develops (Hunt & Jones, 1980; Pertwee et al., 1993; Fan et al., 1994; Kouznetsova et al., 2002). Here, tolerance is defined as either the same amount of drug producing less effect, or more drug being needed to elicit the original response. The psychoactive effects of cannabis preparations appear to be mediated via the CB1 receptor, a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) (Matsuda et al., 1990; Huestis et al., 2001). GPCRs are the most abundant class of receptors in mammals and are key targets of therapeutic (and recreational) drugs. Because of their central role in physiology and pharmacology, considerable effort has been expended in understanding how tolerance develops to GPCR agonists. Given the large number of GPCRs and their diversity it is likely that multiple mechanisms are involved. Well-described mechanisms include downregulation (comprised of both removal of receptors from the cell surface by internalization, and decreased receptor synthesis) and desensitization–uncoupling from effectors (e.g., G proteins) (Luttrell & Lefkowitz, 2002).
In the case of CB1 receptors, desensitization, rather than downregulation appears to dominate as tolerance to Δ9THC or other cannabinoids is developing. For example, in rats chronically treated with Δ9THC, CB1 receptor levels decrease modestly, while G protein coupling, as measured by [35S] GTPγS binding decreases strongly (Breivogel et al., 1998). What might be the mechanism of cannabinoid receptor desensitization? Cannabinoid receptor activation of inwardly rectifying potassium channels (GIRKs) rapidly desensitizes in a process that requires phosphorylation and beta arrestin (Jin et al., 1999). Phosphorylation of the CB1 receptor at both S426 and S430 of its C-terminus is a necessary step for this rapid desensitization (Jin et al., 1999). Interestingly, mutation or deletion of the residues required for CB1 receptor internalization did not impair its desensitization, suggesting that desensitization can occur independently of CB1 internalization (Jin et al., 1999).
Agonist efficacy is a measure of receptor activation at a given fraction of receptor occupancy (Kenakin, 2002). It has been observed that for μ opioid receptor tolerance (Duttaroy & Yoburn, 1995; Walker & Young, 2001) and desensitization (Kovoor et al., 1998) develop to a greater extent with more efficacious agonists. However, other studies dispute this notion, at least for desensitization (Alvarez et al., 2002). One possibility that follows from the hypothesis that agonist efficacy and desensitization are correlated is that more efficacious agonists, while they might be more therapeutically useful, will lead to more rapid desensitization (and tolerance to them may develop more quickly). The relationship between agonist efficacy and desensitization has not been explored for the CB1 receptor and its agonists.
In the current study, we have expressed CB1 receptors, GIRKs, and other signaling molecules in Xenopus oocytes to screen compounds from each major family of CB1 receptor agonist (Howlett et al., 2002) for both efficacy of GIRK activation and rapidity of desensitization. We found that while less efficacious agonists generally do desensitize more slowly than highly efficacious agonists, it is possible to develop potent, highly efficacious agonists that only slowly desensitize.
Methods
Oocyte culture and injection
Xenopus oocytes were prepared as described by Kovoor et al. (1995), and incubated overnight at 18°C in ND96 (96 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 2 mM KCl, 5 mM HEPES, and 1 mM CaCl2, pH 7.5) supplemented with 2.5 mM sodium pyruvate and 50 μg ml−1 gentamycin prior to cRNA injection. Using a Drummond microinjector, oocytes were injected with 50 nl of cRNA. Oocytes for initial CB1 cRNA dose–response experiments were injected with 0.02 total ng oocyte−1 of Kir3.1 and Kir3.4 and either with 2.0 or 0.15 ng oocyte−1 CB1 cRNA. Oocytes for subsequent CB1 agonist dose-response experiments were injected with the following RNAs: 0.025 ng oocyte−1 of CB1 and 0.02 total ng oocyte−1 of Kir3.1 and Kir3.4 (Ambion mMessage transcription kit). Oocytes for desensitization experiments were injected with the following cRNAs: 0.05 ng oocyte−1 of CB1, 0.625 ng oocyte−1 of GRK3, 4 ng oocyte−1 of bovine Arrestin3, and 0.02 total ng oocyte−1of Kir3.1 and Kir3.4. Oocytes were used 48–72 h after injection.
Oocyte electrophysiology
Two electrode voltage clamp was performed using an Axon Geneclamp 500 amplifier and electrodes filled with 3 M KCl (resistances of 0.5–2. 0 MΩ). Data were collected using the FETCHEX program in pClamp6 (Axon Instruments, Foster City, CA, U.S.A.) and a chart recorder. For all experiments, inwardly rectifying potassium (GIRK) current amplitude was enhanced by constant perfusion of a high potassium perfusion buffer (125 mM NaCl, 0.625 mM MgCl2, 60 mM KCl, 3.125 mM HEPES, and 0.625 mM CaCl2 with a final pH of 7.5). Experiments were performed and data were collected over multiple days for each condition.
Dose response
Once the inwardly rectifying current stabilized, oocytes were perfused with agonists at concentrations ranging from 1 nM to 10 μM. The amplitude of the response for each agonist at each concentration was compared with the amplitude of the response to a maximally efficacious concentration of WIN55,212-2 (1 μM) (Figure 1a). Thus, results are expressed as ‘% Maximal WIN Response.' As a control to ensure partial agonism could be measured, several oocytes from each preparation were perfused with 10 μM AM356. These oocytes consistently achieved ∼55% Maximal WIN Response (Figure 2a, right). As another control, oocytes were perfused with 1 μM WIN55,212-2 for 5 min to examine current desensitization in the absence of Arrestin3 and GRK3. Similar to Jin et al. (1999), little desensitization was evident in oocytes injected only with CB1 and GRK cRNA (data not shown).
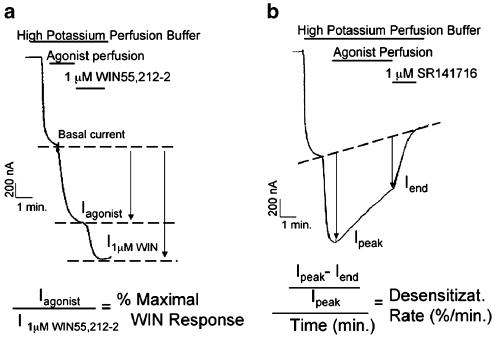
Figure 1.
Calculation of agonist efficacy and rate of desensitization. (a) Oocytes injected with 0.025 ng oocyte−1 of CB1 and 0.02 ng oocyte−1 of GIRK channel were perfused with high potassium buffer. CB1 agonist was applied after GIRK current stabilized. The amplitude of response to agonist (Iagonist) was compared to the amplitude of response to 1 μM WIN55,212-2 (I1μMWIN), giving ‘% Maximal WIN Response' (b) Oocytes were injected with 0.05 ng oocyte−1 CB1 cRNA, 0.02 ng oocyte−1 GIRK channel, 0.625 ng oocyte−1 GRK3, and 4 ng oocyte−1 bovine Arrestin3. After GIRK current stabilized, oocytes were perfused with 1 μM WIN55,212-2 for 5 min followed by application of 1 μM SR141716. Desensitization was defined as the difference between the current at the beginning and end of the trace, normalized to the initial current. The rate was defined as the percent desensitized per minute.
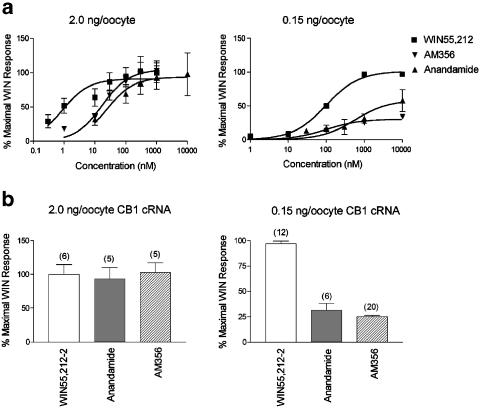
Figure 2.
Decreasing the amount of CB1 cRNA injected reveals partial agonism of anandamide and AM356. (a) Oocytes were injected with 0.02 ng oocyte−1 GIRK channel and either 2.0 or 0.15 ng oocyte−1 CB1 cRNA. WIN55,212-2, anandamide, and AM356 were applied to oocytes in concentrations ranging from 1 nM to 10 μM and results are expressed as ‘% Maximal WIN Response.' In oocytes expressing 2.0 ng oocyte−1 CB1 cRNA, all agonists fully activated the current by 1 μM. However, in oocytes expressing 0.15 ng oocyte−1 CB1 cRNA, 1 μM anandamide and AM356 only activated the current to 25–30% of the WIN55,212-2 response. Thus, 0.15 ng oocyte−1 of CB1 cRNA unmasked the partial agonism of AM356 and anandamide. (b) WIN55,212-2, a full agonist, and AM356 and anandamide, both lower efficacy agonists, elicited the same GIRK current at 1 μM in oocytes injected with 2.0 ng oocyte−1 of CB1 cRNA. However, in oocytes injected with 0.15 ng oocyte−1 of CB1 cRNA, 1 μM AM356 and anandamide only elicited 25–30% of the WIN-activated currents. The number of oocytes tested for each condition is indicated in parentheses.
Desensitization
As for the dose–response assays, oocytes were perfused with cannabinoid agonists after currents stabilized. After 5 min of agonist application, SR141716, a CB1 antagonist, was applied. Desensitization was determined as the difference between the agonist-activated current at the beginning of the trace and the SR141716 blocked component at the end, expressed as percent of initial amount (Figure 1b). To control for differences between oocyte preparations, we performed experiments only on preparations where 1 μM WIN55,212-2 decreased the current by at least 10% min−1.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis of desensitization rates was performed using the one-way ANOVA nonparametric test and the unpaired t-test (GraphPad Prism 3.02). Statistical significance was set at P<0.05. Data from dose–response experiments were fitted to a sigmoidal dose–response model using nonlinear regression analysis.
Results
0. 15 ng oocyte−1 of CB1 cRNA was sufficient to observe partial agonism
Dose–response curves for WIN55,212-2, AM356, and anandamide were determined in oocytes injected with GIRK channel and 2.0 or 0.15 ng oocyte−1 of CB1 cRNA (Figure 2). WIN55,212-2, a full agonist, and AM356 and anandamide, both lower efficacy agonists, activated GIRK to the same extent in oocytes injected with 2.0 ng oocyte−1 of CB1 cRNA (Figure 2a, left). However, in oocytes injected with 0.15 ng oocyte−1 of CB1 cRNA, AM356 and anandamide, even at saturating concentrations only elicited 25–30% of the WIN activated currents (Figure 2a, right). Note that increased cRNA injection also increased the potency of the agonists. Results for agonist concentrations of 1 μM are summarized in Figure 2b. Thus, 0.15 ng oocyte−1 of CB1 cRNA was sufficient to uncover the partial agonism of AM356 or anandamide. Therefore, oocytes were injected with 0.15 ng of CB1 cRNA or less for the subsequent experiments.
Potency and efficacy for CB1 agonists varied widely
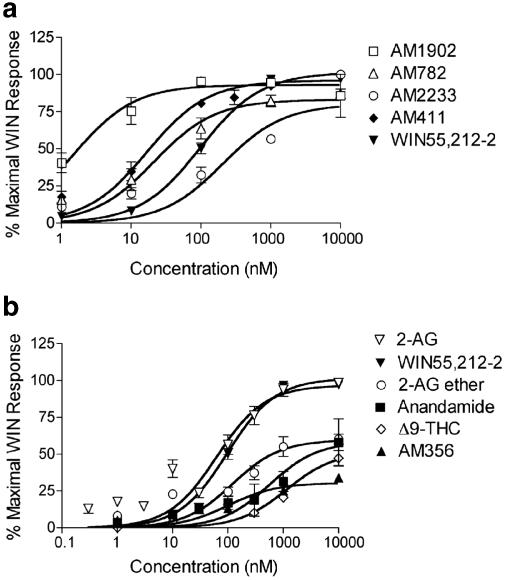
Oocytes were superfused with synthetic and endogenous CB1 agonists from each class of cannabinoid agonist (Table 1 ) in concentrations ranging from 1 nM to 10 μM. Agonists, AM1902, AM782, AM2233, AM411, 2-AG (ester), and WIN55,212-2 all activated GIRK currents to the same extent at saturating concentrations (100% Maximal WIN Response) (Figure 3a and b). However, anandamide, AM356, 2-AG ether, and Δ9-THC were less efficacious, achieving only 35–65% of the WIN response at 10 μM (Figure 3b and Table 1). EC50's of fully efficacious agonists (AM1902, AM411, AM782, AM2233, and 2-AG) ranged from 4 nM (AM1902) to 1350 nM (AM2233). The EC50's of less efficacious agonists (anandamide, AM356, 2-AG ether, and Δ9-THC) were 3–20-fold greater than the EC50 of WIN55,212-2 (Table 2 ).
Table 1.
Cannabinoid agonists used in the current study
| Family | Agonist |
|---|---|
| Classical cannabinoid | Δ9THC, AM411, AM782 |
| Nonclassical cannabinoid | AM1902 |
| Aminoalkylindole | AM2233, WIN55,212-2 |
| Acyl ethanolamide | Anandamide, AM356 |
| Acyl ester | 2-Arachidonoyl glycerol |
| Acyl ether | 2-Arachidonoyl glycerol ether |
Figure 3.
Dose–response curves for endogenous, plant-derived and synthetic agonists. (a) Oocytes were perfused with AM1902, AM782, AM2233, AM411, and WIN55,212-2 at the indicated concentrations. Despite widely varying EC50's, all compounds showed full agonism. (b) Oocytes were perfused with anandamide, AM356, 2-AG (ester), 2-AG ether, Δ9-THC, and WIN55,212-2 at the indicated concentrations. 2-AG and WIN55,212-2 were fully efficacious at 10 μM, whereas, 2-AG ether, Δ9-THC, anandamide, and AM356 elicited only 40–60% of the Maximal WIN Response at 10 μM (N=11–20 per concentration).
Table 2.
Relationship between agonist potency, efficacy, and receptor affinity of the agonists tested in this study
| Agonist | EC50 (nM) | % Maximal WIN response | Ki (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM1902 | 3.7 | 100 | 3 |
| AM411 | 29.5 | 100 | 7 |
| AM782 | 45.5 | 100 | 6 |
| WIN55,212-2 | 105.5 | 100 | 10* |
| 2-AG | 125.3 | 100 | 200* |
| 2-AG ether | 302 | 63 | 21* |
| AM356 | 515 | 35 | 28* |
| AM2233 | 1349 | 100 | 0.4 |
| Anandamide | 1358 | 64 | 90* |
| Δ9THC | 2019 | 56 | 50* |
EC50's and Maximal WIN responses for cannabinoid agonists were determined using nonlinear regression. Ki's denoted by * are from Howlett et al., (2002), others are unpublished results from the Makriyannis lab.
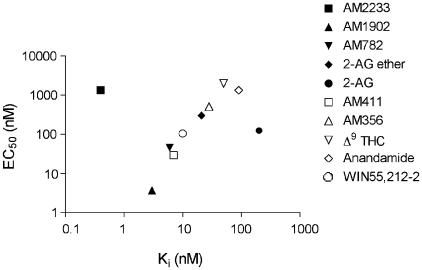
Figure 4 shows the relationship between EC50 for GIRK activation measure in this study and binding affinities for each of the agonists determined in other studies. There is a predictable relationship between EC50 and affinity for all compounds tested except for 2-AG and AM2233. The measured affinity of 2-AG for CB1 receptors is disproportionately lower than predicted based on its EC50. This may be due to degradation of 2-AG during the binding assay. In contrast, the affinity of AM2233 for CB1 receptors is considerably higher than would be predicted by its EC50. A similar discord between affinity and EC50 for stimulation of GTPγS binding and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase is also seen (A. Makriyannis, unpublished results).
Figure 4.
Relationship between CB1 affinity and EC50 for GIRK current activation. EC50's (determined from the data in Figure 3) and Ki (from same sources as Table 2) are well correlated, except for 2-AG (affinity lower than predicted by EC50) and AM2233 (EC50 lower than predicted by affinity).
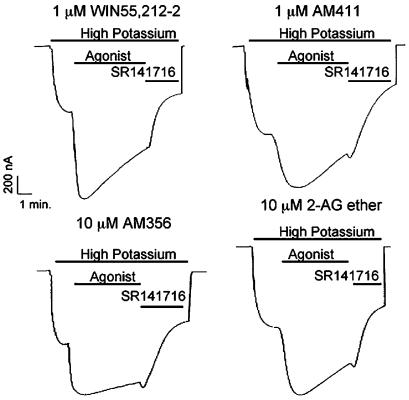
Desensitization rates for CB1 agonists were variable
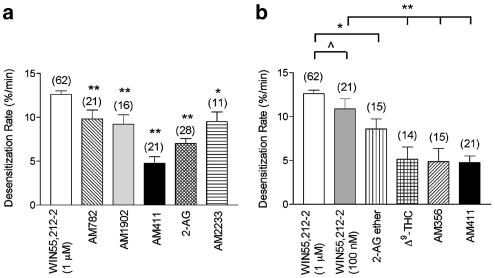
Oocytes injected with CB1, GIRK, GRK3, and Arrestin3 cRNA were superfused with concentrations of CB1 agonists that elicited maximal GIRK activation (1 μM for the full agonists, 10 μM for the partial agonists). Representative traces of highly efficacious agonists (WIN55,212-2 and AM411) and less efficacious agonists (AM356 and 2-AG ether) are shown (Figure 5). Desensitization rates of agonists were compared to the desensitization rate of 1 μM WIN55,212-2, which was 13±1.4% min−1. Results for highly efficacious agonists, WIN55,212-2, AM782, AM1902, 2-AG, AM411, and AM2233 are shown in Figure 6a. Desensitization by AM2233, AM782, and AM1902 was modestly (∼25%) slower than WIN55,212-2. Desensitization by the 2-AG and, notably, the AM411 responses were considerably slower at 7.0±0.6 and 4.8±0.8% min−1, respectively (Figure 6a). Desensitization rates of less efficacious agonists, 2-AG ether, Δ9-THC, and AM356 were all considerably slower than the desensitization rate of 1 μM WIN55,212-2 (Figure 6b). To examine whether desensitization rate correlates with receptor activation, the desensitization rate of WIN55,212-2 at 100 nM (a concentration that elicited the same GIRK activation as the less efficacious agonists) was determined. Eventually, 100 nM WIN55,212-2 desensitized at 11±1.2% min−1 compared to 13±0.4% min−1 for 1 μM WIN55,212-2 (P>0.05). Desensitization rates of AM356 and Δ9-THC were still significantly less (∼50%) than 100 nM WIN55,212-2 (P<0.001), whereas, the desensitization rate of 2-AG ether was only modestly less (∼20%) than 100 nM WIN55,212-2 (P<0.05).
Figure 5.
Representative traces showing desensitization with selected agonists. Oocytes were injected with 0.05 ng oocyte−1 CB1 cRNA, 0.02 ng oocyte−1 GIRK channel, 0.625 ng oocyte−1 GRK3, and 4 ng oocyte−1 Arrestin3. Oocytes were perfused with high potassium buffer. After GIRK currents stabilized, agonists (WIN55,212-2, AM411, AM356, and 2-AG ether, as labeled) were applied at the indicated concentrations for 5 min, followed by application of 1 μM SR141716.
Figure 6.
Agonist desensitization rates. (a) Desensitization rates of fully efficacious agonists varied greatly. Desensitization rates were determined as previously described in ‘Methods.' Using a one-way ANOVA nonparametric test, statistical analysis of the desensitization rates of the highly efficacious agonists (all at 1 μM) were compared to 1 μM WIN55,212-2 (P<0.001 (**), P<0.05 (*)). (b) Less efficacious agonists desensitized more slowly than WIN55,212-2. To evaluate whether or not desensitization rates correlate with agonist efficacy, the desensitization rates of agonists and WIN55,212-2 at equally efficacious concentrations were determined. The desensitization rate of 100 nM WIN55,212-2 was not quite statistically different from 1 μM WIN 55,212-2 with P>0.08 (^). 10 μM Δ9-THC, 10 μM AM356, and 1 μM AM411 all desensitized at significantly slower rates compared to 100 nM WIN55,212-2 (P<0.001(**)), however, the desensitization rate of 10 μM 2-AG ether was not statistically different from 100 nM WIN55,212-2 (P>0.17).
Discussion
In order to examine partial agonism and desensitization of cannabinoid receptor agonists, we needed to develop a robust system for examining these phenomena. Measuring GIRK currents using Xenopus oocytes has many advantages (Dascal, 1987; Kovoor et al., 1995). However, in previous studies known CB1 partial agonists such as anandamide either failed to activate GIRK currents (Henry & Chavkin, 1995) or did so only when oocytes were injected with large amounts (15–25 ng) of CB1 mRNA (McAllister et al., 1999), suggesting inefficient translation of the injected mRNA. Since the identical constructs express well in mammalian cells, we thought it likely that the CB1 mRNA was being poorly transcribed or translated in oocytes. In an attempt to improve expression, we subcloned CB1 into a plasmid that included the 3′ and 5′ untranslated regions (UTR) for the Xenopus beta globin gene (Liman et al., 1992). This manipulation appears to have effectively increased CB1 expression. In oocytes injected with 2 ng of CB1 mRNA prepared from this vector both the full agonist, WIN55,212-2, and the partial agonists, anandamide and methanandamide, elicited maximal responses (Figure 2). When mRNA was decreased to 0.15 ng oocyte−1, the partial agonism of methanandamide and anandamide were evident (Figure 2). Thus, we used CB1 mRNA prepared from this vector (pGEM-HE-CB1) for the remainder of the study.
It is well established that anandamide and Δ9THC have lower intrinsic efficacy compared to synthetic cannabinoid agonists such as WIN 55,212-2 or HU-210. Many of these studies have relied on GTPγS binding, for example (Breivogel et al., 1998) with its attendant limitations. However, a few others have looked at events further along signaling pathways (Mackie et al., 1993; McAllister et al., 1999; Shen & Thayer, 1999). In this study, we wanted to systematically evaluate the intrinsic efficacy of representative members of each of the five major classes of cannabinoid receptor agonist. Synthetic members of the aminoalkylindole, nonclassical cannabinoid, and classical cannabinoid families all behave as full agonists as activators of GIRK in the Xenopus oocyte under the assay conditions used in this study (Figure 3a). As expected from the literature, we found Δ9THC, anandamide and methanandamide (AM356) to be partial agonists (Figure 3b). 2-arachidonoyl glycerol ether also showed partial agonism. Although the efficacy of this compound has not been thoroughly studied, the partial agonism we see is consistent with reports using GTPγS binding (Savinainen et al., 2001). Interestingly, the endogenous cannabinoid, 2-arachidonoyl glycerol ester, acted as a full agonist with a potency similar to WIN55,212-2. While it is generally observed that 2-AG has a higher efficacy than other endogenous cannabinoids (Hillard, 2000), its potency is usually an order of magnitude, or more, lower than that of WIN55,212-2. In our experiments, we found 2-AG to have a potency equivalent to WIN55,212-2 that was an order of magnitude higher than the potency of Δ9THC. Perhaps the apparent higher potency of 2-AG in the present study is due to less degradation. In our recordings, the 2-AG is applied as a free-flowing solution, minimizing the enzymatic breakdown of the applied drug. That 2-AG has a higher intrinsic efficacy than Δ9THC, suggests the intriguing possibility that one component of the psychoactivity of Δ9THC may be due to antagonism of 2-AG by Δ9THC at CB1 receptors. This would explain the rather low efficacy and potency of the CB1 antagonist SR141716A in completely reversing the effects of smoked cannabis (Huestis et al., 2001). Furthermore, the difference in efficacies between 2-AG and anandamide suggests that these endogenous cannabinoids might stimulate CB1-signaling pathways in neurons to substantially different extents, emphasizing the importance of identifying the endogenous cannabinoid released during a particular physiological or pathophysiological state.
The primary goal of this study was to compare agonist efficacy and rate of desensitization, testing the hypothesis that the two are correlated. It must be kept in mind that efficacy was determined in oocytes not expressing GRK3 or Arrestin3 while the desensitization experiments necessarily included these proteins. It is possible that GRK3 and Arrestin3 expression might slightly alter the relative potency and efficacy of the agonists tested, however, these effects are likely to be small. The results in Figure 6 clearly show that efficacy and rate of desensitization are not necessarily correlated. The most striking example is AM411, a synthetic congener of Δ8-THC, one of the key psychoactive constituents of cannabis. AM411 exhibits significant selectivity for CB1 receptors compared to CB2 receptors and was found to behave as a potent agonist in vivo (T.Jarbe and A. Makriyannis, unpublished results). In vitro, AM411 is potent and highly efficacious (Figure 3a), yet desensitizes at a rate similar to the lowest efficacy agonists. Therefore, it is possible to develop high efficacy CB1 ligands that desensitize slowly (Figure 6). Within the limited set of compounds that we examined, the converse does not appear to be true–low efficacy compounds consistently desensitized more slowly than the high efficacy compounds.
What are the implications of these observations? If desensitization is an appropriate marker for tolerance and activation of GIRK currents is a valid surrogate for the signaling pathways stimulated by CB1 receptors in neurons, then the present results suggest that tolerance might develop more slowly with AM411 than with WIN55,212-2 when equi-efficacious doses are administered. However, a more relevant question is the comparison of the tolerance that develops to AM411 and Δ9THC. With animal models it is quite easy to demonstrate the rapid development of tolerance to Δ9THC. But it is important to keep in mind that these paradigms typically use frequent, high doses of Δ9THC (e.g., several fold greater than the ED50 for producing profound behavioral effects), or escalating dose regimens. Neither of these mimics typical therapeutic or social use patterns of Δ9THC. It is also likely that the development of tolerance is dependent in part on receptor occupancy. For all of these reasons it will be very interesting to determine how quickly tolerance develops to AM411 (a high efficacy cannabinoid) compared to Δ9THC (a low efficacy cannabinoid) over a range of dosing regimens.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the following people for their contributions to this study: Neetu Lamba, Paul Temkin, Janet Lowe, Jeremy Celver, Chien Wei, and Jim Wager-Miller for technical assistance. Bill Zagotta for the gift of the pGEM-HE vector. Chris Kearn for constructive comments on an earlier draft of the manuscript. This work was supported by the NIH: DA09158, DA00286, DA11322, DA11672, DA3801.
Abbreviations
- Anandamide
arachidonoylethanolamide
- 2-AG
2-arachidonoylglycerol
- 2-AG ether
2-arachidonoylglycerol ether
- Δ9-THC
Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol
- AM356
arachidonoylamide of R-(−)-2-amino-1-propanol
- AM411
(−) adamantyl-Δ8-tetrahydrocannabinol
- (SR141716
Nz-piperidin-O-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-methyl-3-pyrazole-carbonxamide∣WIN55,212-2, ((R-(+)-[2,3-dihydro-5-methyl-3-(4-morpholinylmethyl)pyrrolo [1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazin-6-yl]-1-1naphthalenylmethanone mesylate)
- UTR
untranslated region of mRNA
References
- ALVAREZ V.A., ARTTAMANGKUL S., DANG V., SALEM A., WHISTLER J.L., VON ZASTROW M., GRANDY D.K., WILLIAMS J.T. mu-Opioid receptors: ligand-dependent activation of potassium conductance, desensitization, and internalization. J. Neurosci. 2002;22:5769–5776. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-13-05769.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREIVOGEL C.S., SELLEY D.E., CHILDERS S.R. Cannabinoid receptor agonist efficacy for stimulating [35S]GTPgammaS binding to rat cerebellar membranes correlates with agonist-induced decreases in GDP affinity. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:16865–16873. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.27.16865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DASCAL N. The use of Xenopus oocytes for the study of ion channels. CRC Crit. Rev. Biochem. 1987;22:317–387. doi: 10.3109/10409238709086960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTTAROY A., YOBURN B.C. The effect of intrinsic efficacy on opioid tolerance. Anesthesiology. 1995;82:1226–1236. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199505000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAN F., COMPTON D.R., WARD S., MELVIN L., MARTIN B.R. Development of cross-tolerance between delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol, CP 55,940 and WIN 55,212. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994;271:1383–1390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRY D.J., CHAVKIN C. Activation of inwardly rectifying potassium channels (GIRK1) by co-expressed rat brain cannabinoid receptors in Xenopus oocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 1995;186:91–94. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)11289-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLARD C.J. Biochemistry and pharmacology of the endocannabinoids arachidonylethanolamide and 2-arachidonylglycerol. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2000;61:3–18. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(00)00051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWLETT A.C., BARTH F., BONNER T.I., CABRAL G., CASELLAS P., DEVANE W.A., FELDER C.C., HERKENHAM M., MACKIE K., MARTIN B.R., MECHOULAM R., PERTWEE R.G. International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002;54:161–202. doi: 10.1124/pr.54.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUESTIS M.A., GORELICK D.A., HEISHMAN S.J., PRESTON K.L., NELSON R.A., MOOLCHAN E.T., FRANK R.A. Blockade of effects of smoked marijuana by the CB1-selective cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR141716. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 2001;58:322–328. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.58.4.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C.A., JONES R.T. Tolerance and disposition of tetrahydrocannabinol in man. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1980;215:35–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JIN W., BROWN S., ROCHE J.P., HSIEH C., CELVER J.P., KOVOOR A., CHAVKIN C., MACKIE K. Distinct domains of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor mediate desensitization and internalization. J. Neurosci. 1999;19:3773–3780. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-10-03773.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENAKIN T. Drug efficacy at G protein-coupled receptors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2002;42:349–379. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.42.091401.113012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOUZNETSOVA M., KELLEY B., SHEN M., THAYER S.A. Desensitization of cannabinoid-mediated presynaptic inhibition of neurotransmission between rat hippocampal neurons in culture. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002;61:477–485. doi: 10.1124/mol.61.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVOOR A., CELVER J.P., WU A., CHAVKIN C. Agonist induced homologous desensitization of mu-opioid receptors mediated by G protein-coupled receptor kinases is dependent on agonist efficacy. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998;54:704–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVOOR A., HENRY D.J., CHAVKIN C. Agonist-induced desensitization of the mu opioid receptor-coupled potassium channel (GIRK1) J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:589–595. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIMAN E.R., TYTGAT J., HESS P. Subunit stoichiometry of a mammalian K+ channel determined by construction of multimeric cDNAs. Neuron. 1992;9:861–871. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90239-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUTTRELL L.M., LEFKOWITZ R.J. The role of beta-arrestins in the termination and transduction of G-protein-coupled receptor signals. J. Cell Sci. 2002;115:455–465. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.3.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKIE K., DEVANE W.A., HILLE B. Anandamide, an endogenous cannabinoid, inhibits calcium currents as a partial agonist in N18 neuroblastoma cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 1993;44:498–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSUDA L.A., LOLAIT S.J., BROWNSTEIN M.J., YOUNG A.C., BONNER T.I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature. 1990;346:561–564. doi: 10.1038/346561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCALLISTER S.D., GRIFFIN G., SATIN L.S., ABOOD M.E. Cannabinoid receptors can activate and inhibit G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels in a Xenopus oocyte expression system. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999;291:618–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERTWEE R.G., STEVENSON L.A., GRIFFIN G. Cross-tolerance between delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and the cannabimimetic agents, CP 55,940, WIN 55,212-2 and anandamide. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993;110:1483–1490. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13989.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAVINAINEN J.R., JARVINEN T., LAINE K., LAITINEN J.T. Despite substantial degradation, 2-arachidonoylglycerol is a potent full efficacy agonist mediating CB(1) receptor-dependent G-protein activation in rat cerebellar membranes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001;134:664–672. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEN M., THAYER S.A. Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol acts as a partial agonist to modulate glutamatergic synaptic transmission between rat hippocampal neurons in culture. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999;55:8–13. doi: 10.1124/mol.55.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER E.A., YOUNG A.M. Differential tolerance to antinociceptive effects of mu opioids during repeated treatment with etonitazene, morphine, or buprenorphine in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2001;154:131–142. doi: 10.1007/s002130000620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]