Abstract
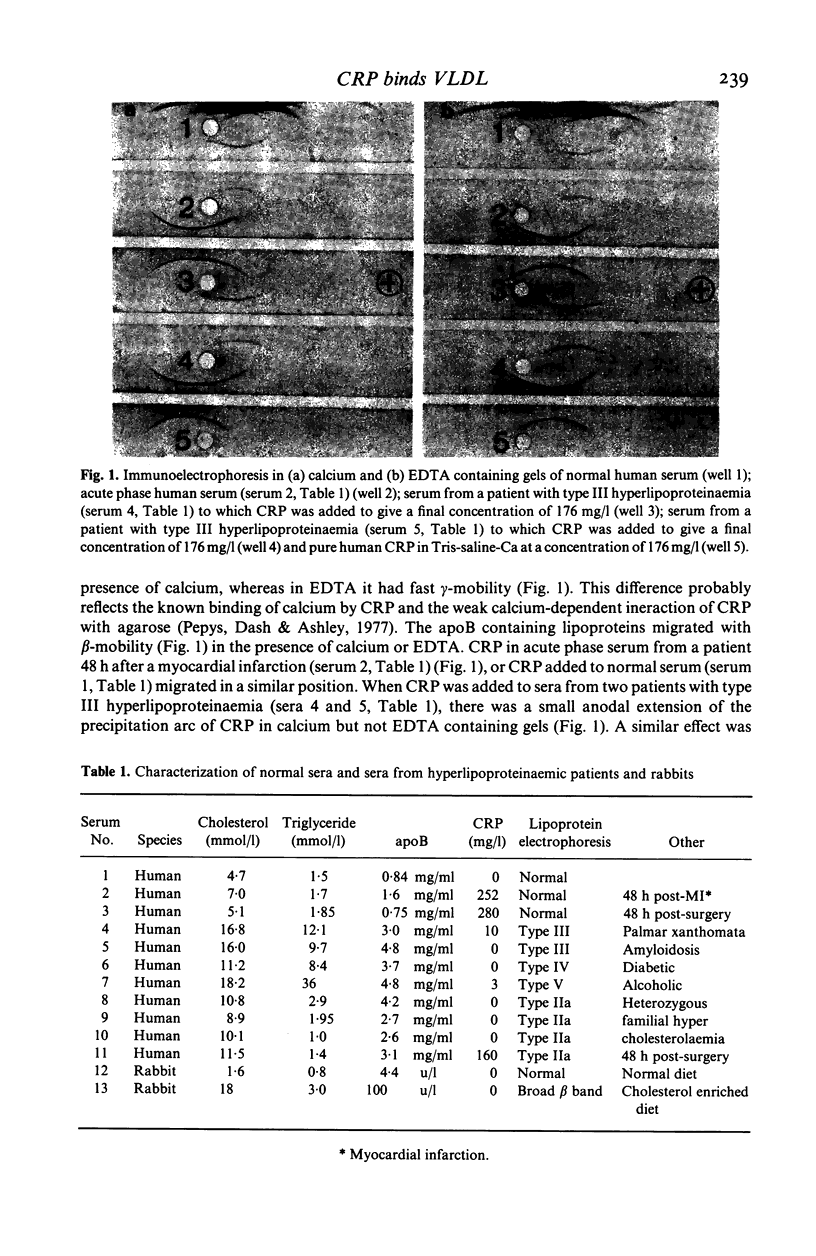
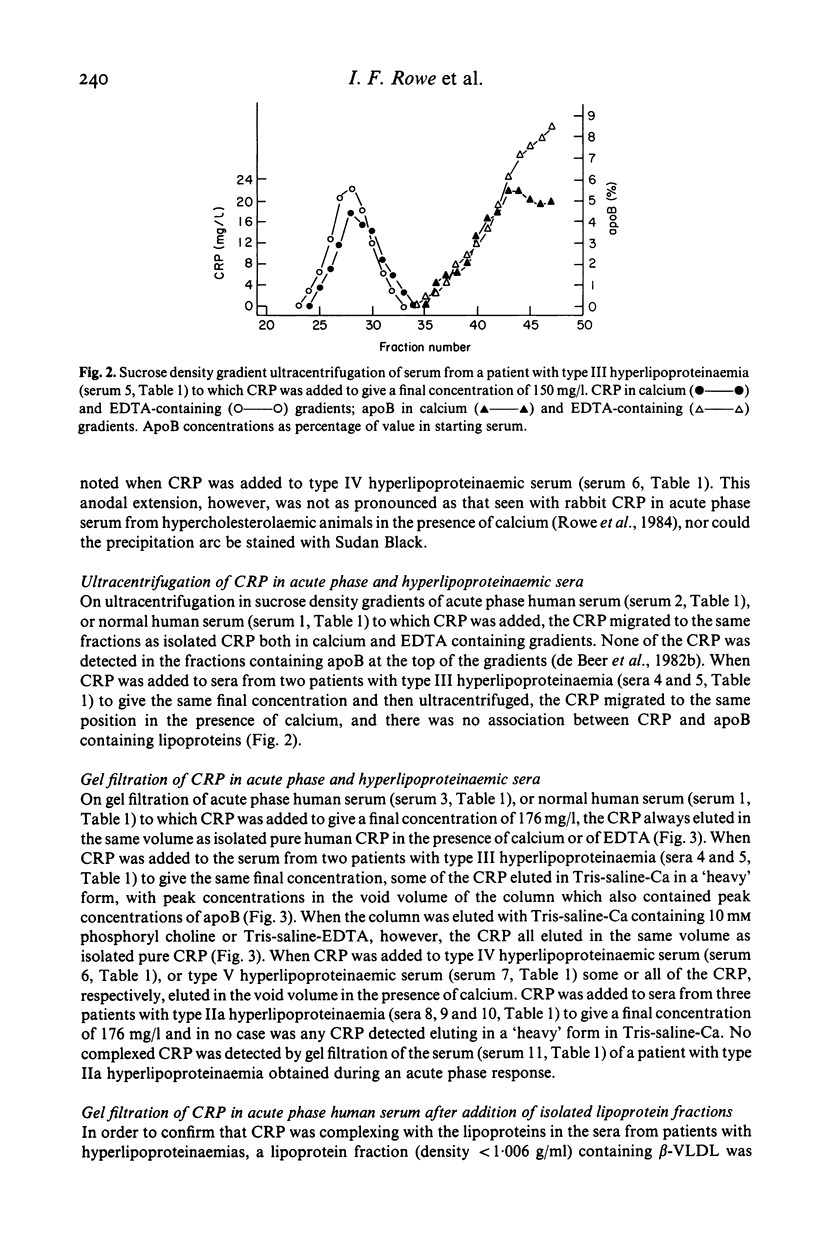
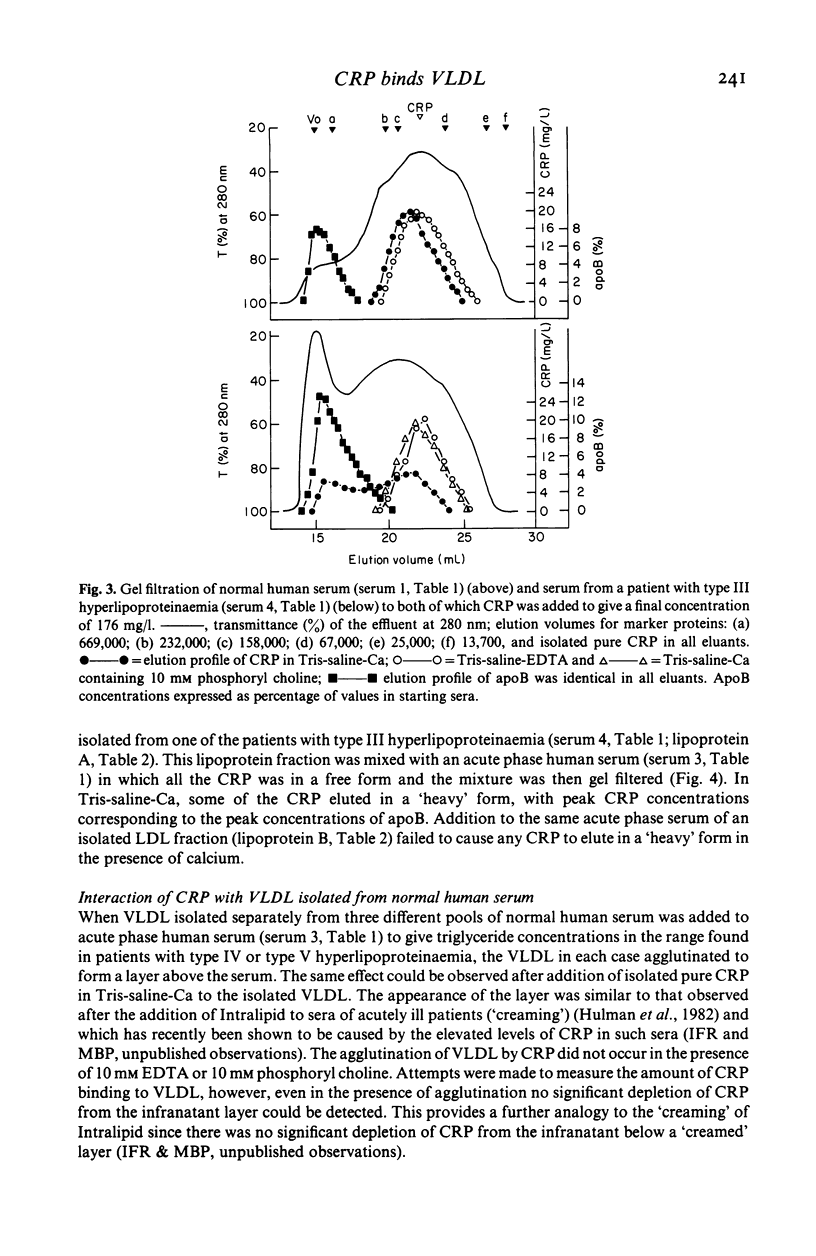
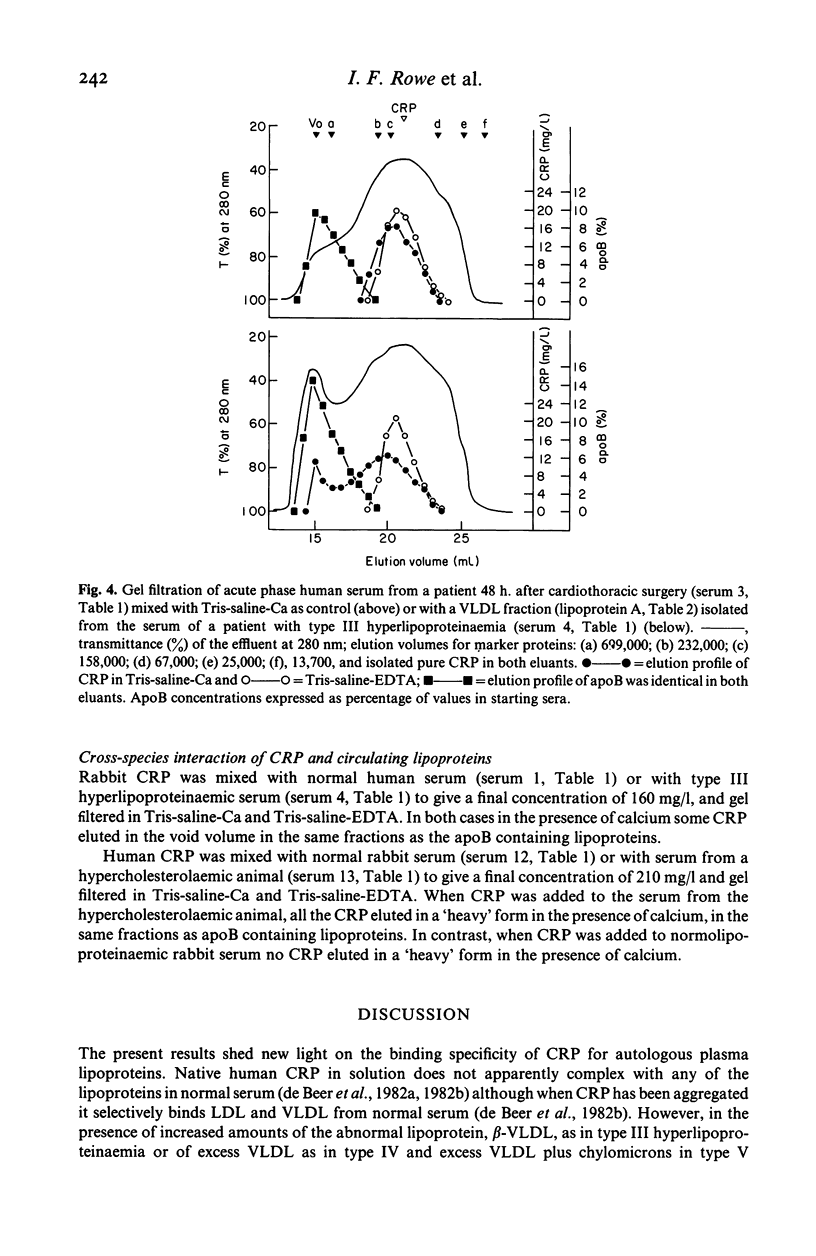
Native human CRP in solution formed complexes with the abnormal lipoprotein beta-VLDL in serum of patients with type III hyperlipoproteinaemia. CRP also formed complexes in sera from individuals with type IV and type V hyperlipoproteinaemia. The binding was calcium-dependent and inhibitable by free phosphoryl choline. No complexes were demonstrable in sera containing high LDL levels from cases of type IIa hyperlipoproteinaemia. Addition of isolated beta-VLDL, but not of isolated LDL, to acute phase normolipoproteinaemic serum caused the appearance of soluble CRP-lipoprotein complexes. In contrast, addition of an excess of isolated normal VLDL to acute phase serum or to isolated CRP was followed by agglutination (creaming) of the lipoprotein particles. Rabbit CRP, on the other hand, formed soluble complexes both with normal human apoB containing lipoproteins and with the abnormal beta-VLDL. Human CRP complexed with rabbit beta-VLDL but not with normal rabbit serum lipoproteins. These interactions may be important for the role of CRP in health and disease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain C. C., Poon L. S., Chan C. S., Richmond W., Fu P. C. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1974 Apr;20(4):470–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz M. L., de Beer F. C., Feinstein A., Munn E. A., Milstein C. P., Fletcher T. C., March J. F., Taylor J., Bruton C., Clamp J. R. Phylogenetic aspects of C-reactive protein and related proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:49–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Beer F. C., Pepys M. B. Isolation of human C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component. J Immunol Methods. 1982;50(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Beer F. C., Shine B., Pepys M. B. Radiometric ligand binding assay for C-reactive protein. Complexed C-reactive protein is not detectable in acute phase serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Oct;50(1):231–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianturco S. H., Brown F. B., Gotto A. M., Jr, Bradley W. A. Receptor-mediated uptake of hypertriglyceridemic very low density lipoproteins by normal human fibroblasts. J Lipid Res. 1982 Sep;23(7):984–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossling H. R., Pellegrini V. D., Jr Fat embolism syndrome: a review of the pathophysiology and physiological basis of treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982 May;(165):68–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y., Oliveira E. Binding of C-reactive protein to C-carbohydrate and PC-substituted protein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:163–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist L., Carlson K., Carlson L. A. Comparison between the use of isopropanol and tetramethylurea for the solubilisation and quantitation of human serum very low density apolipoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):457–460. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90444-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulman G., Fraser I., Pearson H. J., Bell P. R. Agglutination of intralipid by sera of acutely ill patients. Lancet. 1982 Dec 25;2(8313):1426–1427. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91328-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. Cholesteryl ester synthesis in macrophages: stimulation by beta-very low density lipoproteins from cholesterol-fed animals of several species. J Lipid Res. 1980 Nov;21(8):970–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narkates A. J., Volanakis J. E. C-reactive protein binding specificities: artificial and natural phospholipid bilayers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:172–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. P. Electrophoretic separation of plasma lipoproteins in agarose gel. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):693–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira E. B., Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y. Comparative studies on the binding properties of human and rabbit C-reactive proteins. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1396–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L. Acute phase proteins with special reference to C-reactive protein and related proteins (pentaxins) and serum amyloid A protein. Adv Immunol. 1983;34:141–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B. C-reactive protein fifty years on. Lancet. 1981 Mar 21;1(8221):653–657. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91565-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C., Ashley M. J. Isolation of C-reactive protein by affinity chromatography. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):32–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C., Fletcher T. C., Richardson N., Munn E. A., Feinstein A. Analogues in other mammals and in fish of human plasma proteins, C-reactive protein and amyloid P component. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):168–170. doi: 10.1038/273168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C., Markham R. E., Thomas H. C., Williams B. D., Petrie A. Comparative clinical study of protein SAP (amyloid P component) and C-reactive protein in serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Apr;32(1):119–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe I. F., Soutar A. K., Trayner I. M., Baltz M. L., de Beer F. C., Walker L., Bowyer D., Herbert J., Feinstein A., Pepys M. B. Rabbit and rat C-reactive proteins bind apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):604–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V. G., Shore B., Hart R. G. Changes in apolipoproteins and properties of rabbit very low density lipoproteins on induction of cholesteremia. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1579–1585. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treiman N., Waisbrod V., Waisbrod H. Lipoprotein electrophoresis in fat embolism: a preliminary report. Injury. 1981 Sep;13(2):108–110. doi: 10.1016/0020-1383(81)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E., Kaplan M. H. Specificity of C-reactive protein for choline phosphate residues of pneumococcal C-polysaccharide. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Feb;136(2):612–614. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E., Wirtz K. W. Interaction of C-reactive protein with artificial phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Nature. 1979 Sep 13;281(5727):155–157. doi: 10.1038/281155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. M., Nguyen N. Y., Yonaha K., Robey F., Liu T. Y. Primary structure of rabbit C-reactive protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13610–13615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Beer F. C., Soutar A. K., Baltz M. L., Trayner I. M., Feinstein A., Pepys M. B. Low density lipoprotein and very low density lipoprotein are selectively bound by aggregated C-reactive protein. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):230–242. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



