Abstract
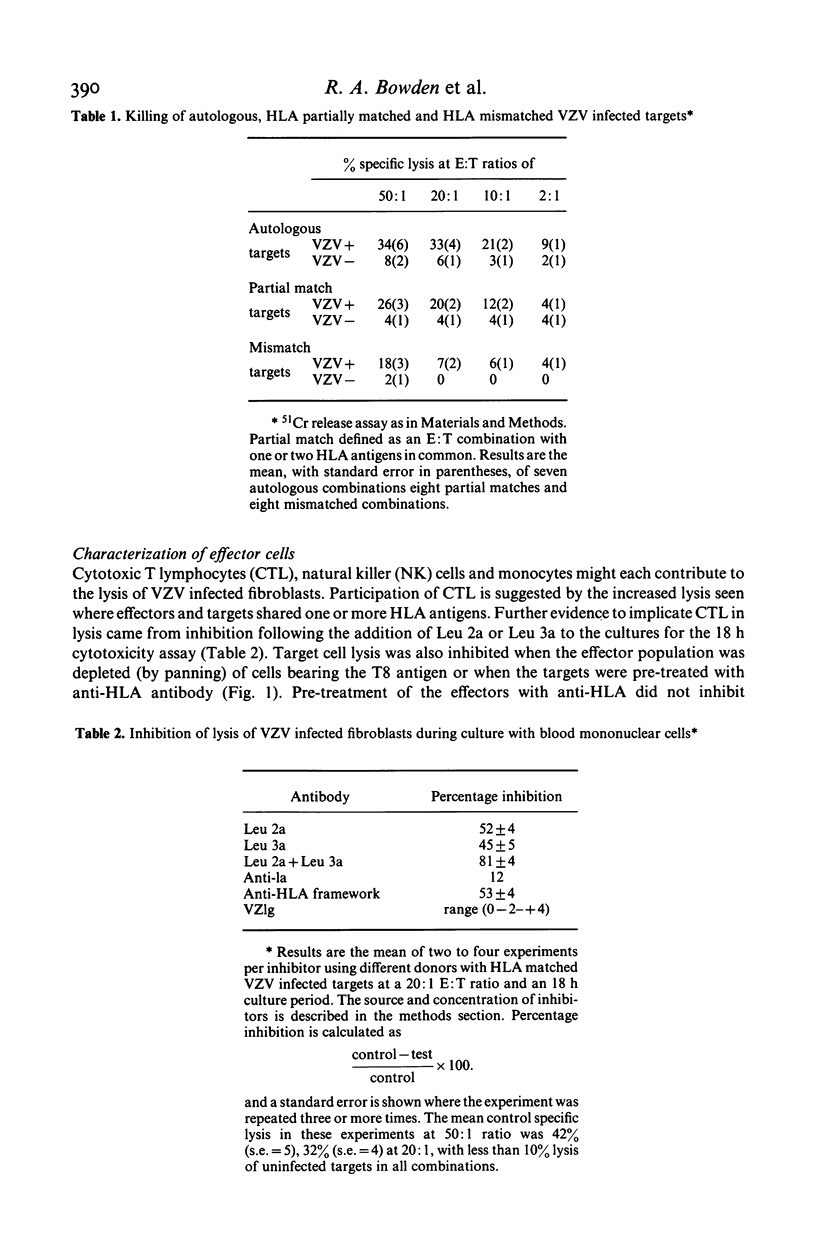
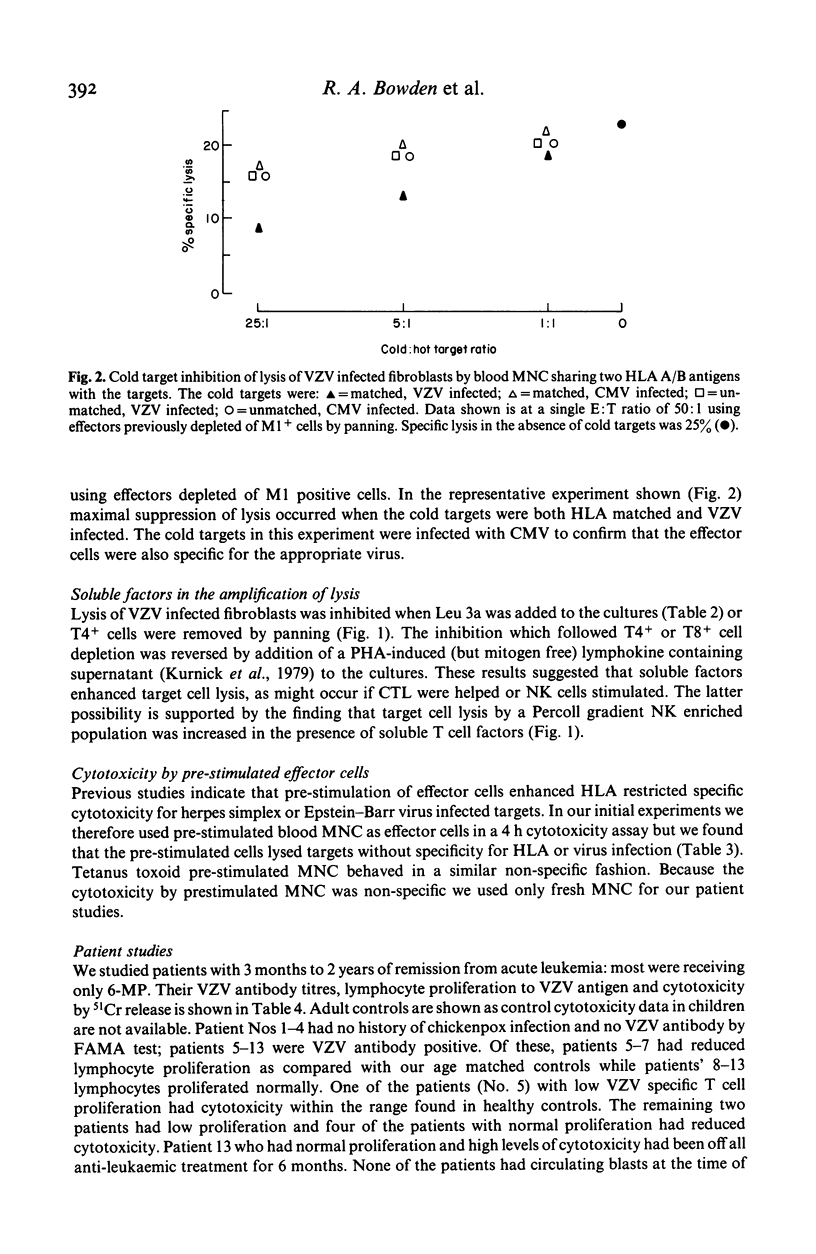
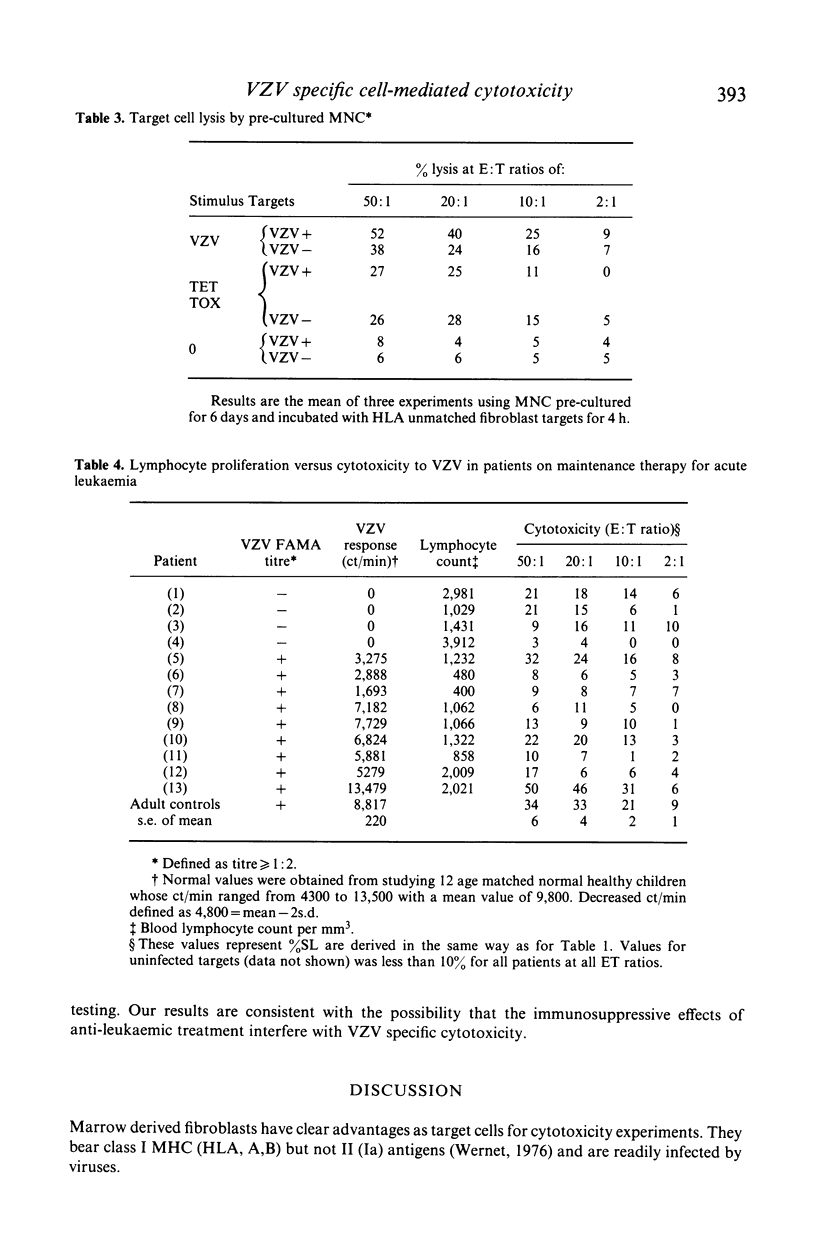
Varicella zoster virus (VZV) is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in immunosuppressed children but little is known of the cellular mechanisms of VZV immunity. We therefore developed a clinically applicable system to study responses to VZV infected cells. Fresh blood mononuclear cells (MNC) from VZV immune donors killed VZV infected fibroblasts in an 18 h 51Cr release assay. The specificity for virus was confirmed by cold target inhibition. An enhancing role for HLA matching was demonstrated using targets mismatched for HLA, and blocking by antibodies to HLA framework and T cell subsets. Cytotoxicity was not blocked with anti-Ia or anti-VZV antibodies. Killing of VZV infected target cells was reduced in seven out of nine VZV antibody positive patients in remission who were receiving maintenance treatment for acute lymphocytic leukaemia. Three of these patients had normal lymphocyte proliferative responses to VZV. Of the two patients with normal cytotoxic responses to VZV, one had reduced proliferation. It therefore appears that presence of VZV antibody, T cell proliferative responses, and cytotoxicity are independently variable. Cytotoxicity may be more susceptible to immunosuppression than either antibody or T cell proliferation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Cooper M. D., Balch C. M. Postnatal expansion of the natural killer and keller cell population in humans identified by the monoclonal HNK-1 antibody. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):321–326. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellgrau D. Induction of cytotoxic T cell precursors in vivo. Role of T helper cells. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1505–1515. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop G. A., Glorioso J. C., Schwartz S. A. Relationship between expression of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins and susceptibility of target cells to human natural killer activity. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1544–1561. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braciale T. J. Immunologic recognition of influenza virus-infected cells. I. Generation of a virus-strain specific and a cross-reactive subpopulation of cytotoxic T cells in the response to type A influenza viruses of different subtypes. Cell Immunol. 1977 Oct;33(2):423–436. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolin R., Reichman R. C., Mazur M. H., Whitley R. J. NIH conference. Herpes zoster-varicella infections in immunosuppressed patients. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Sep;89(3):375–388. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-3-375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. M., Thompson G. S. Functionally restricted, allospecific, human helper T cell lines that amplify either B cell or cytolytic T cell responses. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1675–1680. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Kuribayashi K., Kern D. E., Gillis S. Interleukin-2 augments natural killer cell activity. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):335–338. doi: 10.1038/291335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. R., Ortaldo J. R., Bonnard G. D. Augmentation by interferon of human natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):221–223. doi: 10.1038/277221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurnick J. T., Grönvik K. O., Kimura A. K., Lindblom J. B., Skoog V. T., Sjöberg O., Wigzell H. Long term growth in vitro of human T cell blasts with maintenance of specificity and function. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1255–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Evans R. L., Lipinski M., Cunningham-Rundles C., Good R. A., Herzenberg L. A. Evolutionary conservation of surface molecules that distinguish T lymphocyte helper/inducer and cytotoxic/suppressor subpopulations in mouse and man. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):310–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linderkamp O., Wu P. Y., Meiselman H. J. Geometry of neonatal and adult red blood cells. Pediatr Res. 1983 Apr;17(4):250–253. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198304000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage M. G., McHugh L. L., Rothstein T. L. Mouse lymphocytes with and without surface immunoglobulin: preparative scale separation in polystyrene tissue culture dishes coated with specifically purified anti-immunoglobulin. J Immunol Methods. 1977;15(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen B., Rebai N., Liabeuf A., Mawas C. Human cytotoxic T cell structures associated with expression of cytolysis. I. Analysis at the clonal cell level of the cytolysis-inhibiting effect of 7 monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Sep;12(9):739–747. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hodgdon J. C., Cooper D. A., Hussey R. E., Fitzgerald K. A., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Human cytotoxic T cell clones directed at autologous virus-transformed targets: further evidence for linkage of genetic restriction to T4 and T8 surface glycoproteins. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):186–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. D., Flournoy N., Thomas E. D. Cell-mediated immunity to varicella-zoster virus after allogeneic marrow transplant. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):479–487. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. A., Yoonessi S., O'Malley J., Freeman A., Gershon A., Ogra P. L. Cell-mediated immunity to varicella-zoster virus infection in subjects with lymphoma or leukemia. J Pediatr. 1979 Feb;94(2):223–230. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80828-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Jr, Kirmani N., Esber E., Saral R., Manischewitz J. F., Rogers J. L., Rook A. H., Santos G. W., Burns W. H. HLA-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte and nonthymic cytotoxic lymphocyte responses to cytomegalovirus infection of bone marrow transplant recipients. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):2036–2041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H., Bevan M. J. A differentiation factor required for the expression of cytotoxic T-cell function. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):754–757. doi: 10.1038/296754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slovin S. F., Schooley R. T., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Analysis of cellular immune response to EBV by using cloned T cell lines. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2127–2132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele R. W., Hensen S. A., Vincent M. M., Fuccillo D. A., Bellanti J. A. A 51 Cr microassay technique for cell-mediated immunity to viruses. J Immunol. 1973 Jun;110(6):1502–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Saksela E. Isolation of human NK cells by density gradient centrifugation. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(3-4):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernet P. Human Ia-type alloantigens: methods of detection, aspects of chemistry and biology, markers for disease states. Transplant Rev. 1976;30:271–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa M., Shiroguchi T., Kobayashi Y. HLA-restricted T lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against herpes simplex virus-infected cells in humans. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):190–197. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.190-197.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaia J. A., Leary P. L., Levin M. J. Specificity of the blastogenic response of human mononuclear cells to herpesvirus antigens. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):646–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.646-651.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaia J. A., Oxman M. N. Antibody to varicella-zoster virus-induced membrane antigen: immunofluorescence assay using monodisperse glutaraldehyde-fixed target cells. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):519–530. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Kung P. C. Monoclonal antibodies which distinguish between human NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):394–396. doi: 10.1038/288394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


