Abstract
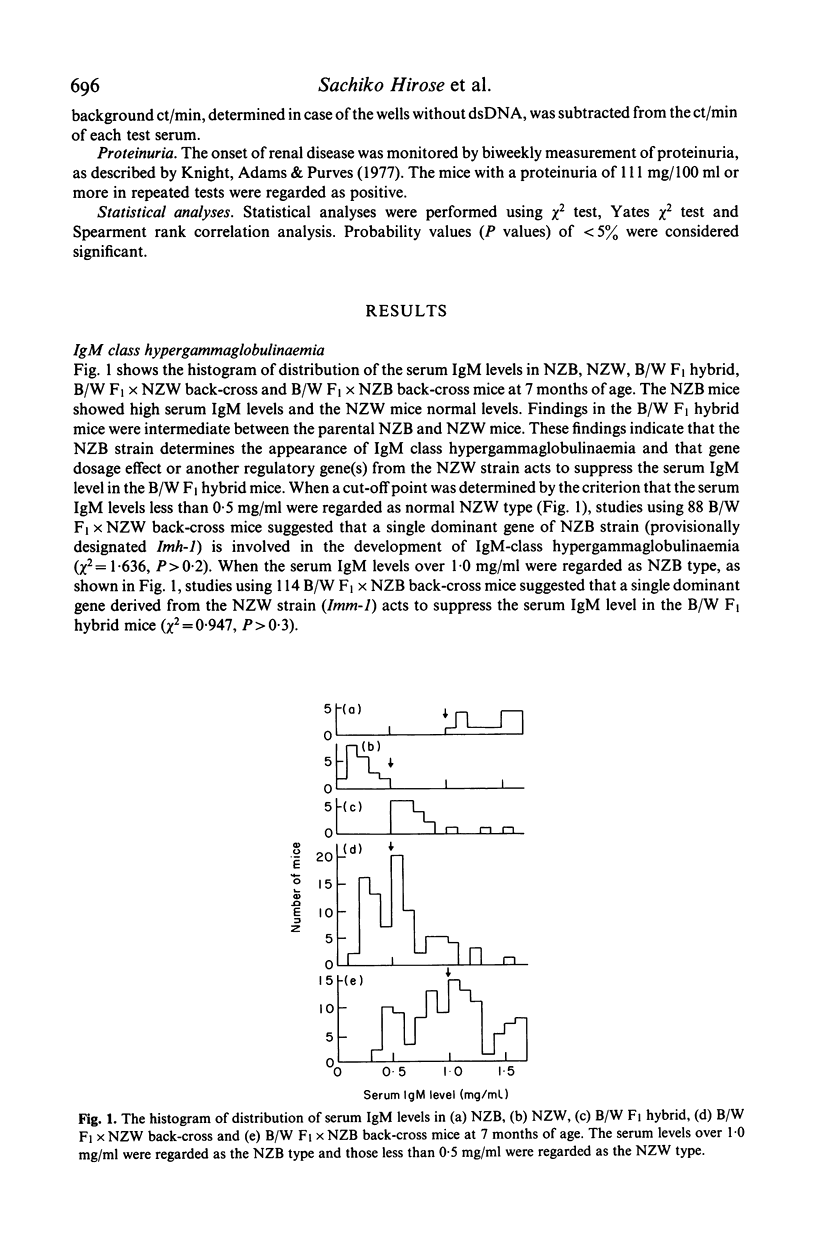
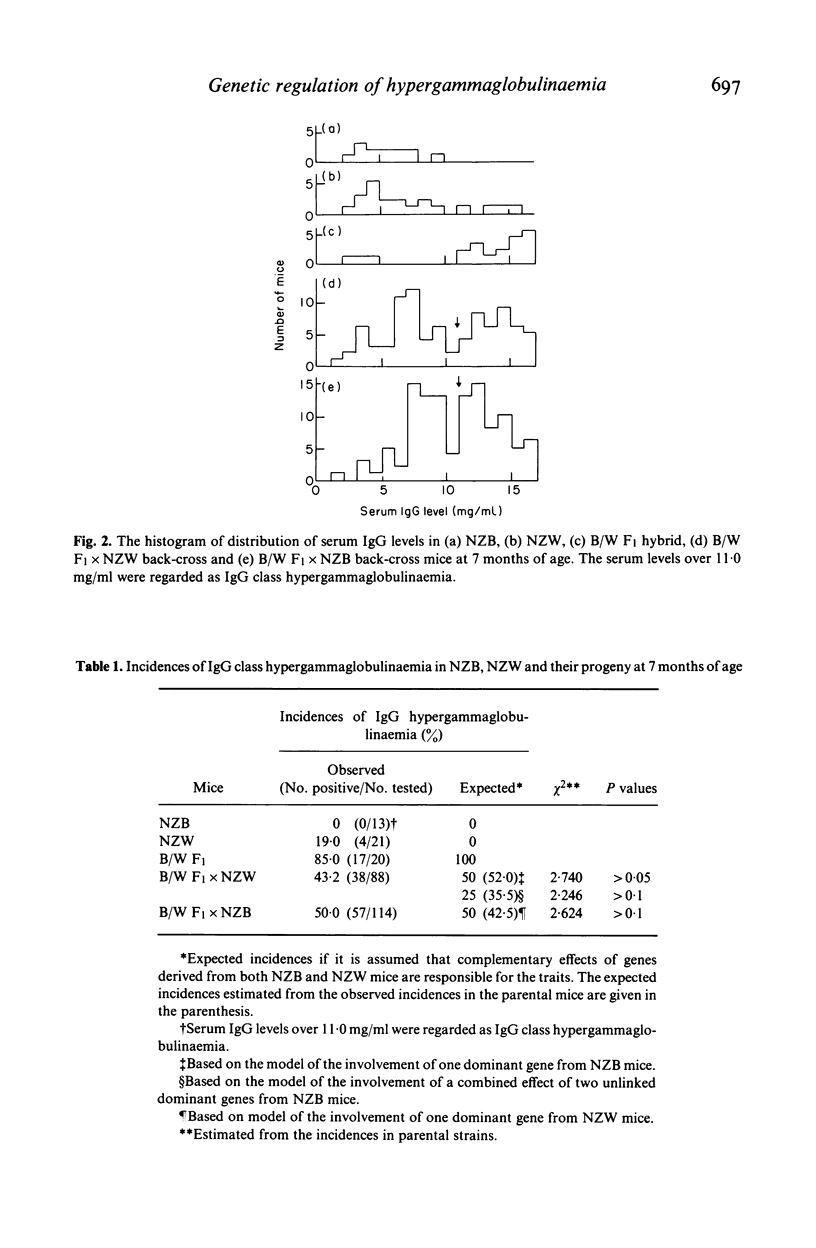
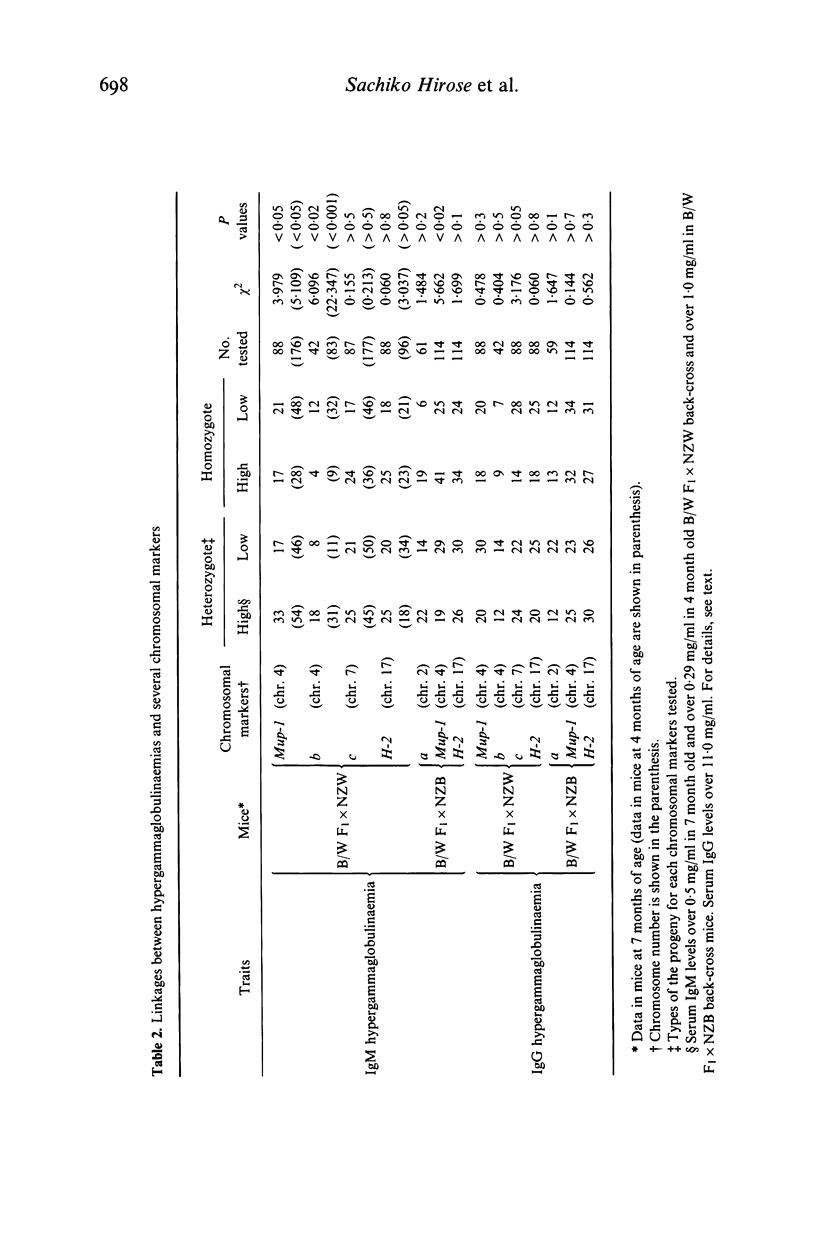
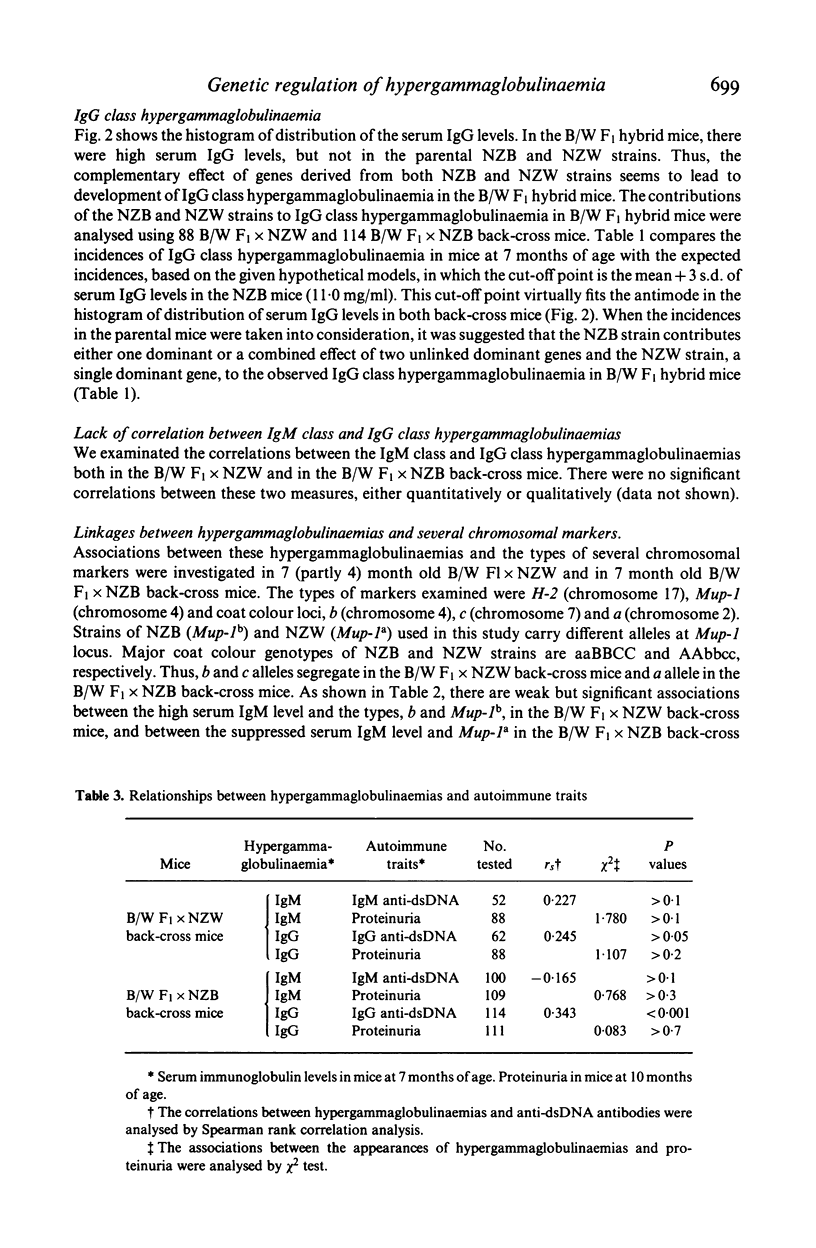
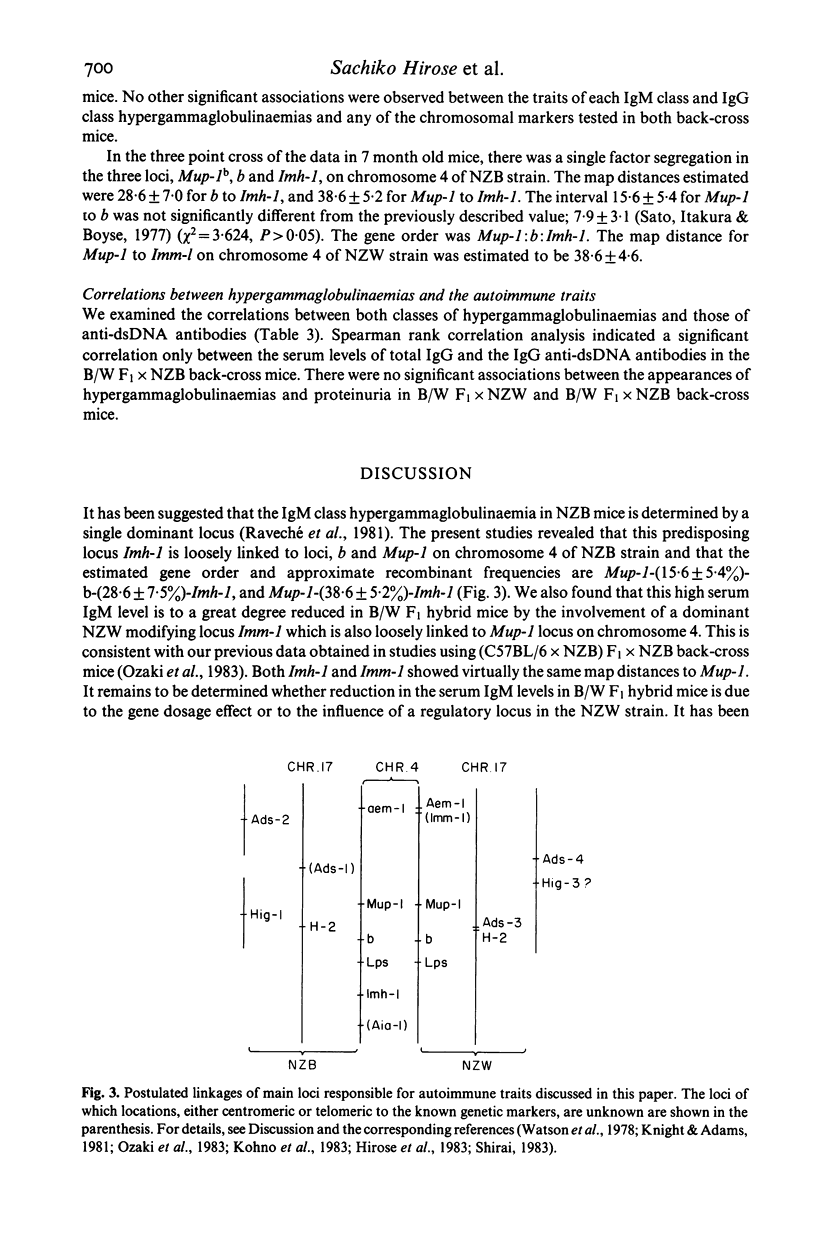
To determine the inheritance patterns of both IgM class and IgG class hypergammaglobulinaemias, the locations of genes and the relations of these genes to other autoimmune traits in NZB X NZW (B/W) F1 hybrid, we measured serum levels of both IgM and IgG in NZB, NZW, B/W F1 hybrid, B/W F1 X NZW back-cross and B/W F1 X NZB back-cross mice. The highest serum IgM levels were observed in NZB mice, however the serum IgG levels were normal. In contrast, a large amount of IgG was produced in B/W F1 hybrids, in which the serum IgM levels were lower than those observed in NZB mice. The NZW mice had fairly normal values for both measures. Progeny studies suggested that a single dominant locus (Imh-1) of NZB strain, which is loosely linked to brown-black coat colour locus b and Mup-1 locus on chromosome 4, determines the IgM class hypergammaglobulinaemia. The estimated gene order was Mup-1:b:Imh-1. This IgM class hypergammaglobulinaemia in NZB mice was suppressed to a considerable extent in B/W F1 hybrid mice by either a gene dosage effect or more likely, a regulatory gene locus of NZW strain, being also loosely linked to Mup-1 locus on chromosome 4. As for the IgG class hypergammaglobulinaemia, a complementary effect of two or three genes, either one or two dominant genes derived from NZB and a single dominant gene from NZW strains, determines this trait in B/W F1 hybrid mice. There appeared to be no relationships between the genes responsible for the IgM class and IgG class hypergammaglobulinaemias. When looking at the correlations between the hypergammaglobulinaemias and the traits, anti-double stranded DNA (dsDNA) antibodies and renal disease in both back-cross mice, we found a significant quantitative correlation only between the IgG class hypergammaglobulinaemia and the IgG class anti-dsDNA antibodies in B/W F1 X NZB back-cross mice.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen P., Ziff M., Vitetta E. S. Characterization of a B cell defect in the NZB mouse manifested by an increased ratio of surface IgM to IgD. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):973–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S. K., Owen F. L., Womack J. E., Riblet R. J. Analysis of recombinant inbred lines derived from "autoimmune" (NZB) and "high leukemia" (C58) strains: independent multigenic systems control B cell hyperactivity, retrovirus expression, and autoimmunity. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1539–1544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson W. F., Chused T. M., Morse H. C., 3rd Genetic control of B- and T-lymphocyte abnormalities of NZB mice in crosses with B10.D2 mice. Immunogenetics. 1981;13(5):421–434. doi: 10.1007/BF00346023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. B., Schnneider G., Schur P. H. Enzyme immunoassay for antibodies to native DNA. Specificity and quality of antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jan;26(1):52–62. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa K., Hardy R. R., Parks D. R., Herzenberg L. A. The "Ly-1 B" cell subpopulation in normal immunodefective, and autoimmune mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):202–218. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Maruyama N., Ohta K., Shirai T. Polyclonal B cell activation and autoimmunity in New Zealand mice. I. Natural thymocytotoxic autoantibody (NTA). J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):610–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Nagasawa R., Sekikawa I., Hamaoki M., Ishida Y., Sato H., Shirai T. Enhancing effect of H-2-linked NZW gene(s) on the autoimmune traits of (NZB X NZW)F1 mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):228–233. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. Increased spontaneous polyclonal activation of B lymphocytes in mice with spontaneous autoimmune disease. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2213–2219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight J. G., Adams D. D. Genes determining autoimmune disease in New Zealand mice. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1981 May;5(3):165–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight J. G., Adams D. D., Purves H. D. The genetic contribution of the NZB mouse to the renal disease of the NZB x NZW hybrid. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 May;28(2):352–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno A., Yoshida H., Sekita K., Maruyama N., Ozaki S., Hirose S., Shirai T. Genetic regulation of the class conversion of dsDNA-specific antibodies in (NZB X NZW)F1 hybrid. Immunogenetics. 1983;18(5):513–524. doi: 10.1007/BF00364392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELLORS R. C. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE IN NZB/BL MICE. I. PATHOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS OF A MODEL SYSTEM OF SPONTANEOUS GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:25–40. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manny N., Datta S. K., Schwartz R. S. Synthesis of IgM by cells of NZB and SWR mice and their crosses. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1220–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manohar V., Brown E., Leiserson W. M., Chused T. M. Expression of Lyt-1 by a subset of B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):532–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moutsopoulos H. M., Boehm-Truitt M., Kassan S. S., Chused T. M. Demonstration of activation of B lymphocytes in New Zealand black mice at birth by an immunoradiometric assay for murine IgM. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1639–1644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki S., Honda H., Maruyama N., Hirose S., Hamaoki M., Sato H., Shirai T. Genetic regulation of erythrocyte autoantibody production in New Zealand black mice. Immunogenetics. 1983;18(3):241–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00952963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raveche E. S., Novotny E. A., Hansen C. T., Tjio J. H., Steinberg A. D. Genetic studies in NZB mice. V. Recombinant inbred lines demonstrate that separate genes control autoimmune phenotype. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1187–1197. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Mellors R. C. Natural thymocytotoxic autoantibody and reactive antigen in New Zealand black and other mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1412–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L. Genetic aspects of immunologic abnormalities in New Zealand mouse strains. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jun;21(5 Suppl):S106–S112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L., Wistar R., Jr Immunoglobulins in NZB-BL mice. I. Serum immunoglobulin levels and immunoglobulin class of erythrocyte autoantibody. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):169–183. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox F. H. Simplified procedure for electrophoresis of the major urinary protein of Mus musculus. Biochem Genet. 1975 Apr;13(3-4):243–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00486018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


