Abstract
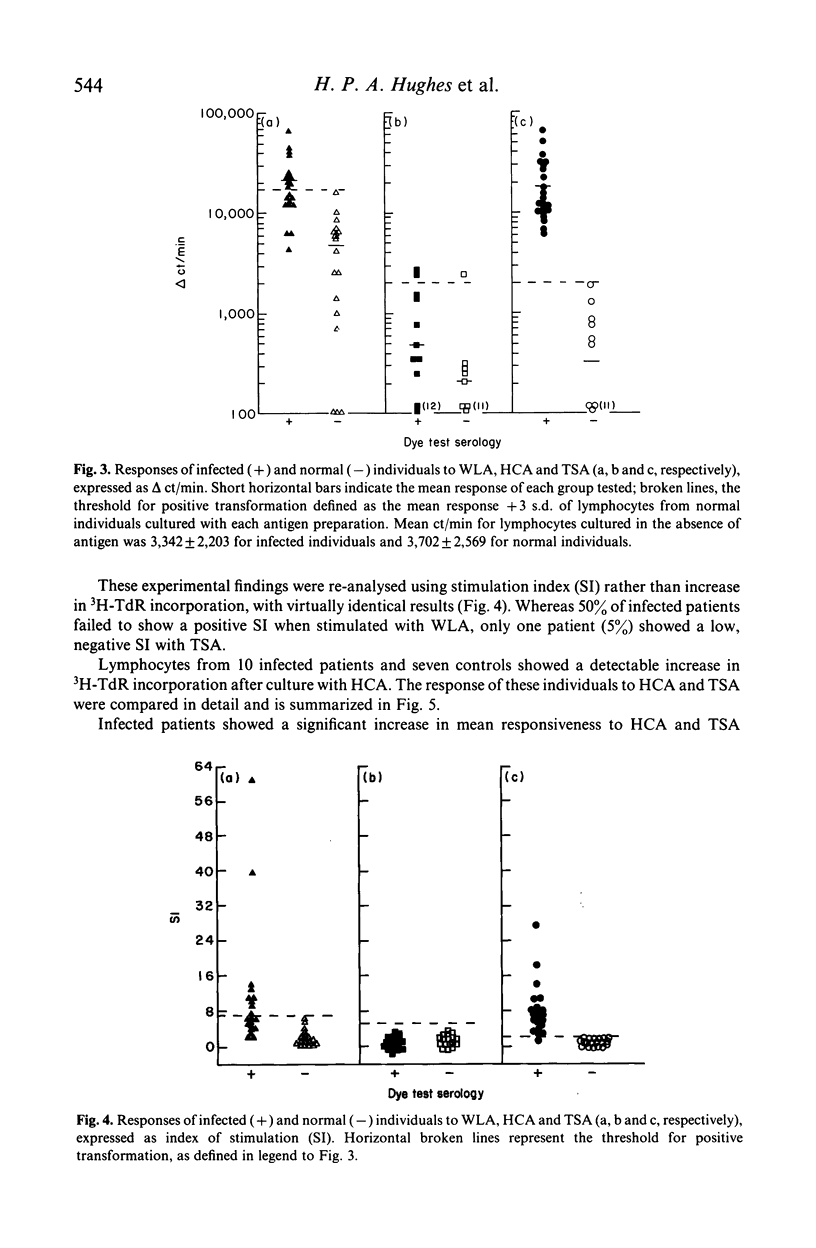
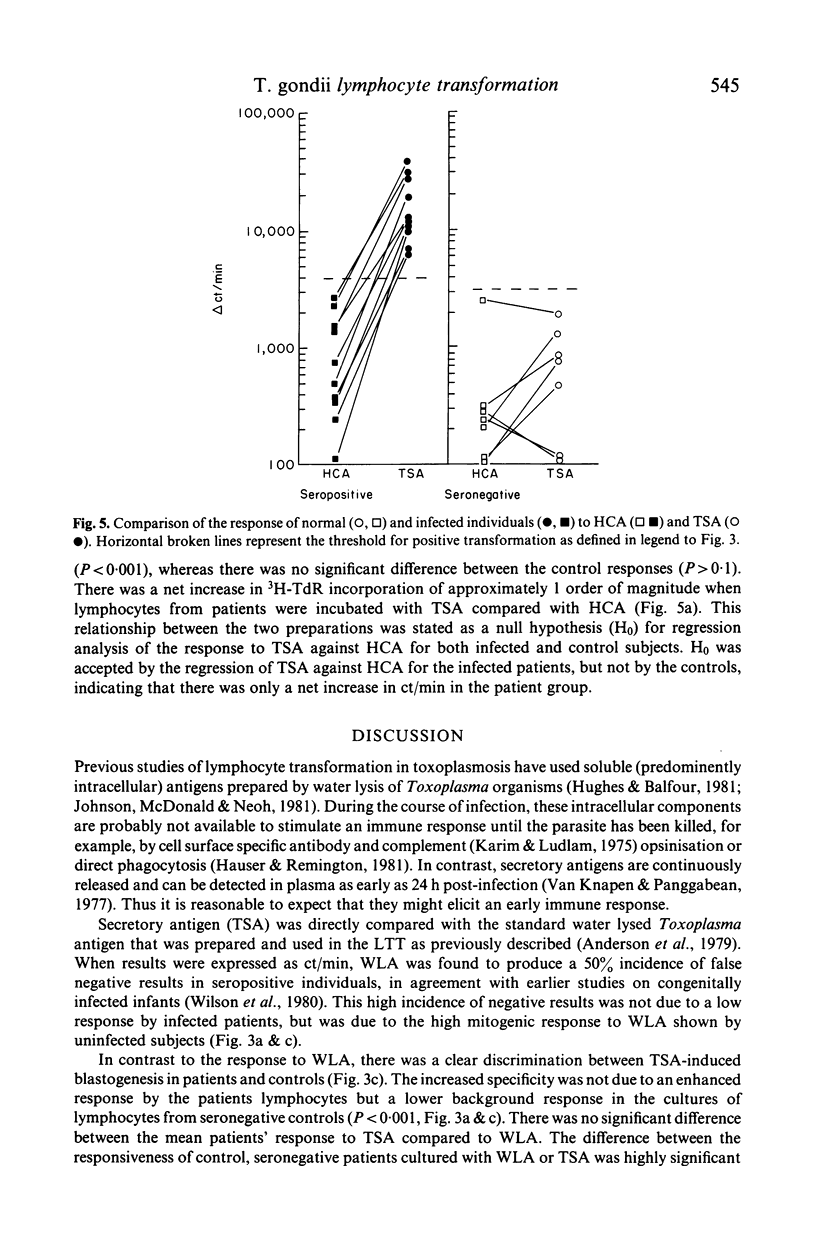
Secreted (TSA) and water lysed (WLA) antigens derived from cell culture of the RH strain of Toxoplasma gondii have been used to induce antigen specific mitogenesis of lymphocytes from patients with symptomatic and asymptomatic toxoplasmosis. Lymphocyte responsiveness to WLA was similar to previous reports, with about 50% of patients showing a false negative reaction. Responses to TSA however were highly specific, with no false negative reactions. This increased specificity was not due to an increased response against TSA by patients' lymphocytes (P less than 0.001), but a lower TSA response by uninfected subjects' lymphocytes (P greater than 0.1) compared with WLA in both cases. In a minority of both infected and uninfected subjects, there was a low but detectable response to antigens secreted by the host cell line (HCA), and this was directly compared to their responses against TSA. There was at least a 10-fold increase in the patients' responses to TSA when compared with HCA (P less than 0.001), whereas there was no significant difference between the uninfected subjects' responses to these antigens (P greater than 0.1). Preliminary observations have suggested that TSA is distinct from other defined secreted antigens as both heat treatment and solid phase immunosorption did not have any noticeable effect on TSA-induced mitogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. P., Atlas E., Ahern M. J., Weisbrot I. M. Central nervous system toxoplasmosis in homosexual men. Am J Med. 1983 Nov;75(5):877–881. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90420-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. E., Jr, Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. Longitudinal studies of lymphocyte response to Toxoplasma antigen in humans infected with T. gondii. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1979 Nov;2(4):293–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balfour A. H., Fleck D. G., Hughes H. P., Sharp D. Comparative study of three tests (dye test, indirect haemagglutination test, latex agglutination test) for the detection of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in human sera. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Feb;35(2):228–232. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.2.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsari A., Poli G., Molina V., Dovis M., Petruzzelli E., Boniolo A., Rolleri E. ELISA for toxoplasma antibody detection: a comparison with other serodiagnostic tests. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jul;33(7):640–643. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.7.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gransden W. R., Brown P. M. Pneumocystis pneumonia and disseminated toxoplasmosis in a male homosexual. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 May 21;286(6378):1614–1614. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6378.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser W. E., Jr, Remington J. S. Effect of monoclonal antibodies on phagocytosis and killing of Toxoplasma gondii by normal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):637–640. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.637-640.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. P., Balfour A. H. An investigation of the antigenic structure of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasite Immunol. 1981 Autumn;3(3):235–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1981.tb00403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. P. Characterization of the circulating antigen of Toxoplasma gondii. Immunol Lett. 1981 Jun;3(2):99–102. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(81)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. P., van Knapen F. Characterisation of a secretory antigen from Toxoplasma gondii and its role in circulating antigen production. Int J Parasitol. 1982 Oct;12(5):433–437. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(82)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. M., McDonald P. J., Neoh S. H. Molecular weight analysis of the major polypeptides and glycopeptides of Toxoplasma gondii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun 16;100(3):934–943. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91913-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim K. A., Ludlam G. B. The relationship and significance of antibody titres as determined by various serological methods in glandular and ocular toxoplasmosis. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Jan;28(1):42–49. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Gaines J. D., Remington J. S. Lymphocyte transformation in human toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):283–288. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londner M. V., Frankenburg S., Slutzky G. M., Greenblatt C. L. Action of leishmanial excreted factor (EF) on human lymphocyte blast transformation. Parasite Immunol. 1983 May;5(3):249–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1983.tb00741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubayashi H., Akao S. Immuno-electron microscopic studies on toxoplasma gondii. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Jul;15(4):486–491. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor C. G., Fleck D. G., Nagington J., Stovin P. G., Cory-Pearce R., English T. A. Disseminated toxoplasmosis in cardiac transplantation. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jan;37(1):74–77. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. A., Chiappino M. L., O'Connor G. R. Secretion from the rhoptries of Toxoplasma gondii during host-cell invasion. J Ultrastruct Res. 1983 Apr;83(1):85–98. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(83)90067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordonez G. A., Newman J. T., Stone M. J. Serological diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infections by rapid separation of serum immunoglobulins M and G with CM Bio-Gel A. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):751–753. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.751-753.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Krahenbuhl J. L., Mendenhall J. W. A role for activated macrophages in resistance to infection with Toxoplasma. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):829–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.829-834.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano A., Yui K., Yamamoto M., Aosai F., Furuta S., Kojima S. Immune response to Toxoplasma gondii. I. Toxoplasma-specific proliferation response of peripheral blood lymphocytes from patients with toxoplasmosis. Microbiol Immunol. 1983;27(5):455–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1983.tb00604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Knapen F., Panggabean S. O. Detection of circulating antigen during acute infections with Toxoplasma gondii by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):545–547. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.545-547.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]