Abstract
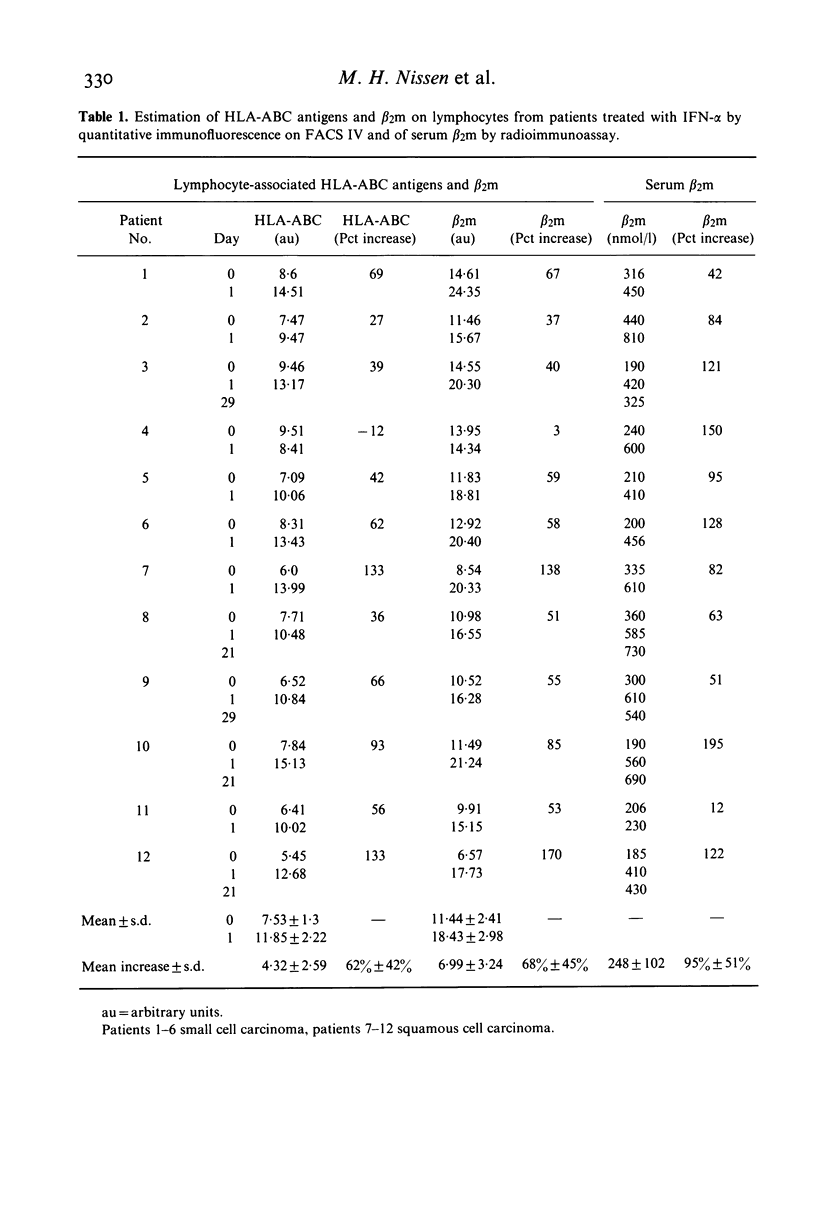
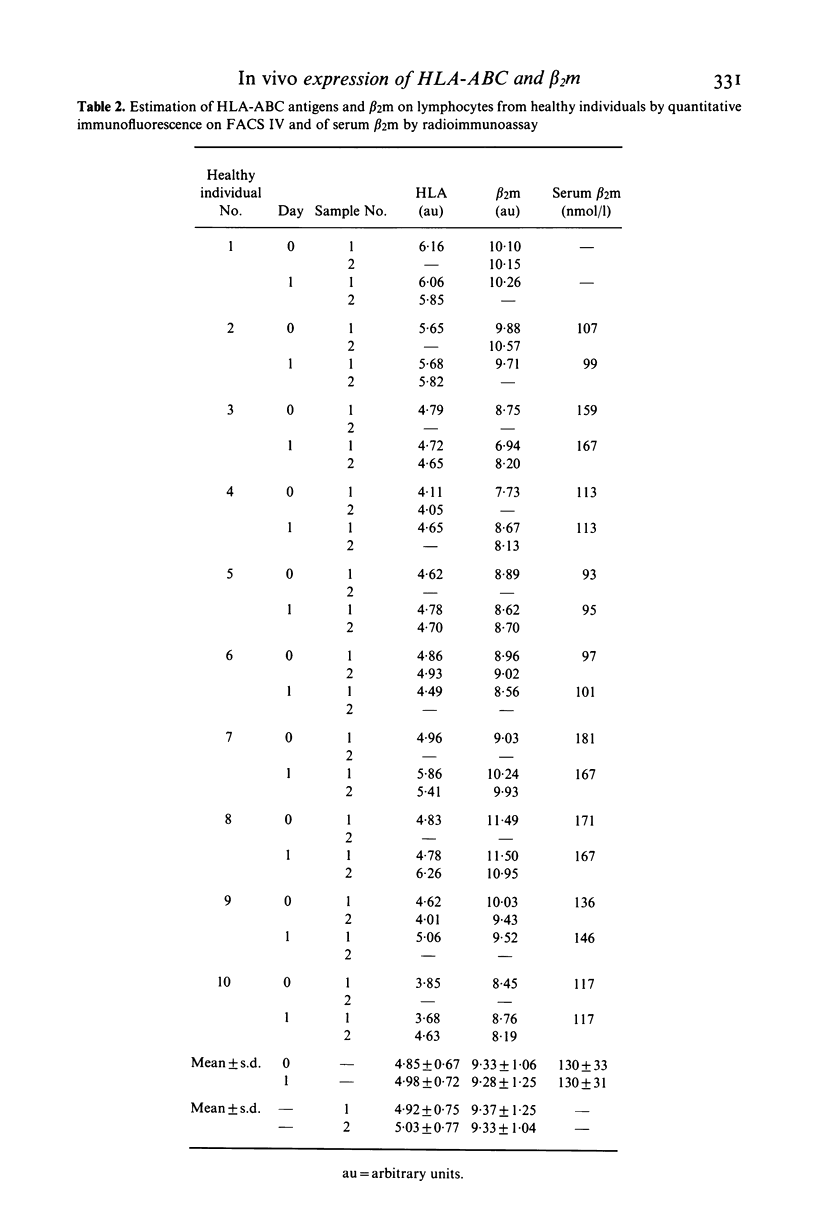
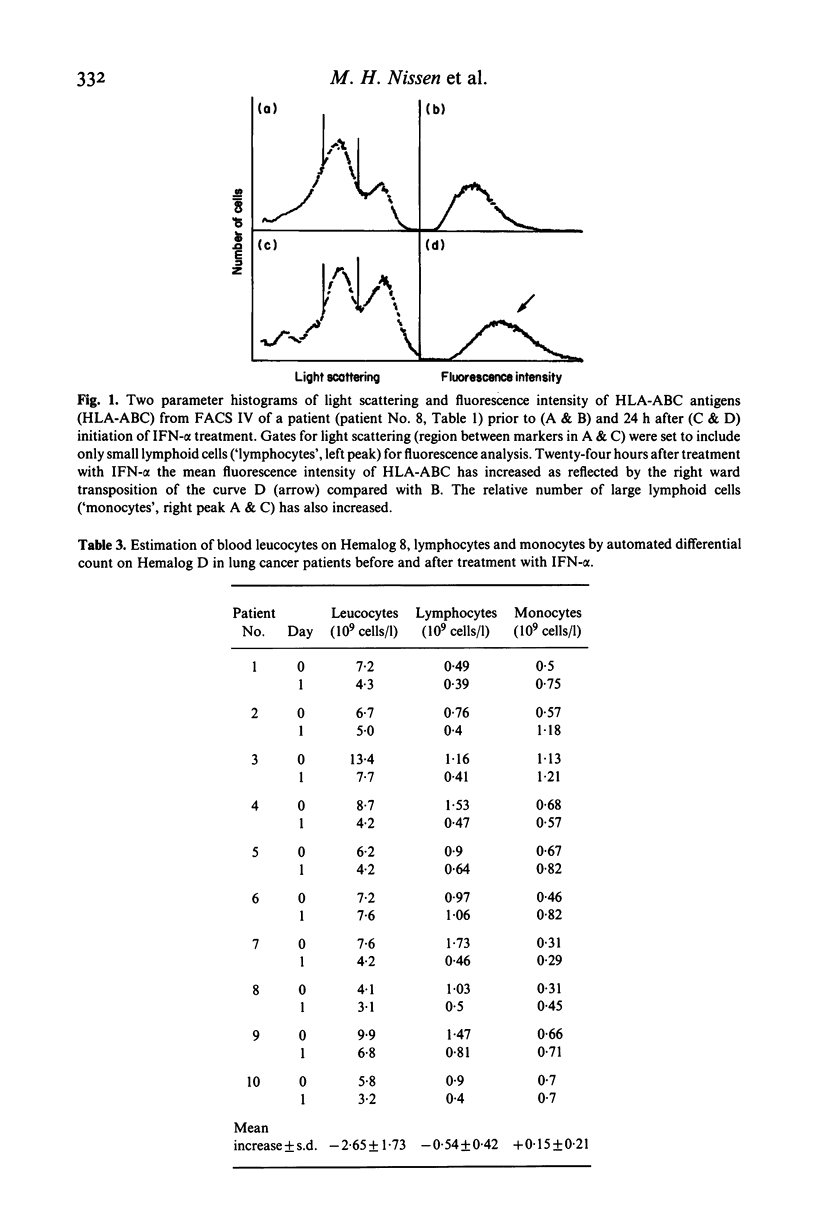
The effect of cloned human interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) on the expression of HLA-ABC antigens (HLA-ABC) and beta 2-microglobulin (beta 2m) on human peripheral lymphoid cells in vivo was studied by cytofluorometry using monoclonal antibodies and fluorescein-labelled rabbit anti-mouse immunoglobulin. A significant increase in the mean fluorescence intensity of HLA-ABC (median 59%, P less than 0.001) and beta 2m (median 57%, P less than 0.001) on small lymphoid cells was observed 24 h after initiation of IFN-alpha treatment (50 X 10(6) units IFN-alpha/m2 three times a week). The enhanced expression of these antigens in vivo was found in 11 of 12 examined patients with primary bronchial carcinoma. A concomitant increase in serum beta 2m (median 90%, P less than 0.001) was found in all patients. In contrast the amount of cell-associated HLA-ABC and beta 2m remained unchanged (P greater than 0.1 and P greater than 0.5, respectively) by day-to-day analysis of an untreated healthy control group. An increased expression of both HLA-ABC (mean 55%, P less than 0.0005) and beta 2m (mean 23%, P less than 0.01) was also observed prior to treatment in the lung cancer patients when compared to a group of age matched healthy individuals. Treatment with IFN-alpha caused a significant redistribution of mononuclear cells resulting in both absolute and relative lymphopenia. Pre-treatment lymphocyte counts were 1.09 X 10(9)/1 (range 0.49-1.73), post-treatment counts were 0.55 X 10(9)/1 (range 0.39-1.06).
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C. Recombinant interferon-gamma increases HLA-DR synthesis and expression. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1492–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Bodmer W. F., Parham P. Characterization of a monoclonal anti-beta 2-microglobulin antibody and its use in the genetic and biochemical analysis of major histocompatibility antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jul;9(7):536–545. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidlund M., Orn A., Wigzell H., Senik A., Gresser I. Enhanced NK cell activity in mice injected with interferon and interferon inducers. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):759–761. doi: 10.1038/273759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. R., Ortaldo J. R., Bonnard G. D. Augmentation by interferon of human natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):221–223. doi: 10.1038/277221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heron I., Hokland M., Berg K. Enhanced expression of beta2-microglobulin and HLA antigens on human lymphoid cells by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6215–6219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokland M., Heron I., Berg K., Hokland P. Natural killer cell activity correlates with the amount of beta 2-microglobulin on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1982 Sep 1;72(1):40–51. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90281-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokland M., Heron I., Berg K. Increased expression of beta 2-microglobulin and histocompatibility antigens on human lymphoid cells induced by interferon. J Interferon Res. 1981;1(4):483–494. doi: 10.1089/jir.1981.1.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight M., Cayley P. J., Silverman R. H., Wreschner D. H., Gilbert C. S., Brown R. E., Kerr I. M. Radioimmune, radiobinding and HPLC analysis of 2-5A and related oligonucleotides from intact cells. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):189–192. doi: 10.1038/288189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Warner N. L. Paraformaldehyde fixation of hematopoietic cells for quantitative flow cytometry (FACS) analysis. J Immunol Methods. 1981;47(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl-Magnusson P., Leary P., Gresser I. Interferon inhibits DNA synthesis induced in mouse lymphocyte suspensions by phytohaemagglutinin or by allogeneic cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 24;237(73):120–121. doi: 10.1038/newbio237120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl P., Gresser I., Leary P., Tovey M. Interferon treatment of mice: enhanced expression of histocompatibility antigens on lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1284–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plesner T., Karle H., Rubin B., Thomsen M. Evidence for a change in the expression of beta2-microglobulin-assoicated membrane structures on leukaemic human cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Feb;31(2):269–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plesner T., Nörgaard-Pedersen B., Boenisch T. Radioimmunoassay of beta2-microglobulin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1975 Dec;35(8):729–735. doi: 10.3109/00365517509095804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Fellous M., Revel M. Preferential effect of gamma interferon on the synthesis of HLA antigens and their mRNAs in human cells. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):833–836. doi: 10.1038/299833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



