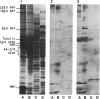
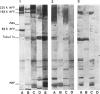
Abstract
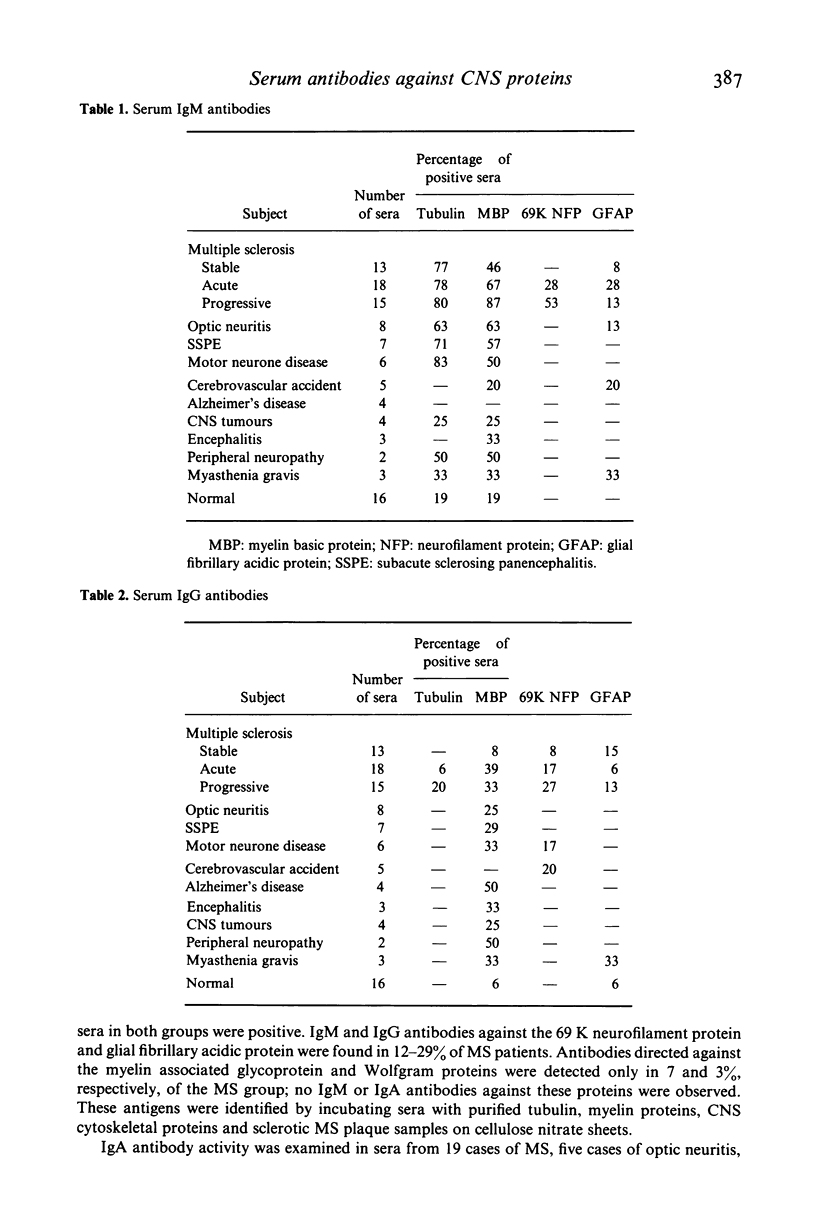
An immunoblotting technique has been used to screen serum samples from patients with demyelinating disease for antibody directed against central nervous system proteins. Antibodies of the IgM, IgG and IgA class directed against one or more of the particulate fraction proteins tubulin, myelin basic protein, 69 K neurofilament protein, glial fibrillary acidic protein, myelin associated glycoprotein or Wolfgram protein were present in 94, 54 and 47%, respectively, of multiple sclerosis sera examined. IgM antibodies against tubulin and myelin basic protein predominated. A similar antibody spectrum was seen in a significant proportion of sera from patients with optic neuritis, subacute sclerosing panencephalitis and motor neurone disease, in which primary or secondary demyelination occurs. Antibodies of all three classes directed against the 169 K and 220 K neurofilament proteins and against some unidentified proteins of human peripheral nerve, kidney, liver, spleen and skeletal muscle were detected in sera from healthy subjects and patients with neurological disease.
Full text
PDF

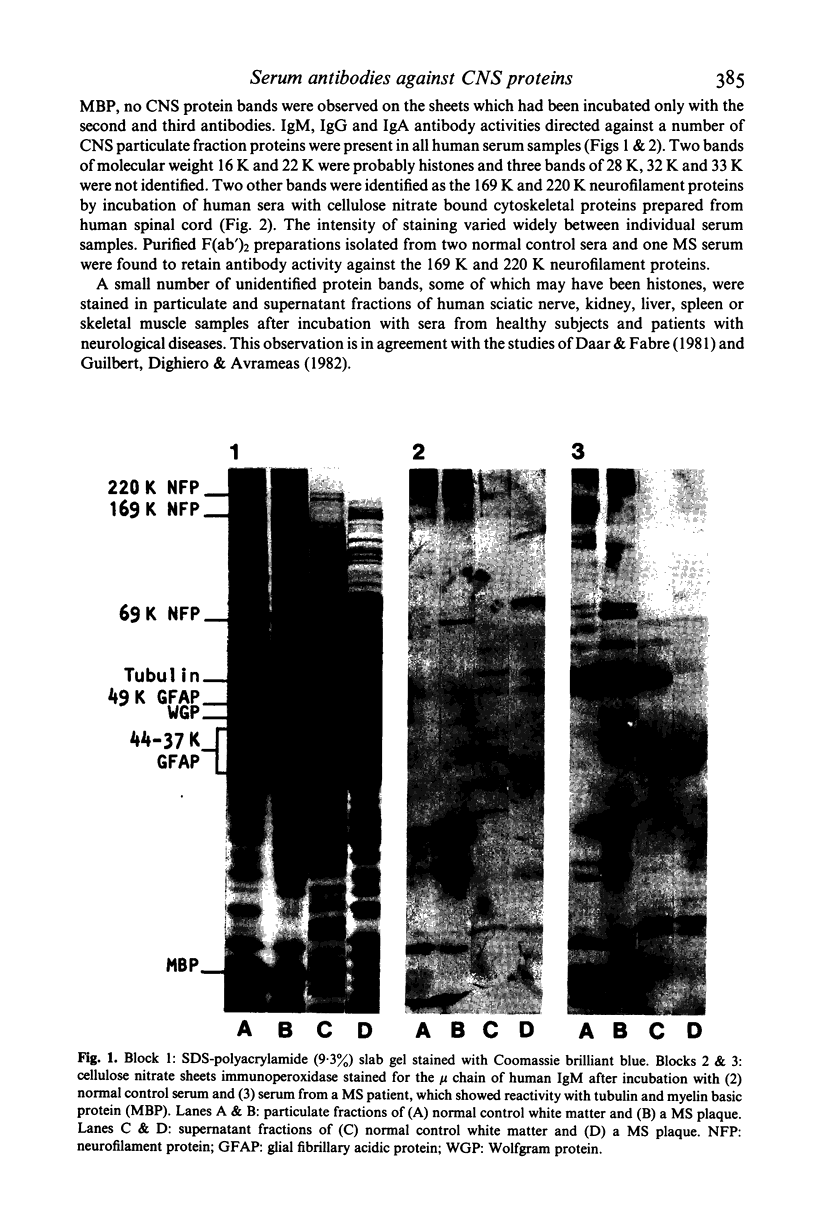
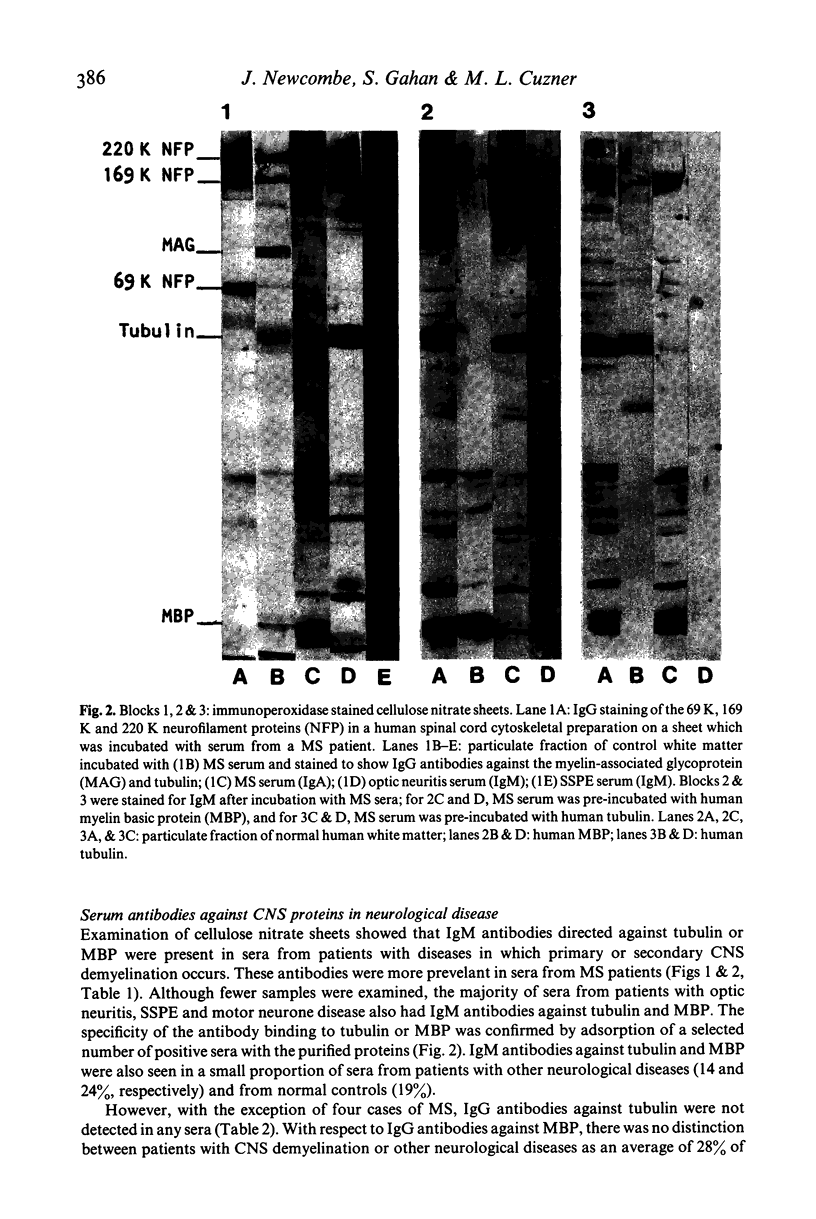



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banik N. L., Davison A. N. Isolation of purified basic protein from human brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Sep;21(3):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb05994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu F. C., Norton W. T., Fields K. L. The cytoskeleton of primary astrocytes in culture contains actin, glial fibrillary acidic protein, and the fibroblast-type filament protein, vimentin. J Neurochem. 1981 Jul;37(1):147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb05302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar A. S., Fabre J. W. Organ-specific IgM autoantibodies to liver, heart and brain in man: generalized occurrence and possible functional significance in normal individuals, and studies in patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jul;45(1):37–47. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn P., Gilbert H., Newcombe J., Cuzner M. L. Rapid analysis of immunoglobulin isoelectric focusing patterns with cellulose nitrate sheets and immunoperoxidase staining. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Jun 11;51(2):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gozes I., Richter-Landsberg C. Identification of tubulin associated with rat brain myelin. FEBS Lett. 1978 Nov 1;95(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabar P. Hypothesis. Auto-antibodies and immunological theories: an analytical review. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Nov;4(4):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilbert B., Dighiero G., Avrameas S. Naturally occurring antibodies against nine common antigens in human sera. I. Detection, isolation and characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2779–2787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyypiä T., Viander M., Reunanen M., Salmi A. Antibodies to nuclear and smooth muscle antigens in multiple sclerosis and control patients. Acta Neurol Scand. 1982 Jun;65(6):629–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1982.tb03116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurki P., Helve T., Virtanen I. Antibodies to cytoplasmic intermediate filaments in rheumatic diseases. J Rheumatol. 1983 Aug;10(4):558–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan S. A., Haire M. The specificity of IgG- and IgM-class smooth muscle antibody in the sera of patients with multiple sclerosis and active chronic hepatitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Oct;14(2):256–263. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead G. M., Cowin P., Whitehouse J. M. Antitubulin antibody in healthy adults and patients with infectious mononucleosis and its relationship to smooth muscle antibody (SMA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Feb;39(2):328–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe J., Cuzner M. L., Röyttä M., Frey H. White matter proteins in multiple sclerosis. J Neurochem. 1980 Mar;34(3):700–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe J., Glynn P., Cuzner M. L. Analysis by transfer electrophoresis of reactivity of IgG with brain proteins in multiple sclerosis. J Neurochem. 1982 Oct;39(4):1192–1194. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb11515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe J., Glynn P., Cuzner M. L. The immunological identification of brain proteins on cellulose nitrate in human demyelinating disease. J Neurochem. 1982 Jan;38(1):267–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb10880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y., Day E. D., Whitacre C. C., Berenberg R. A., Harter D. H. Endogenous myelin basic protein-serum factors (MBP-SFs) and anti-MBP antibodies in humans. Occurrence in sera of clinically well subjects and patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 1981 Oct;52(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(81)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen J. S., Toh B. H., Locarnini S. A., Gust I. D., Shyamala G. N. Autoantibody to intermediate filaments in viral hepatitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Nov;21(2):154–161. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen F., Hjort T. A simple method for the production of F(ab')2 preparations by pepsin digestion of total serum protein. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1980 Oct;88(5):241–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb00101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset B., Bernier-Valentin F., Poncet C., Orgiazzi J., Madec A. M., Monier J. C., Mornex R. Anti-tubulin antibodies in autoimmune thyroid disorders. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 May;52(2):325–332. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo J., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Autoantibodies against axonal neurofilaments in patients with Kuru and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Science. 1980 Oct 10;210(4466):190–193. doi: 10.1126/science.6997994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H., Yildiz A., Sotelo J., Osung O., Holborow E. J., Kanakoudi F., Small J. V. Viral infections and IgM autoantibodies to cytoplasmic intermediate filaments. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):76–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr, Lee J. C. Preparation of tubulin from brain. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):376–385. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Néchaud B., Wolff A., Jeantet C., Bourre J. M. Characterization of tubulin in mouse brain myelin. J Neurochem. 1983 Dec;41(6):1538–1544. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb00861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]