Abstract
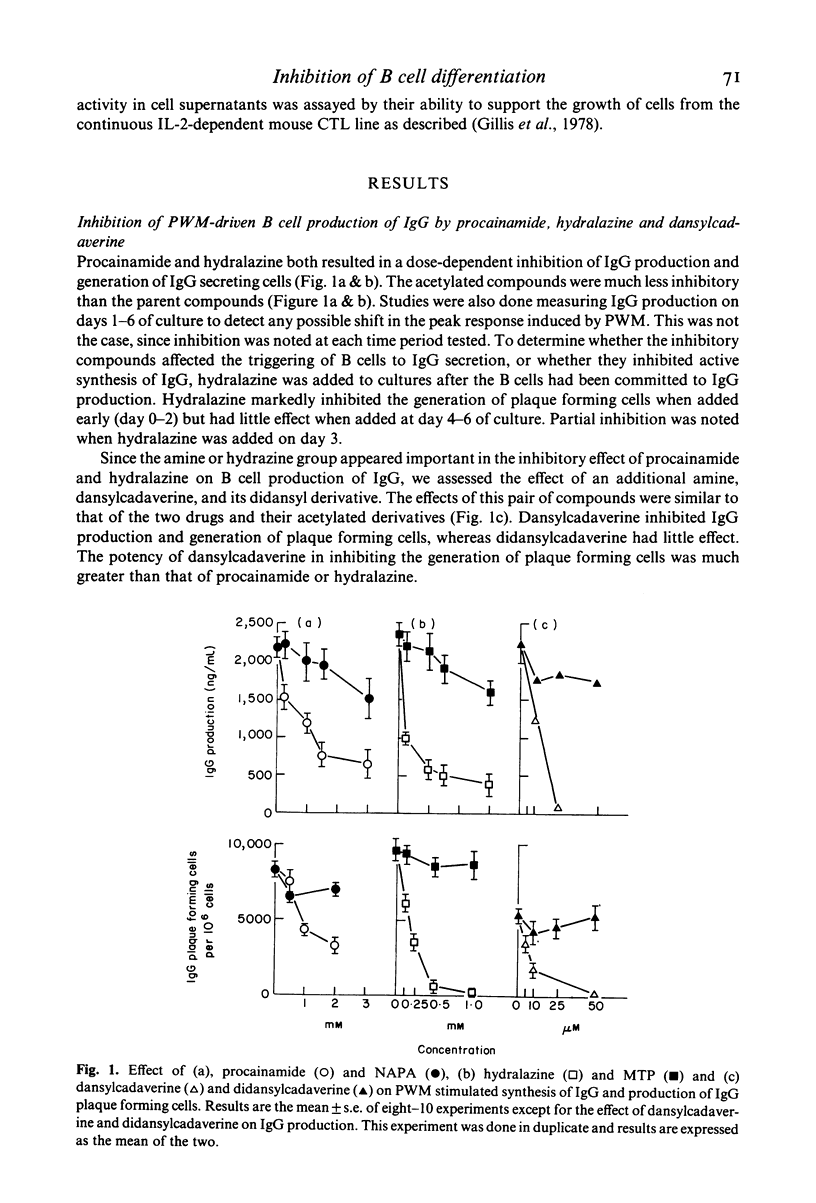
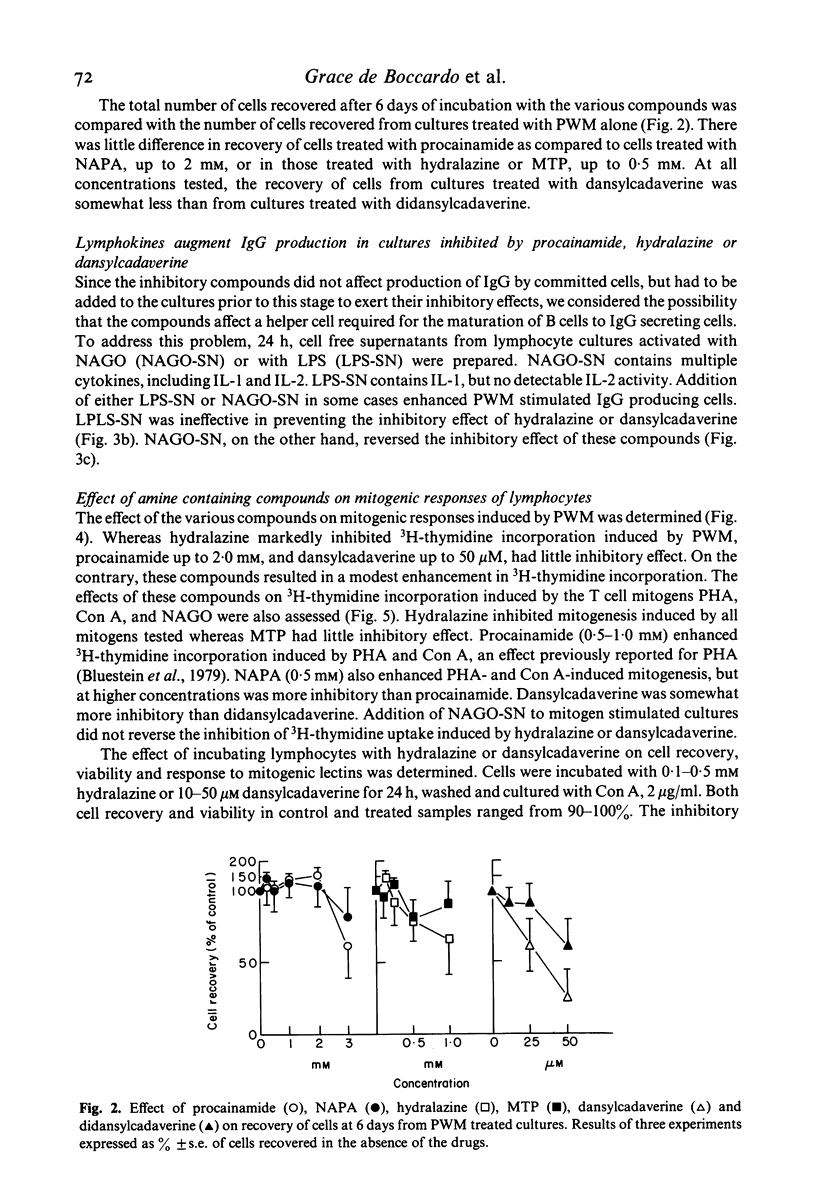
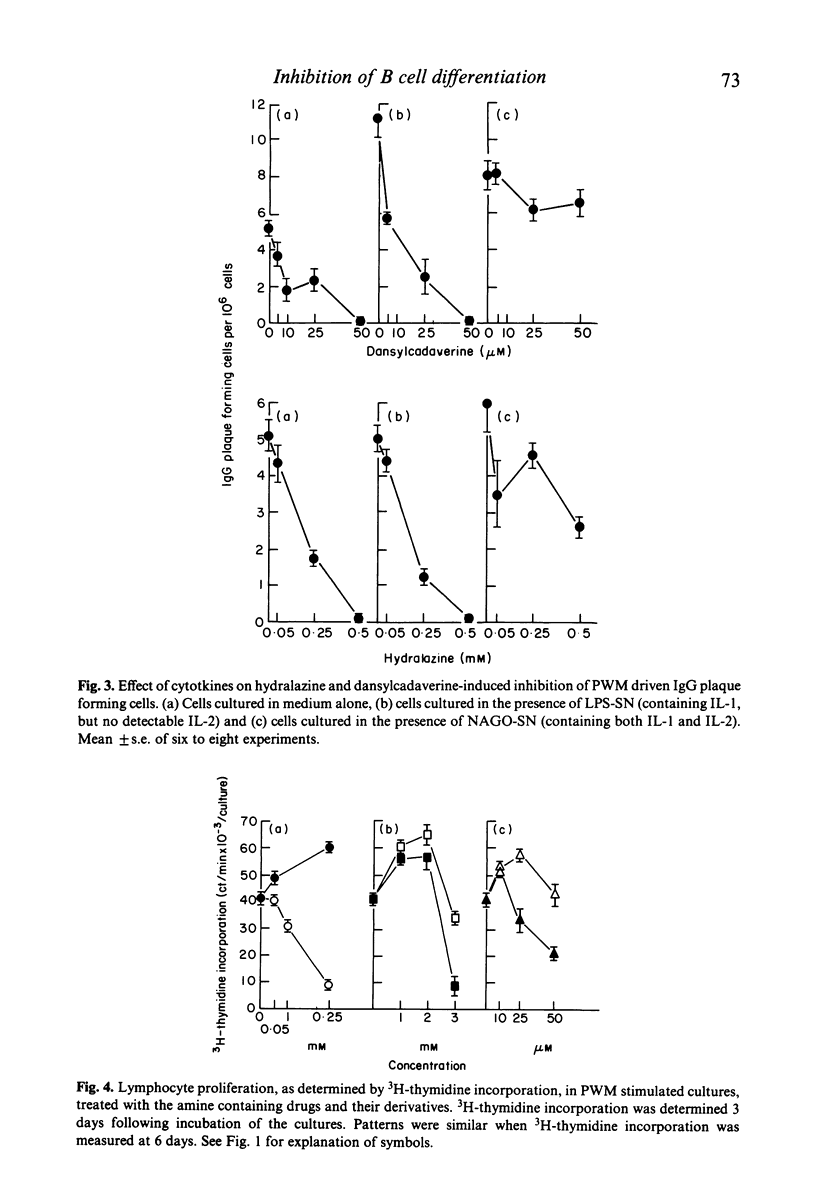
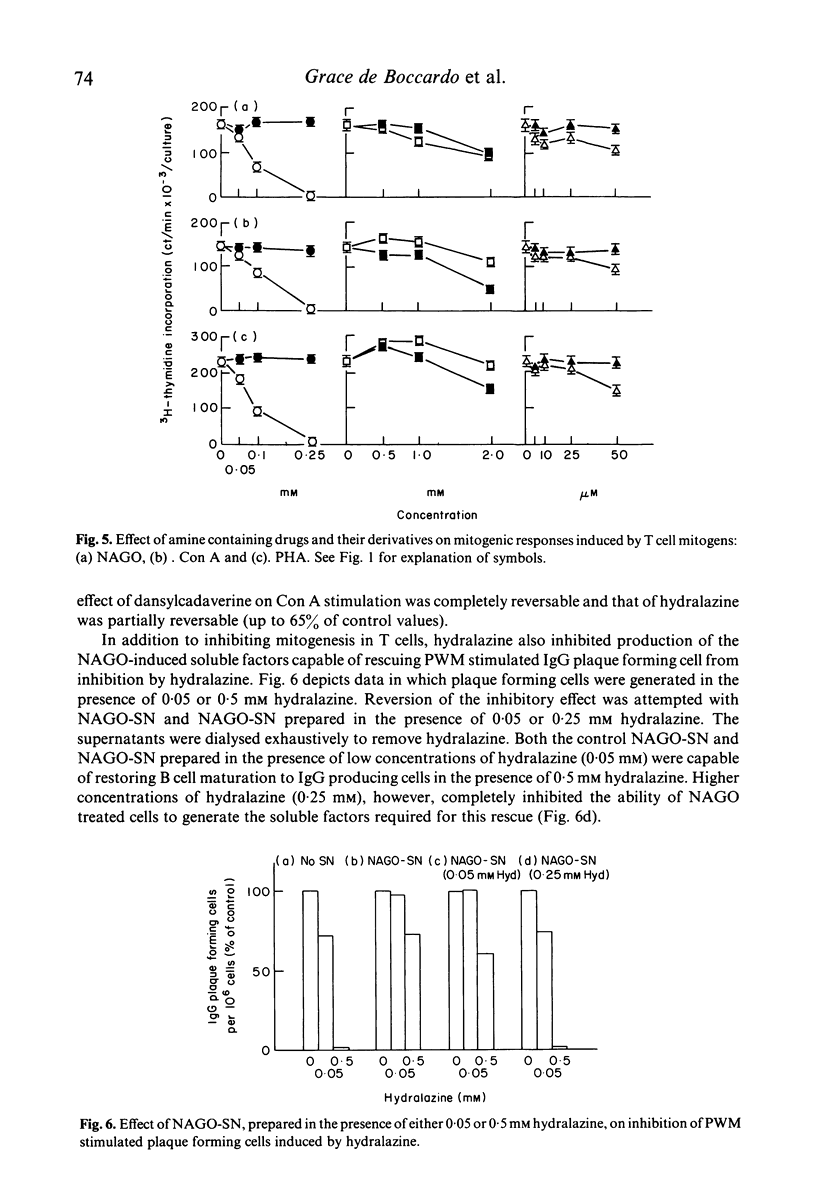
The present study examined the effect of two drugs, which contain either an aromatic amine or hydrazine moiety and are known to induce lupus like syndromes in man (procainamide and hydralazine) and an aliphatic amine (dansylcadaverine), on pokeweed mitogen (PWM)-induced B cell production of immunoglobulin G (IgG). These compounds all inhibited IgG production and generation of IgG plaque forming cells, whereas derivatives of them, without free amine groups, had little or no effect. The compounds inhibited differentiation of B cells to plasma cells, rather than production and secretion of IgG. Mitogen free culture supernatants of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBM) activated by the oxidizing mitogen, neuraminidase and galactose oxidase (NAGO), prevented the inhibition of B cell maturation. Moreover, incubation of NAGO treated PBM with hydralazine prevented the production of soluble factors capable of promoting B cell maturation in the presence of hydralazine. We conclude from these studies that procainamide, hydralazine and dansylcadaverine inhibit PWM-induced B cell maturation to plasma cells by an indirect mechanism, via inhibition of production of lymphokines by helper cells. The primary amine or hydrazine group appears to be required for the inhibitory effect, since analogues of the inhibitory compounds, without primary amine groups, are non-inhibitory.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bluestein H. G., Zvaifler N. J., Weisman M. H., Shapiro R. F. Lymphocyte alteration by procainamide: relation to drug-induced lupus erythematosus syndrome. Lancet. 1979 Oct 20;2(8147):816–819. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLASS C. D., HOGAN R. A metabolite of 1-hydrazinophthalazine (hydralazine). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Mar;100(3):446–448. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayer D. E., Reidenberg M. M. Clinical consequences of polymorphic acetylation of basic drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Sep;22(3):251–258. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977223251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois E. L. Procainamide induction of a systemic lupus erythematosus-like syndrome. Presentation of six cases, review of the literature, and analysis and followup of reported cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 May;48(3):217–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg W. W., Finkelman F. D., Lipsky P. E. Circulating and mitogen-induced immunoglobulin-secreting cells in human peripheral blood: evaluation by a modified reverse hemolytic plaque assay. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):33–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A., Melchers F. A plaque assay for all cells secreting Ig of a given type or class. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Schwartz S. A., Good R. A. Subpopulations of human T lymphocytes. VII. Cellular basis of concanavalin A-induced T cell-mediated suppression of immunoglobulin production by B lymphocytes from normal humans. Cell Immunol. 1979 May;44(2):242–251. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian C., Speck N. A., Pierce S. K. Primary amines inhibit the triggering of B lymphocytes to antibody synthesis. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunde P. K., Frislid K., Hansteen V. Disease and acetylation polymorphism. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1977 May-Jun;2(3):182–197. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197702030-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow M. R., Bardana E. J., Jr, Pirofsky B., Craig S., McLaughlin P. Systemic lupus erythematosus-like syndrome in monkeys fed alfalfa sprouts: role of a nonprotein amino acid. Science. 1982 Apr 23;216(4544):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.7071589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Katchalski E. Induction of lymphocyte transformation by sequential treatment with neuraminidase and galactose oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1824–1827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Quittner S., Rubin A. L., Stenzel K. H. Transglutaminase activity in human lymphocytes: early activation by phytomitogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1157–1161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Stenzel K. H., Rubin A. L. Stimulation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes by periodate, galactose oxidase, soybean agglutinin, and peanut agglutinin: differential effects of adherent cells. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):852–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Suthanthiran M., Saltz B., Newman D., Rubin A. L., Stenzel K. H. Generation of a lymphocyte growth factor by treatment of human cells with neuraminidase and galactose oxidase. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):755–760. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi T., Goldings E. A., Lipsky P. E., Ziff M. Immunomodulatory effect of procainamide in man. Inhibition of human suppressor T-cell activity in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):36–45. doi: 10.1172/JCI110749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry H. M., Jr Late toxicity to hydralazine resembling systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1973 Jan;54(1):58–72. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidenberg M. M., Durant P. J., Harris R. A., De Boccardo G., Lahita R., Stenzel K. H. Lupus erythematosus-like disease due to hydrazine. Am J Med. 1983 Aug;75(2):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stec G. P., Lertora J. J., Atkinson A. J., Jr, Nevin M. J., Kushner W., Jones C., Schmid F. R., Askenazi J. Remission of procainamide-induced lupus erythematosus with N-acetylprocainamide therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1979 May;90(5):799–801. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-5-799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woosley R. L., Drayer D. E., Reidenberg M. M., Nies A. S., Carr K., Oates J. A. Effect of acetylator phenotype on the rate at which procainamide induces antinuclear antibodies and the lupus syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1978 May 25;298(21):1157–1159. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197805252982101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


