Abstract
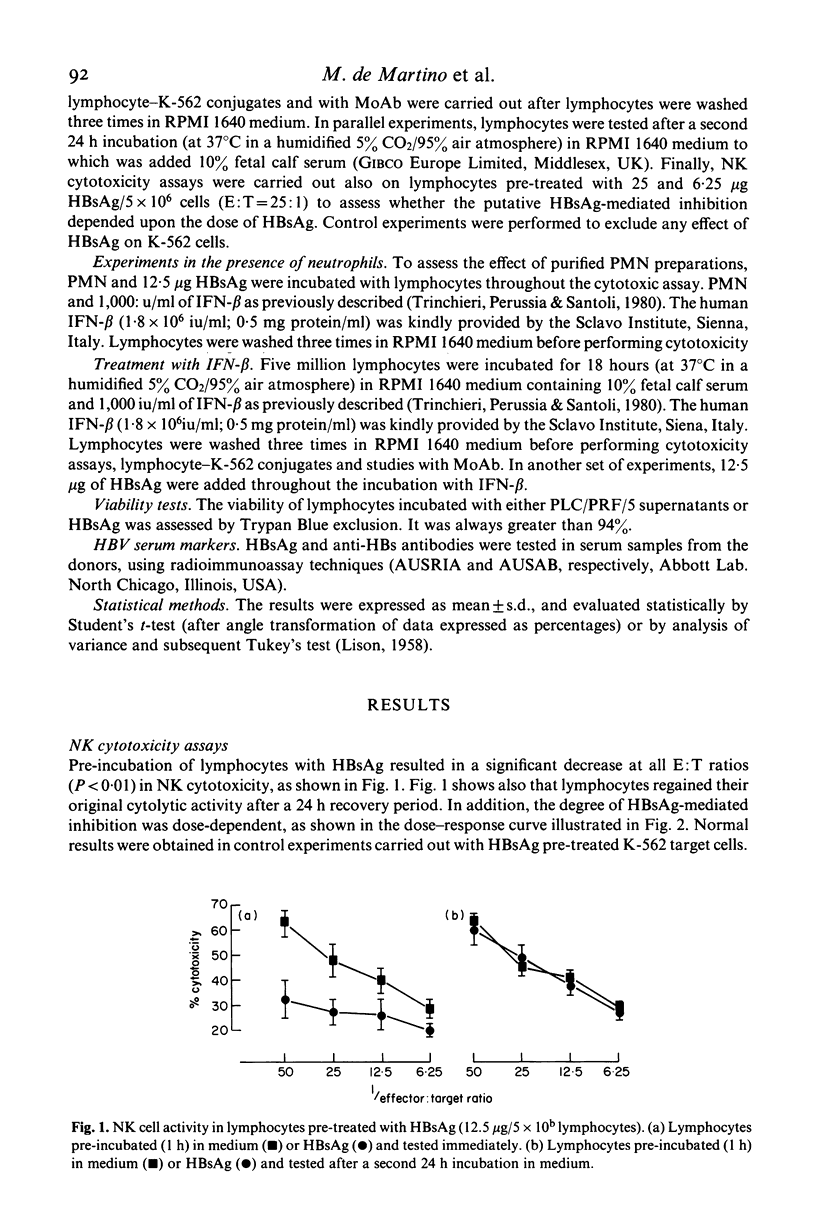
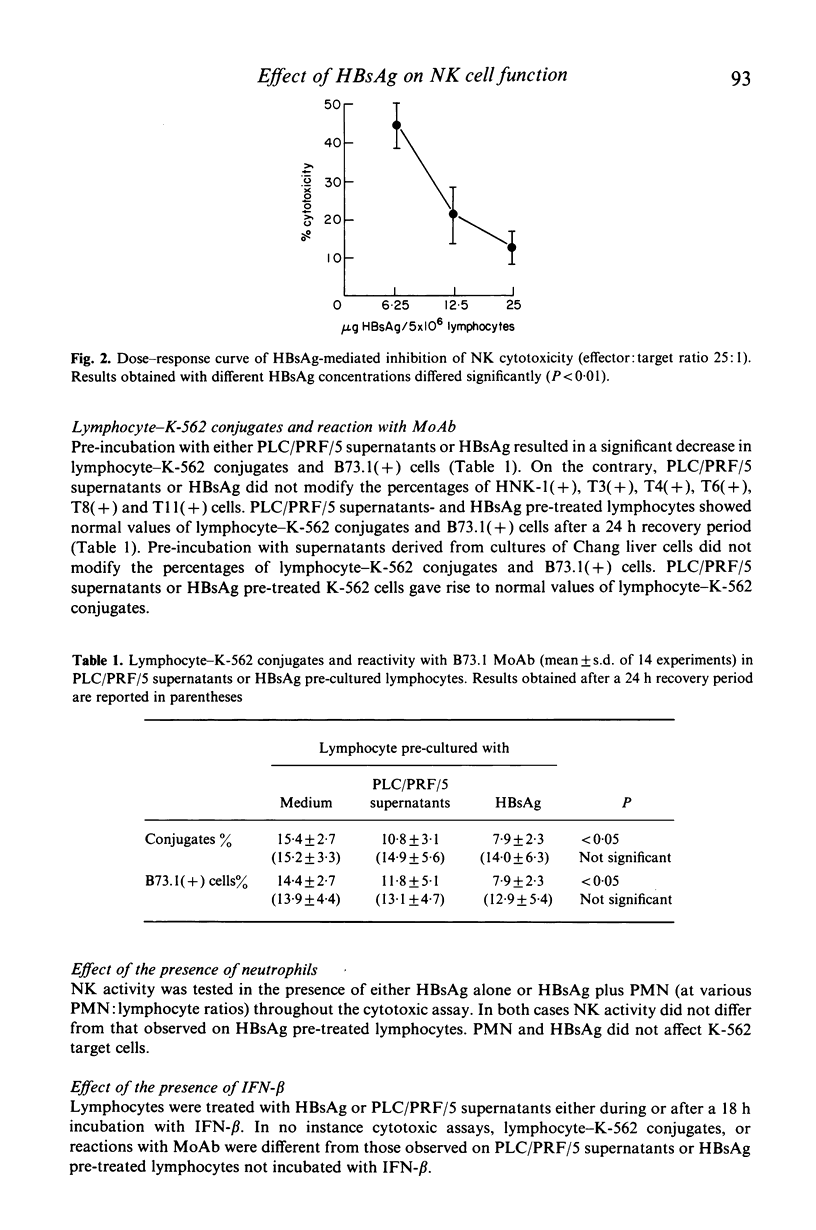
The influence of purified hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) preparations or of supernatants derived from PLC/PRF/5 cell line (which produces HBsAg) on human natural killer (NK) activity was examined. Lymphocytes pre-incubated with HBsAg and subsequently washed showed a significant decrease in NK cytotoxicity against K-562 target cells. This effect was reversible and dose-dependent. In addition, pre-incubation with either HBsAg or PLC/PRF/5 supernatants inhibited in a reversible manner lymphocyte--K-562 conjugates and the binding of B73.1 monoclonal antibody (MoAb), which recognizes Fc receptors on NK cells. This effect was not observed with HNK-1, T3, T4, T6, T8 and T11 MoAb. HBsAg was non-toxic to lymphocytes, and ineffective with K-562 target cells. Beta-interferon did not modify HBsAg-mediated inhibition, when added either before or during the contact with HBsAg. Moreover, no modification was observed when neutrophils (at various neutrophil:lymphocyte ratios) were added, even though HBsAg is known to stimulate neutrophils to produce oxygen radicals which may modulate NK activity. We speculate that HBsAg produces these effects by reacting into receptor sites (possibly Fc receptor sites) on NK cell membrane. The overall significance of our results in relation to hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiuti F., Quinti I., Seminara R., Sirianni M. C., Vierucci A., Abo T., Cooper M. D. Usefulness of monoclonal antibodies in the diagnosis and monitoring of patients with primary immunodeficiencies: combined experience in three clinical immunology centers. Diagn Immunol. 1983;1(3):188–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. A., Rees R. C., Oxford J. Modulation of human natural killer cytotoxicity by influenza virus and its subunit protein. Immunology. 1984 Aug;52(4):687–695. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron C. A., Welsh R. M. Activation and role of natural killer cells in virus infections. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1982;170(3):155–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02298196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin T. W., Hollinger F. B., Rich R. R., Troisi C. L., Dreesman G. R., Melnick J. L. Cytotoxicity by NK-like cells from hepatitis B-immune patients to a human hepatoma cell line secreting HBsAg. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Bhan A. K. Enhanced in vitro cell-mediated cytotoxicity in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: absence of specificity for virus-expressed antigen on target cell membranes. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2269–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobloug J. H., Førre O., Kvien T. K., Egeland T., Degré M. Natural killer (NK) cell activity of peripheral blood, synovial fluid, and synovial tissue lymphocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Oct;41(5):490–494. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.5.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiki A. T., Lozzio B. B., Wust C. J., Lozzio C. B. Relationship between the Fc receptor for IgG and the specific associated antigen of the pluripotential leukaemia cell line, K-562. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Nov;50(2):360–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Zaytoun A. M., Lee J. H., Jr Mechanisms of human cell-mediated cytotoxicity. III. Dependence of natural killing on microtubule and microfilament integrity. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2816–2825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay H. D., Smith D. L. Regulation of human lymphocyte-mediated natural killer (NK) cell activity. I. Inhibition in vitro by peripheral blood granulocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):475–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keong A., Herman J., Rabson A. R. Supernatant derived from a human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (PLC/PRF/5) depresses natural killer (NK) cell activity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1983;15(3):183–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00199162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Starr S., Abraham S., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Human natural killer cells analyzed by B73.1, a monoclonal antibody blocking Fc receptor functions. I. Characterization of the lymphocyte subset reactive with B73.1. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2133–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaman W. E., Gindhart T. D., Blackman M. A., Dalal B., Talal N., Werb Z. Suppression of natural killing in vitro by monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes: requirement for reactive metabolites of oxygen. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):876–888. doi: 10.1172/JCI110527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toy J. L. The interferons. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):1–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierucci A., De Martino M., Graziani E., Rossi M. E., London W. T., Blumberg B. S. A mechanism for liver cell injury in viral hepatitis: effects of hepatitis B virus on neutrophil function in vitro and in children with chronic active hepatitis. Pediatr Res. 1983 Oct;17(10):814–820. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198310000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierucci A., London W. T., De Martino M., Blumberg B. S. Neutrophil function in children who are carriers of hepatitis-B surface antigen. Lancet. 1977 Jan 22;1(8004):157–160. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91761-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierucci A., de Martino M., Rossi M. E., Vullo C., Borgatti L., London W. T., Blumberg B. S. Raised IgE levels in beta-thalassaemia: correlation with splenectomy and hepatitis B virus infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Oct;58(1):199–205. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


