Abstract
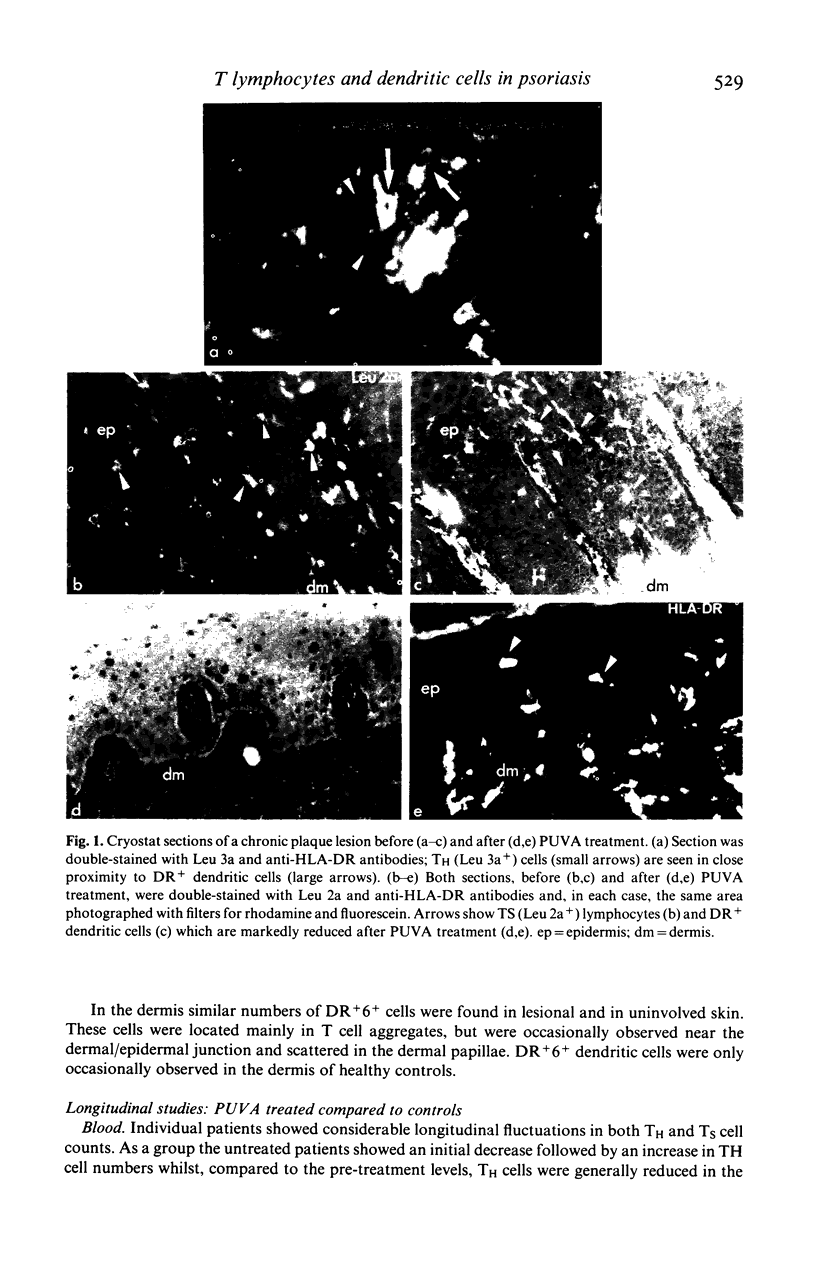
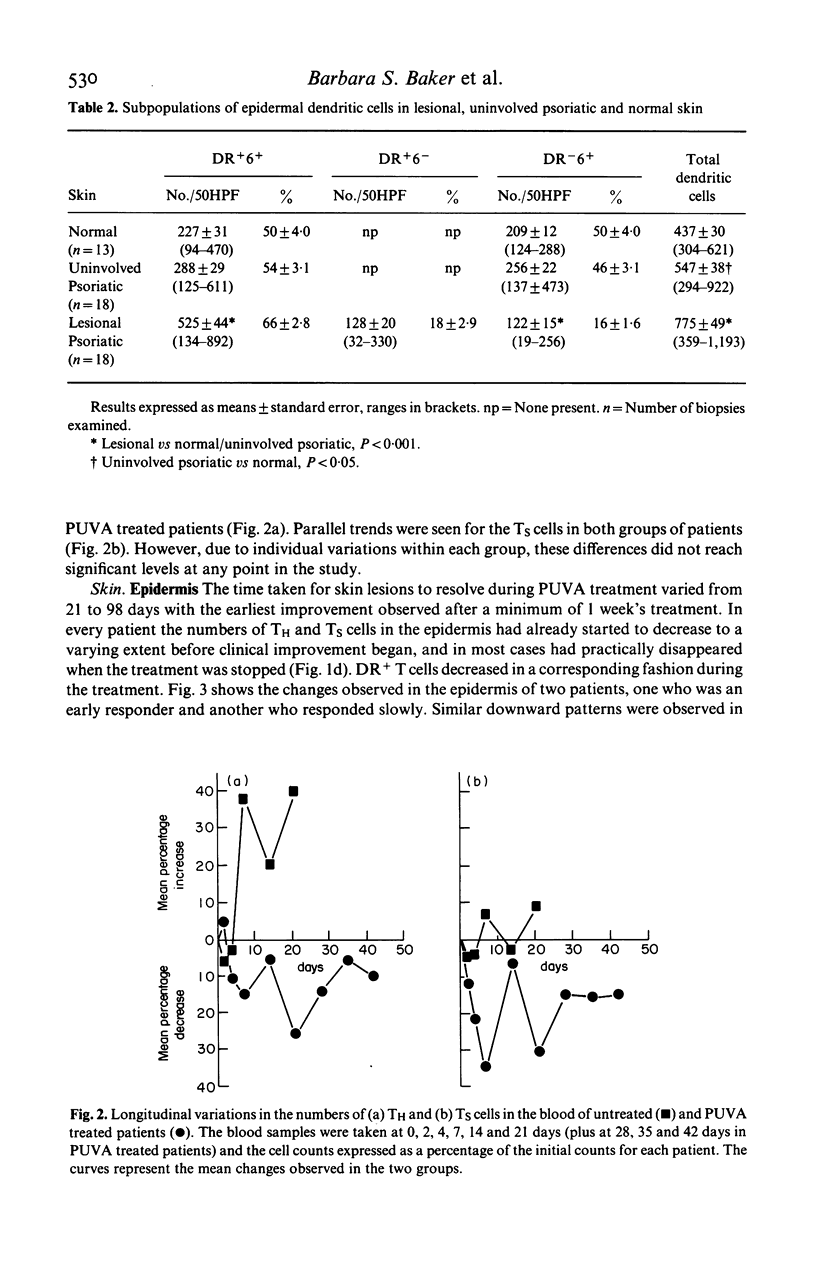
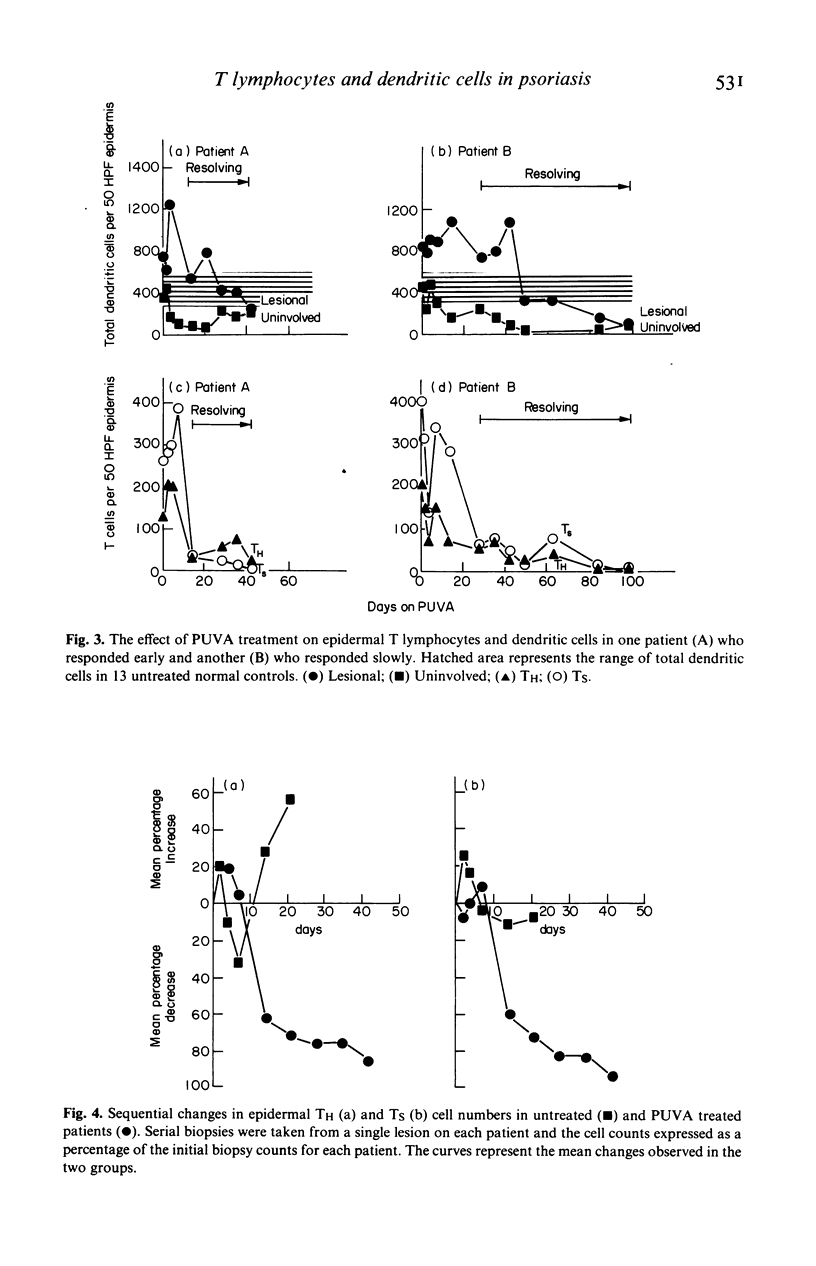
The numbers and HLA-DR expression of T cell subsets and dendritic cells in chronic psoriatic plaques were compared to previously reported findings in spontaneously resolving guttate lesions, and the effects of PUVA treatment on these cell populations studied. The chronic lesions showed a similar T helper/T suppressor (TH/TS) ratio (0.66 +/- 0.10) to resolving guttate lesions. However, in contrast to the resolving lesions which do not contain activated epidermal TH cells, a substantial proportion of the TH cells in the persistent plaques were DR+. Moreover, these persistent lesions contained markedly increased numbers of DR+ dendritic cells, approximately 20% of which were T6 negative. PUVA-induced resolution of chronic lesions was associated with depletion of epidermal TH and TS cells, and a subsequent reduction in DR+ dendritic cells. In each patient the rate of disappearance of both cell types correlated with the rate of resolution. Furthermore, the epidermal T cell depletion preceded the onset of clinical improvement. In contrast, significant reduction of the dendritic cells was generally not observed until the lesions were largely resolved. Dendritic cells decreased faster in uninvolved than in lesional skin and to a subnormal level. Dermal T cells also decreased during PUVA therapy but this did not show any obvious correlation with resolution of the lesions. Blood T cell levels were not significantly affected by the treatment. These findings support the concept that the initiation and maintenance of the psoriatic process requires activation of TH cells in the epidermis via interaction with antigen presenting cells. Furthermore PUVA treatment may clear psoriasis by interfering with such a mechanism through its effects on T lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF


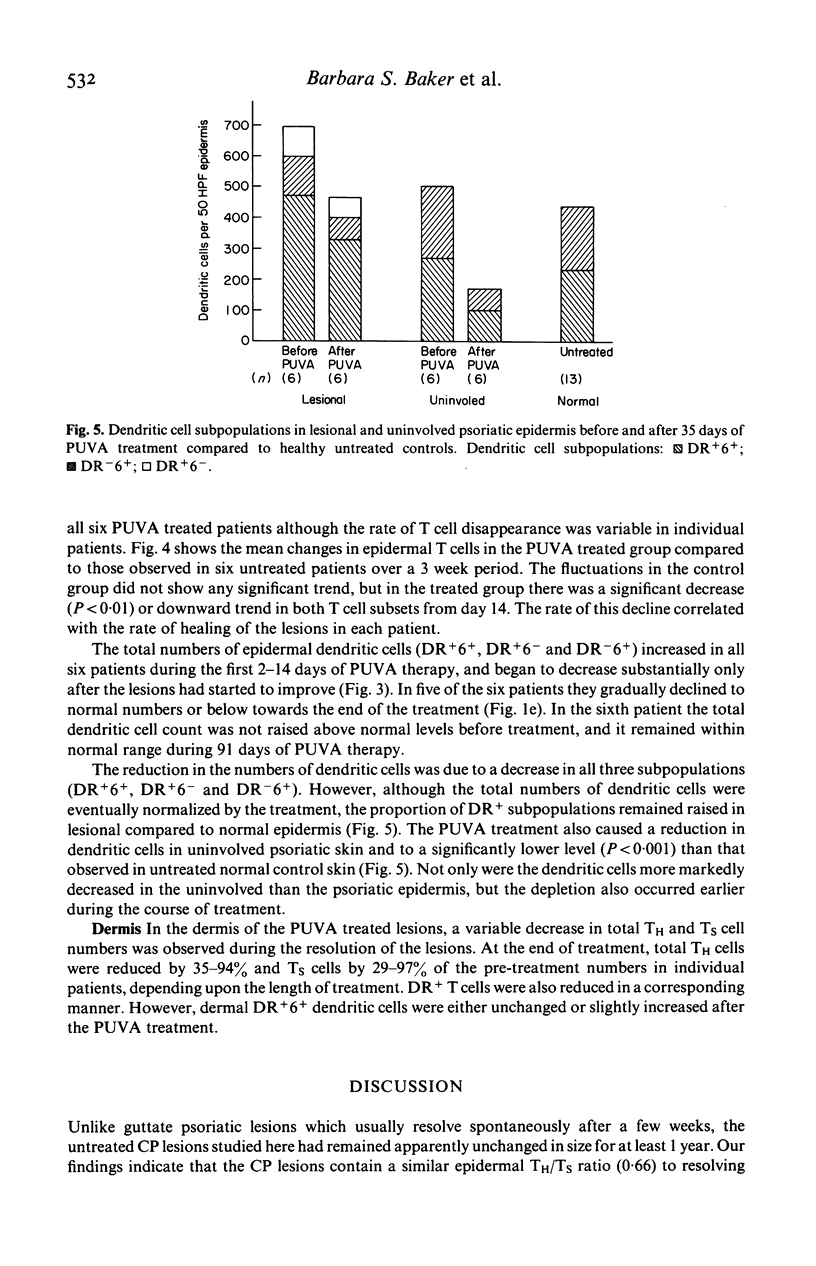


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aberer W., Schuler G., Stingl G., Hönigsmann H., Wolff K. Ultraviolet light depletes surface markers of Langerhans cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Mar;76(3):202–210. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12525745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S., Swain A. F., Fry L., Valdimarsson H. Epidermal T lymphocytes and HLA-DR expression in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1984 May;110(5):555–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1984.tb04678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S., Swain A. F., Valdimarsson H., Fry L. T-cell subpopulations in the blood and skin of patients with psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1984 Jan;110(1):37–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1984.tb07309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerke J. R., Krogh H. K., Matre R. Characterization of mononuclear cell infiltrates in psoriatic lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Nov;71(5):340–343. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12529841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. D., Hulsebosch H. J., Krieg S. R., Bakker P. M., Cormane R. H. Immunocompetent cells in psoriasis. In situ immunophenotyping by monoclonal antibodies. Arch Dermatol Res. 1983;275(3):181–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00510050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickell P. M., McConnell I., Milstein C., Wright B. A monoclonal antibody to the HLA-DR product recognizes a polymorphic Ia determinant in mice. Immunology. 1981 Jul;43(3):493–501. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fithian E., Kung P., Goldstein G., Rubenfeld M., Fenoglio C., Edelson R. Reactivity of Langerhans cells with hybridoma antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2541–2544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann P. S. Disappearance of epidermal Langerhans cells during PUVA therapy. Br J Dermatol. 1981 Aug;105(2):219–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1981.tb01209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haftek M., Gliński W., Jabłońska S., Obałek S. T lymphocyte E rosette function during photochemotherapy (PUVA) of psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 May;72(5):214–218. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12530762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton J. E., Raisz L. G., Simmons H. A., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. Bone resorbing activity in supernatant fluid from cultured human peripheral blood leukocytes. Science. 1972 Sep 1;177(4051):793–795. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4051.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korszun A. K., Wilton J. M., Johnson N. W. The in vivo effects of lymphokines on mitotic activity and keratinization in guinea pig epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Jun;76(6):433–437. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12521027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maini R. N., Bryceson A. D., Wolstencroft R. A., Dumonde D. C. Lymphocyte mitogenic factor in man. Nature. 1969 Oct 4;224(5214):43–44. doi: 10.1038/224043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melski J. W., Tanenbaum L., Parrish J. A., Fitzpatrick T. B., Bleich H. L. Oral methoxsalen photochemotherapy for the treatment of psoriasis: a cooperative clinical trial. J Invest Dermatol. 1977 Jun;68(6):328–335. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12496022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morhenn V. B., Benike C. J., Engleman E. G. Inhibition of cell mediated immune responses by 8-methoxypsoralen and long-wave ultraviolet light: a possible explanation for the clinical effects of photoactivated psoralen. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Sep;75(3):249–252. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12523271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morison W. L., Wimberly J., Parrish J. A., Bloch K. J. Abnormal lymphocyte function following long-term PUVA therapy for psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1983 Apr;108(4):445–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1983.tb04597.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscicki R. A., Morison W. L., Parrish J. A., Bloch K. J., Colvin R. B. Reduction of the fraction of circulating helper-inducer T cells identified by monoclonal antibodies in psoriatic patients treated with long-term psoralen/ultraviolet-A radiation (PUVA). J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Sep;79(3):205–208. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12500058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. F., Bhan A. K., Sato S., Mihm M. C., Jr, Harrist T. J. A new immunologic marker for human Langerhans cells. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 26;304(13):791–792. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103263041320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund J. J., Ackles A. E., Lerner A. B. The effects of ultraviolet light and certain drugs on La-bearing Langerhans cells in murine epidermis. Cell Immunol. 1981 May 1;60(1):50–63. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G., Lewis M. G. Langerhans cells: involvement in the pathogenesis of mycosis fungoides. Br J Dermatol. 1976 Dec;95(6):665–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1976.tb07044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Nogueira N., Witmer M. D., Tydings J. D., Mellman I. S. Lymphokine enhances the expression and synthesis of Ia antigens on cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1248–1261. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Wolff K., Diem E., Baumgartner G., Knapp W. In situ identification of lymphoreticular cells in benign and malignant infiltrates by membrane receptor sites. J Invest Dermatol. 1977 Aug;69(2):231–235. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12506348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Janossy G., Graham-Brown R. A., Kung P. C., Goldstein G. The relationship between T lymphocyte subsets and Ia-like antigen positive nonlymphoid cells in early stages of cutaneous T cell lymphoma. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Feb;78(2):169–176. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12506339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Wahl L. M., McCarthy J. B. Lymphocyte-mediated activation of fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):942–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]