Abstract
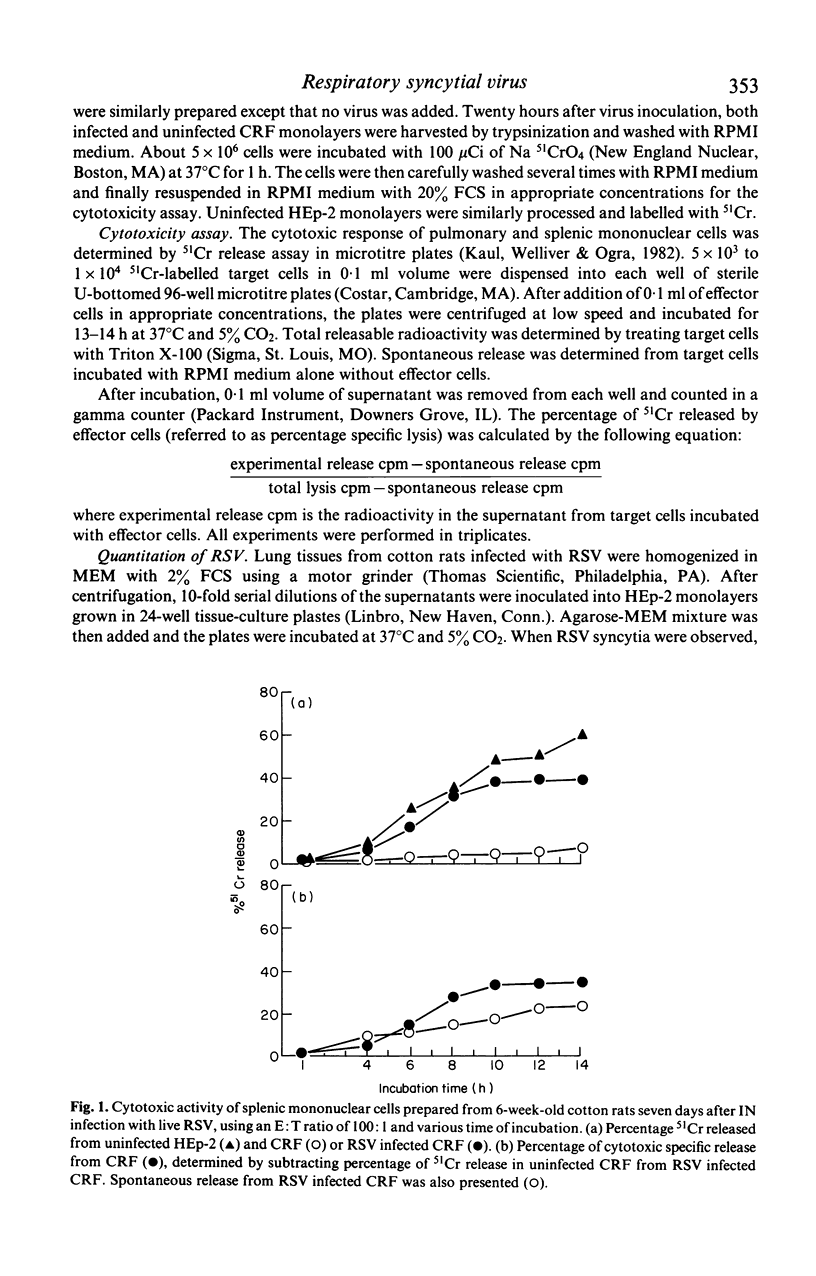
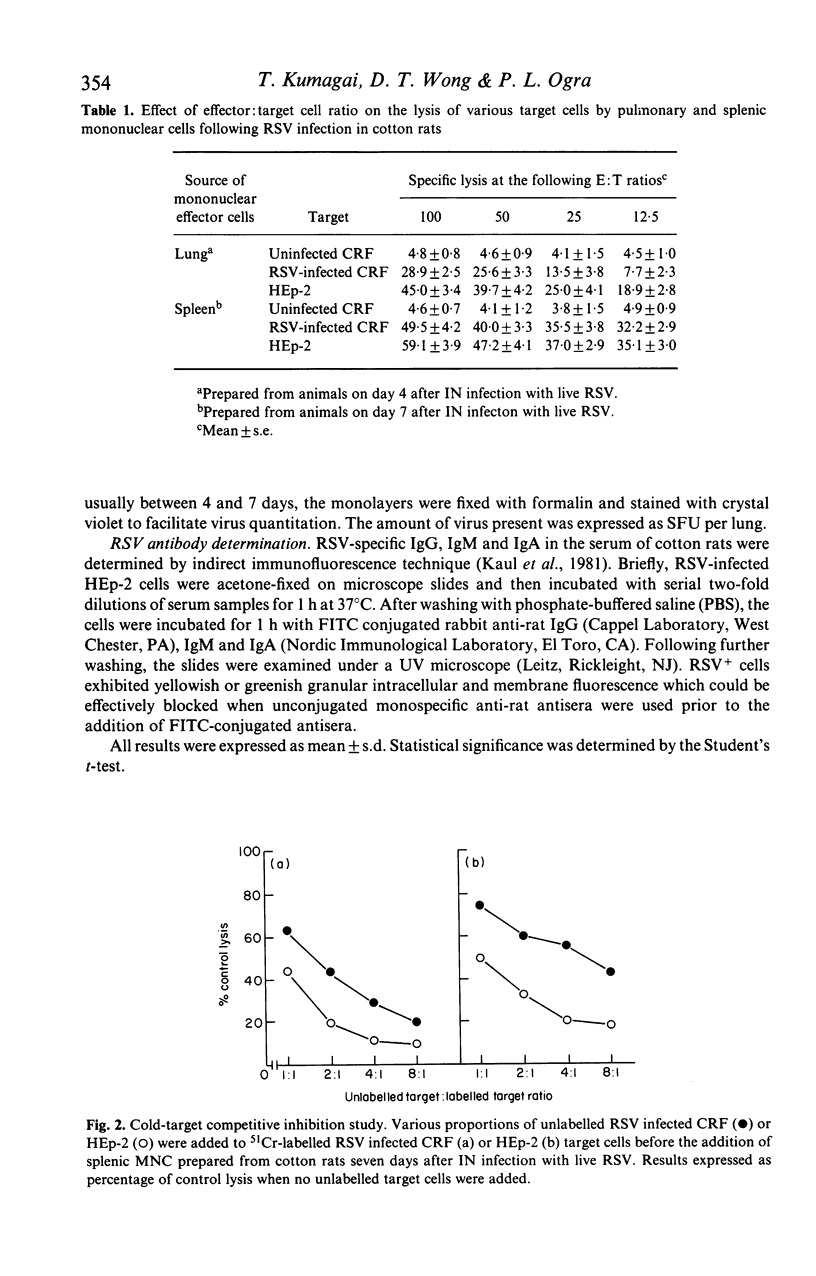
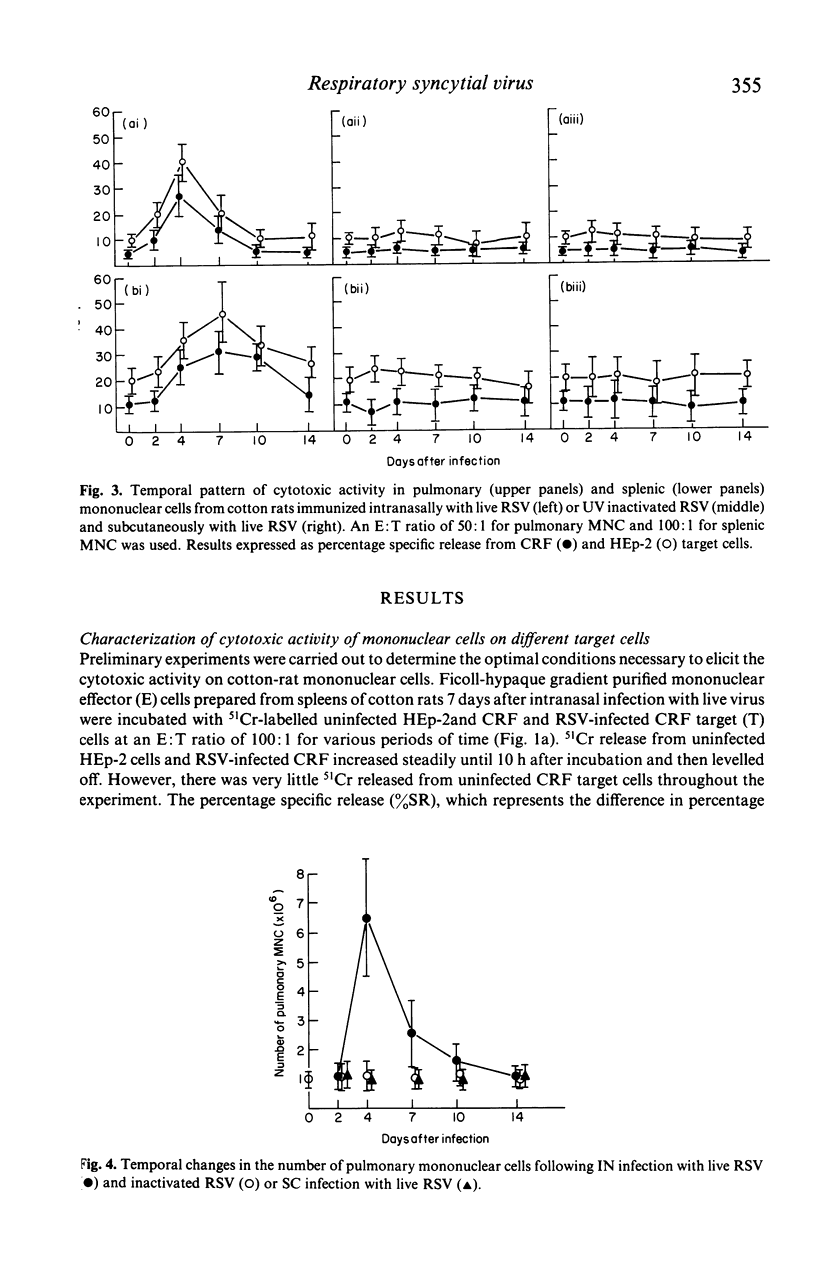
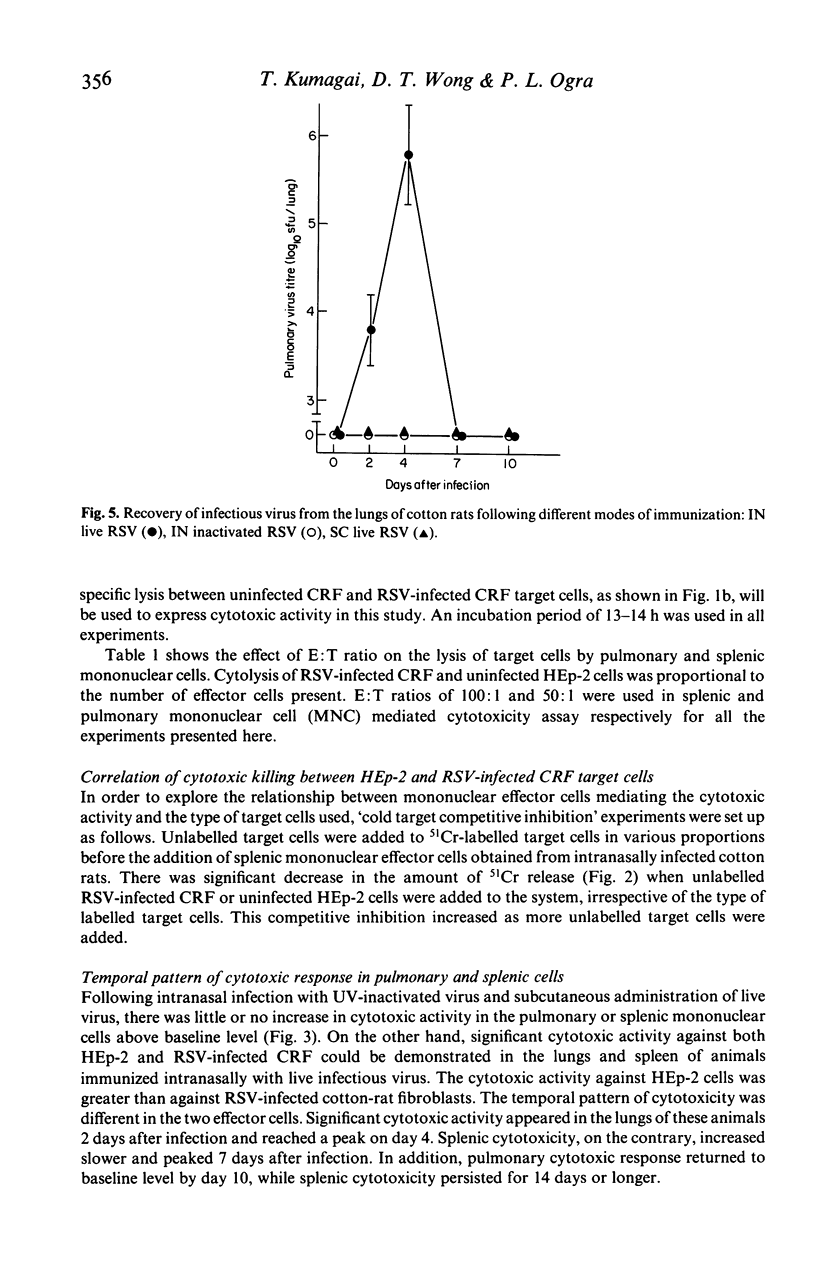
The development of natural killer cell and other antibody-independent cellular cytotoxic response to RSV were studied in splenic and pulmonary mononuclear effector cells obtained from groups of 6-week-old cotton rats after subcutaneous (SC) or intranasal (IN) immunization with live virulent or ultra-violet (UV) inactivated respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). No virus-induced cytotoxic activity was observed after SC immunization with live virus or IN inoculation of inactivated non-infectious virus. On the other hand significant cytotoxic activity was observed after IN infection with live RSV. The peak responses appeared on day 4 in the pulmonary cells and on day 7 in the splenic mononuclear cells. These cytotoxic activities declined to baseline levels 10 and 15 days after immunization in pulmonary and splenic cells respectively. In addition, the amount of 51Cr released was significantly reduced when unlabelled 'cold' HEp-2 cells were added to 51Cr-labelled RSV-infected CRF target cells and vice versa in the cytotoxic assay. It is suggested that viral replication at the mucosal site is essential for the induction of local as well as systemic cytotoxic activity following RSV infection. The development of such cellular reactivity may be important in the elimination of RSV following human infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruhn F. W., Yeager A. S. Respiratory syncytial virus in early infancy. Circulating antibody and the severity of infection. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Feb;131(2):145–148. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120150027004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J., Magoffin R. L., Shearer L. A., Schieble J. H., Lennette E. H. Field evaluation of a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine and a trivalent parainfluenza virus vaccine in a pediatric population. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Apr;89(4):449–463. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching C., Lopez C. Natural killing of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected target cells: normal human responses and influence of antiviral antibody. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):49–56. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.49-56.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishaut M., Tubergen D., McIntosh K. Cellular response to respiratory viruses with particular reference to children with disorders of cell-mediated immunity. J Pediatr. 1980 Feb;96(2):179–186. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80799-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glezen W. P., Paredes A., Allison J. E., Taber L. H., Frank A. L. Risk of respiratory syncytial virus infection for infants from low-income families in relationship to age, sex, ethnic group, and maternal antibody level. J Pediatr. 1981 May;98(5):708–715. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80829-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul T. N., Welliver R. C., Ogra P. L. Development of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in the respiratory tract after natural infection with respiratory syncytial virus. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):492–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.492-498.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul T. N., Welliver R. C., Wong D. T., Udwadia R. A., Riddlesberger K., Ogra P. L. Secretory antibody response to respiratory syncytial virus infection. Am J Dis Child. 1981 Nov;135(11):1013–1016. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1981.02130350017007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. W., Canchola J. G., Brandt C. D., Pyles G., Chanock R. M., Jensen K., Parrott R. H. Respiratory syncytial virus disease in infants despite prior administration of antigenic inactivated vaccine. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Apr;89(4):422–434. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morag A., Beutner K. R., Morag B., Ogra P. L. Development and characteristics of in-vitro correlates of cellular immunity to rubella virus in the systemic and mucosal sites in guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1703–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott R. H., Kim H. W., Arrobio J. O., Hodes D. S., Murphy B. R., Brandt C. D., Camargo E., Chanock R. M. Epidemiology of respiratory syncytial virus infection in Washington, D.C. II. Infection and disease with respect to age, immunologic status, race and sex. Am J Epidemiol. 1973 Oct;98(4):289–300. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Horswood R. L., Camargo E., Koenig D., Chanock R. M. Mechanisms of immunity to respiratory syncytial virus in cotton rats. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):81–87. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.81-87.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Jenson A. B., Horswood R. L., Camargo E., Chanock R. M. The pathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus infection in cotton rats. Am J Pathol. 1978 Dec;93(3):771–791. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R., Kaul A., Scott M., Chiba Y., Ogra P. L. Development of in vitro correlates of cell-mediated immunity to respiratory syncytial virus infection in humans. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jun;137(6):810–817. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.6.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun C. S., Wyde P. R., Wilson S. Z., Knight V. Cell-mediated cytotoxic responses in lungs of cotton rats infected with respiratory syncytial virus. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Apr;127(4):460–464. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.4.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welliver R. C., Kaul A., Ogra P. L. Cell-mediated immune response to respiratory syncytial virus infection: relationship to the development of reactive airway disease. J Pediatr. 1979 Mar;94(3):370–375. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80573-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



