Abstract
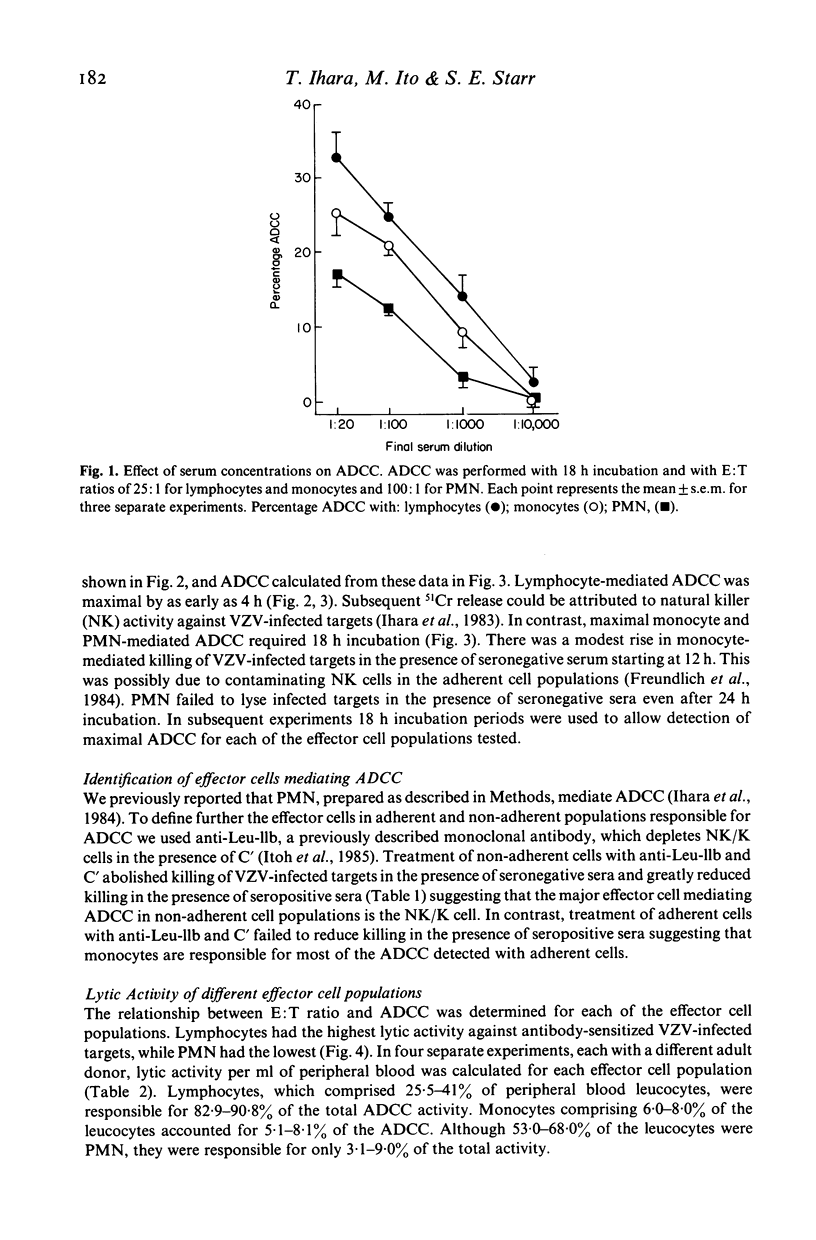
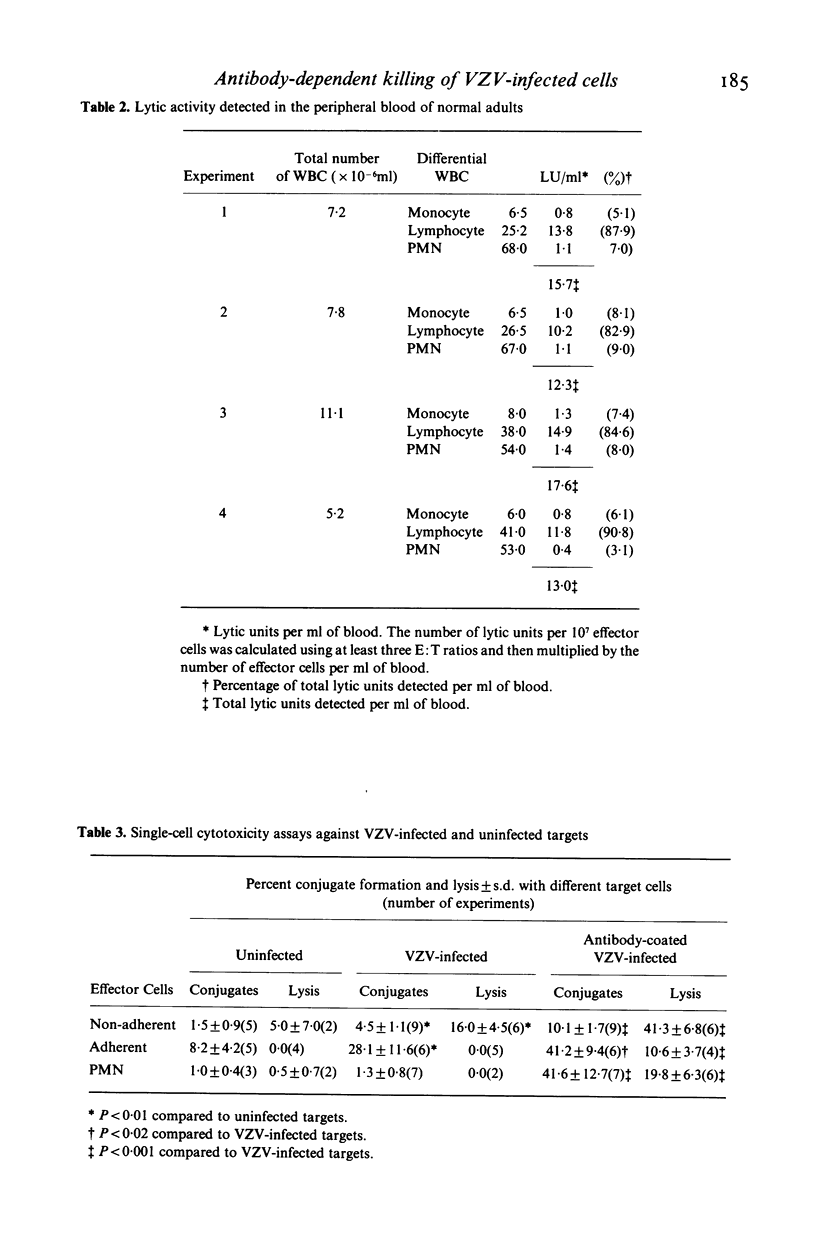
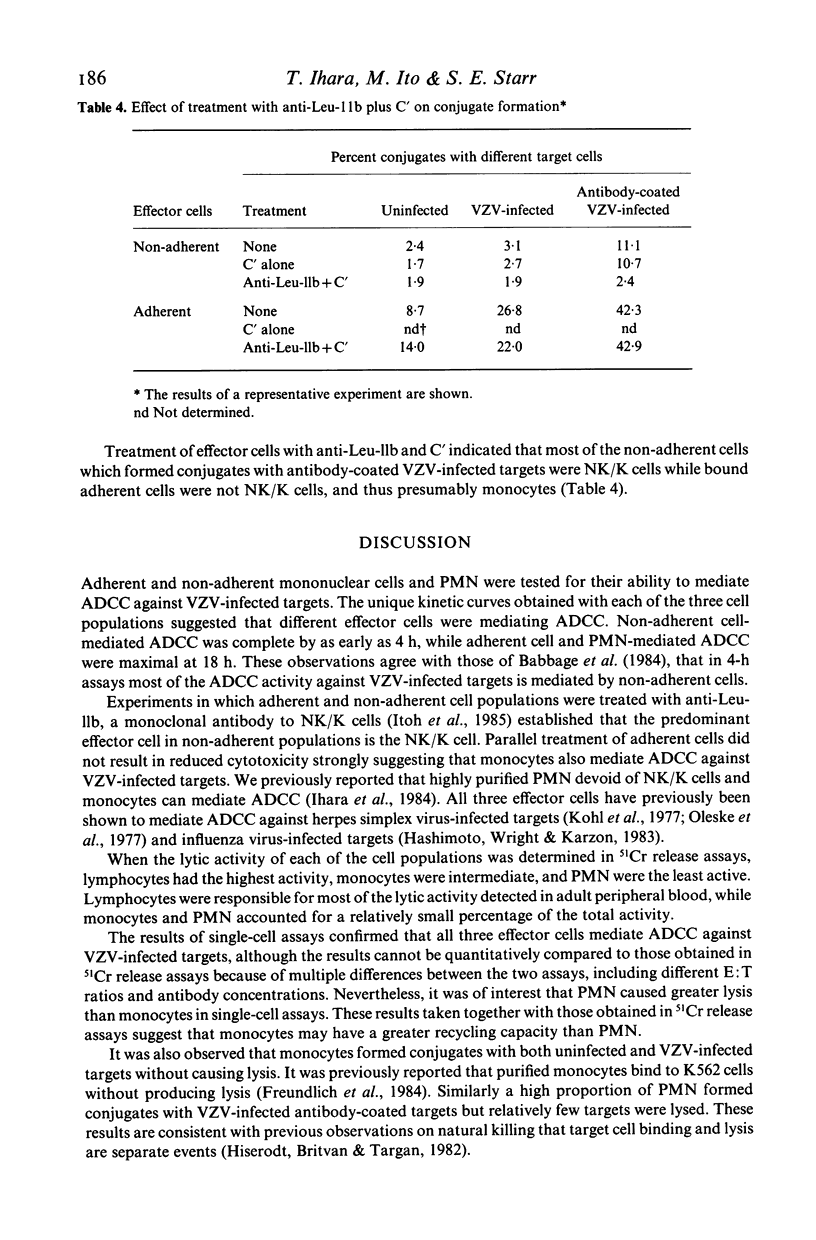
The ability of lymphocytes, monocytes and polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMN) to mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) against varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infected fibroblasts was tested in 51Cr release and single-cell assays. Lymphocytes had the greatest lytic activity, monocytes were intermediate in activity and PMN were the least active. Lymphocyte-mediated ADCC was complete by as early as 4 h, while maximal monocyte and PMN-mediated ADCC required 18 h. In single-cell assays, monocytes formed conjugates with both uninfected and VZV-infected targets, but did not cause lysis. PMN failed to bind or lyse either target. Few lymphocytes formed conjugates with uninfected targets, while a higher percentage bound to VZV-infected targets and caused lysis. In the presence of human antibodies to VZV conjugate formation and lysis of VZV-infected targets was significantly increased with each of the effector-cell populations. Lymphocytes had the highest lytic activity in single-cell assays as well as in 51Cr release assays, and were responsible for most of the ADCC detected in adult peripheral blood against VZV-infected targets.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. K., Douglas S. D. Purification of human monocytes on microexudate-coated surfaces. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1372–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babbage J., Sigfusson A., Souhami R. L. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity to Varicella zoster. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Oct;58(1):217–222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Optimal conditions for simultaneous purification of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leucocytes from human blood by the Hypaque-Ficoll method. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(2):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich B., Trinchieri G., Perussia B., Zurier R. B. The cytotoxic effector cells in preparations of adherent mononuclear cells from human peripheral blood. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1255–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto G., Wright P. F., Karzon D. T. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against influenza virus-infected cells. J Infect Dis. 1983 Nov;148(5):785–794. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.5.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiserodt J. C., Britvan L. J., Targan S. R. Characterization of the cytolytic reaction mechanism of the human natural killer (NK) lymphocyte: resolution into binding, programming, and killer cell-independent steps. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1782–1787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara T., Starr S. E., Ito M., Douglas S. D., Arbeter A. M. Human polymorphonuclear leukocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against varicella-zoster virus-infected fibroblasts. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.110-116.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Tilden A. B., Kumagai K., Balch C. M. Leu-11+ lymphocytes with natural killer (NK) activity are precursors of recombinant interleukin 2 (rIL 2)-induced activated killer (AK) cells. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):802–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya H., Starr S. E., Arbeter A. M., Plotkin S. A. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against varicella-zoster virus-infected targets. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):554–557. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.554-557.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Starr S. E., oleske J. M., Shore S. L., Ashman R. B., Nahmias A. J. Human monocyte-macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai K., Itoh K., Hinuma S., Tada M. Pretreatment of plastic Petri dishes with fetal calf serum. A simple method for macrophage isolation. J Immunol Methods. 1979;29(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville M. E., Grimm E., Bonavida B. Frequency determination of K cells by a single cell cytotoxic assay. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(3-4):255–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleske J. M., Ashman R. B., Kohl S., Shore S. L., Starr S. E., Wood P., Nahmias A. J. Human polymorphonuclear leucocytes as mediators of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):446–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., Nicola N., Lopez A. F., Metcalf D., Johnson G., Pereira A. Mononuclear cell-mediated enhancement of granulocyte function in man. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):202–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams V., Gershon A., Brunell P. A. Serologic response to varicella-zoster membrane antigens measured by direct immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):669–672. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


