Abstract
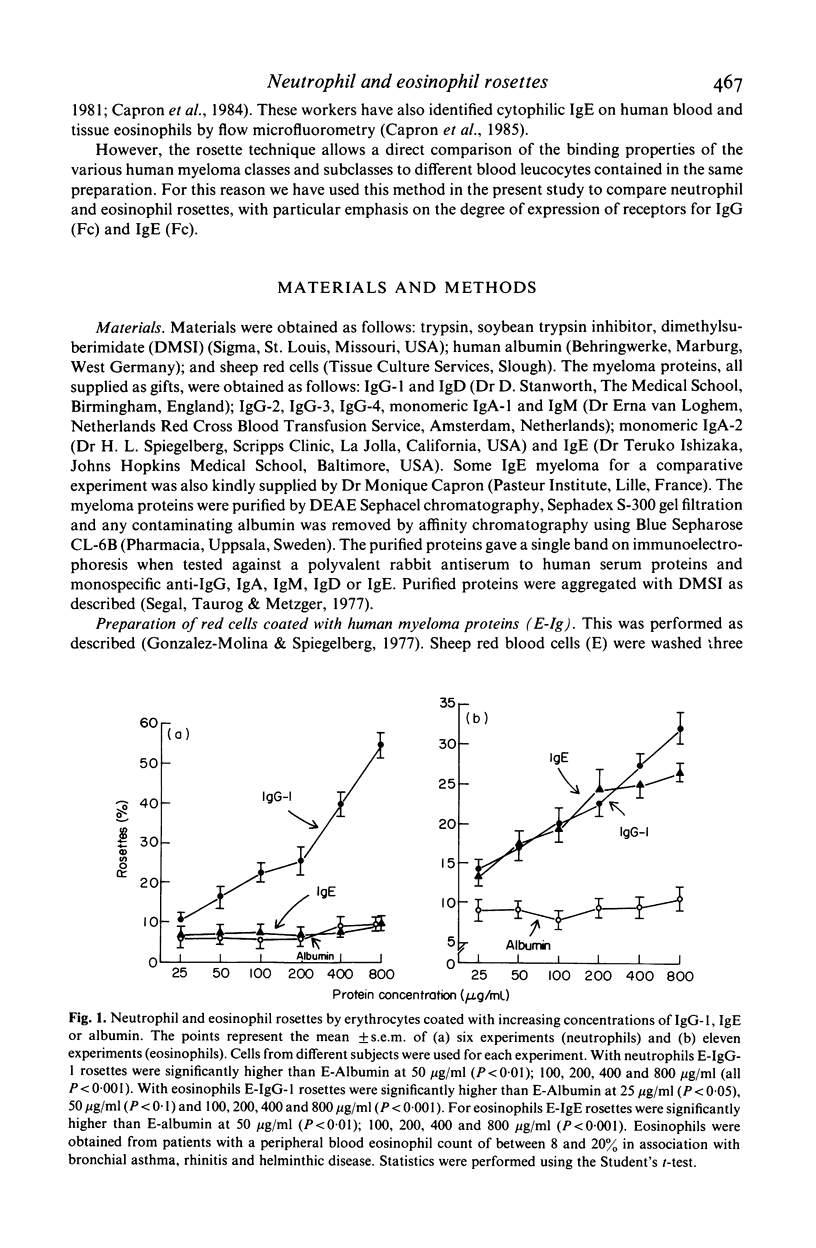
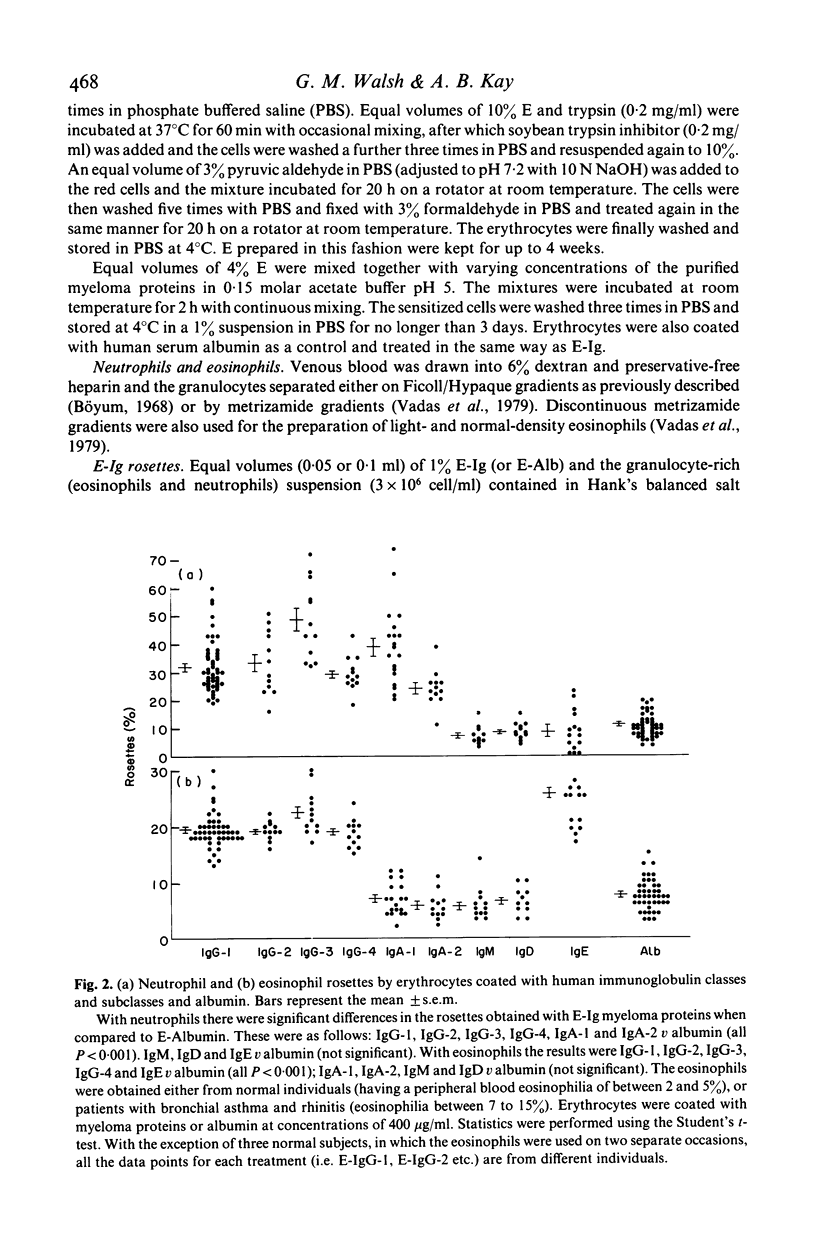
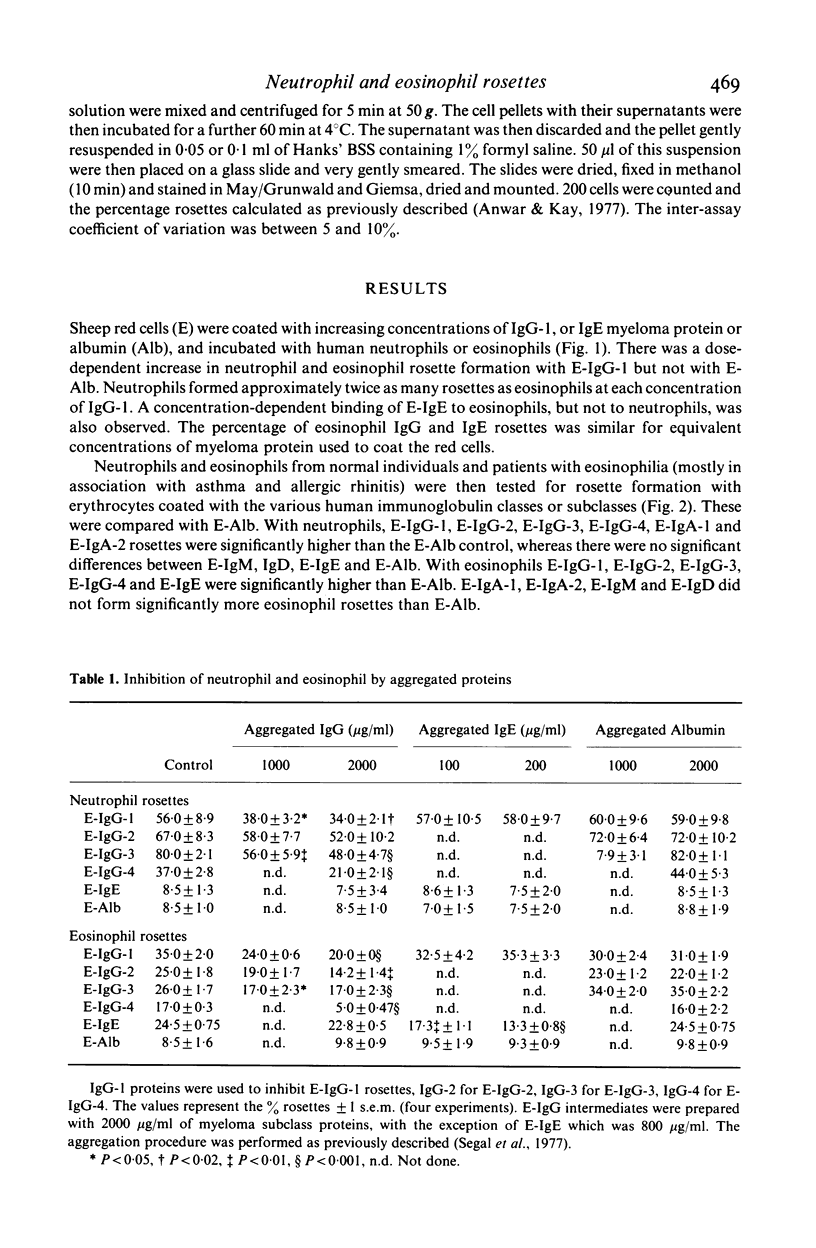
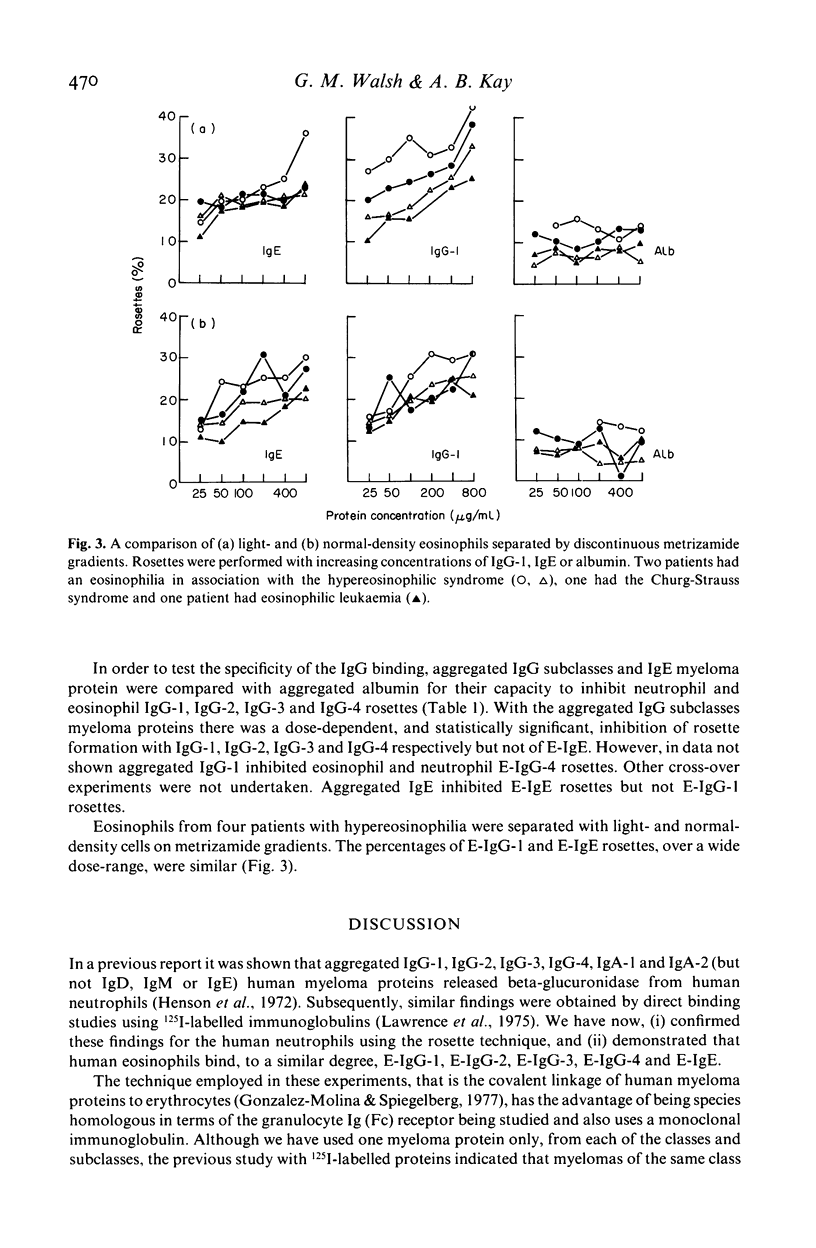
A comparative study of membrane expression of immunoglobin (Fc) receptors on human eosinophils and neutrophils has been undertaken using human IgG-1, IgG-2, IgG-3, IgG-4, IgA-1, IgA-2, IgM, IgD and IgE myeloma proteins. Sheep erythrocytes (E) coated with either human IgG-1, IgG-2, IgG-3 or IgG-4 myeloma proteins formed rosettes with human neutrophils and eosinophils. Proportionally more (1 1/2-2 times) rosettes were observed with neutrophils compared to eosinophils. In contrast, E-IgE bound to eosinophils (but not to neutrophils) to a degree that was comparable to E-IgG-1. Although IgG and IgE rosettes were inhibited by aggregates prepared from their corresponding myeloma protein there was no evidence that eosinophils and neutrophils have distinct receptors for IgG subclasses. Cells from four patients with hypereosinophilia were separated on density (metrizamide) gradients. The percentages of E-IgG-1 and E-IgE rosettes with normal- and light-density eosinophils were similar. Neutrophils, but not eosinophils, also bound significantly more E-IgA-1 and E-IgA-2 than the E-human albumin (E-Alb) control. In contrast, neutrophil and eosinophil rosette formation with E-IgM and E-IgD was not significantly different from E-Alb or E alone. These experiments indicate that human neutrophils and eosinophils bind homologous IgG subclass myeloma proteins, eosinophils, but not neutrophils, bind E-IgE with a similar avidity to that observed with E-IgG1, neutrophils, but not eosinophils, readily express demonstrable receptors for IgA-1 and IgA-2 and neither neutrophils nor eosinophils form E-IgM or E-IgD rosettes in greater numbers than the E-Alb controls.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwar A. R., Kay A. B. Membrane receptors for IgG and complement (C4, C3b and C3d) on human eosinophils and neutrophils and their relation to eosinophilia. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):976–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Capron A., Dessaint J. P., Torpier G., Johansson S. G., Prin L. Fc receptors for IgE on human and rat eosinophils. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2087–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Kusnierz J. P., Prin L., Spiegelberg H. L., Ovlaque G., Gosset P., Tonnel A. B., Capron A. Cytophilic IgE on human blood and tissue eosinophils: detection by flow microfluorometry. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3013–3018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron M., Spiegelberg H. L., Prin L., Bennich H., Butterworth A. E., Pierce R. J., Ouaissi M. A., Capron A. Role of IgE receptors in effector function of human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):462–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger M. W., Goldstine S. N., Shen L. The properties and role of receptors for IgA on human leukocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:552–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Molina A., Spiegelberg H. L. A subpopulation of normal human peripheral B lymphcytes that bind IgE. J Clin Invest. 1977 Apr;59(4):616–624. doi: 10.1172/JCI108679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Ross G. D., Good R. A., Siegal F. P. Surface markers of human eosinophils. Blood. 1976 Nov;48(5):755–763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Johnson H. B., Spiegelberg H. L. The release of granule enzymes from human neutrophils stimulated by aggregated immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. J Immunol. 1972 Dec;109(6):1182–1192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. A., Weigle W. O., Spiegelberg H. L. Immunoglobulins cytophilic for human lymphocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):368–376. doi: 10.1172/JCI107940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melewicz F. M., Spiegelberg H. L. Fc receptors for IgE on a subpopulation of human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1026–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottesen E. A., Stanley A. M., Gelfand J. A., Gadek J. E., Frank M. M., Nash T. E., Cheever A. W. Immunoglobulin and complement receptors on human eosinophils and their role in cellular adherence to schistosomules. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Nov;26(6 Pt 2):134–141. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Spry C. J. Enzymes altering the binding capacity of human blood eosinophils for IgG antibody-coated erythrocytes (EA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Apr;40(1):206–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Spry C. J. Studies on blood eosinophils. I. Patients with a transient eosinophilia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):415–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., David J. R., Butterworth A., Pisani N. T., Siongok T. A. A new method for the purification of human eosinophils and neutrophils, and a comparison of the ability of these cells to damage schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1228–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


