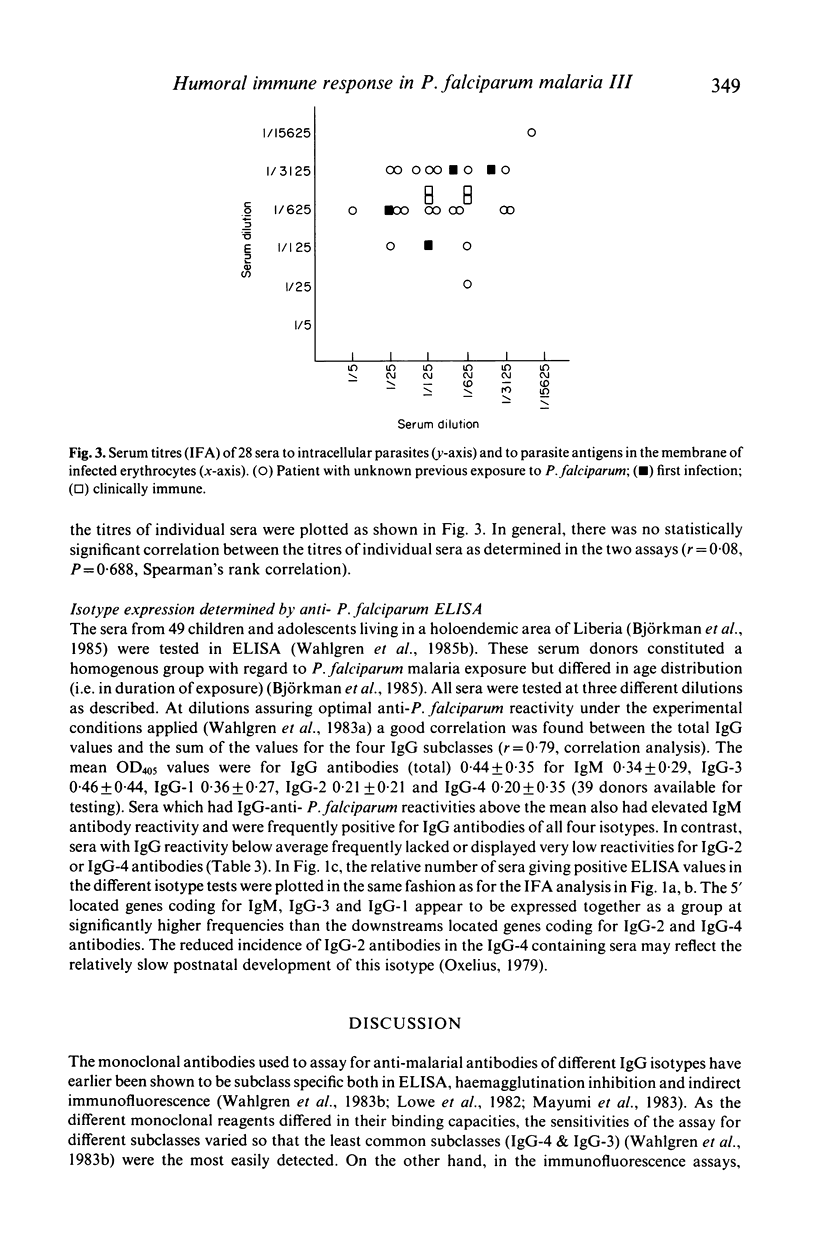
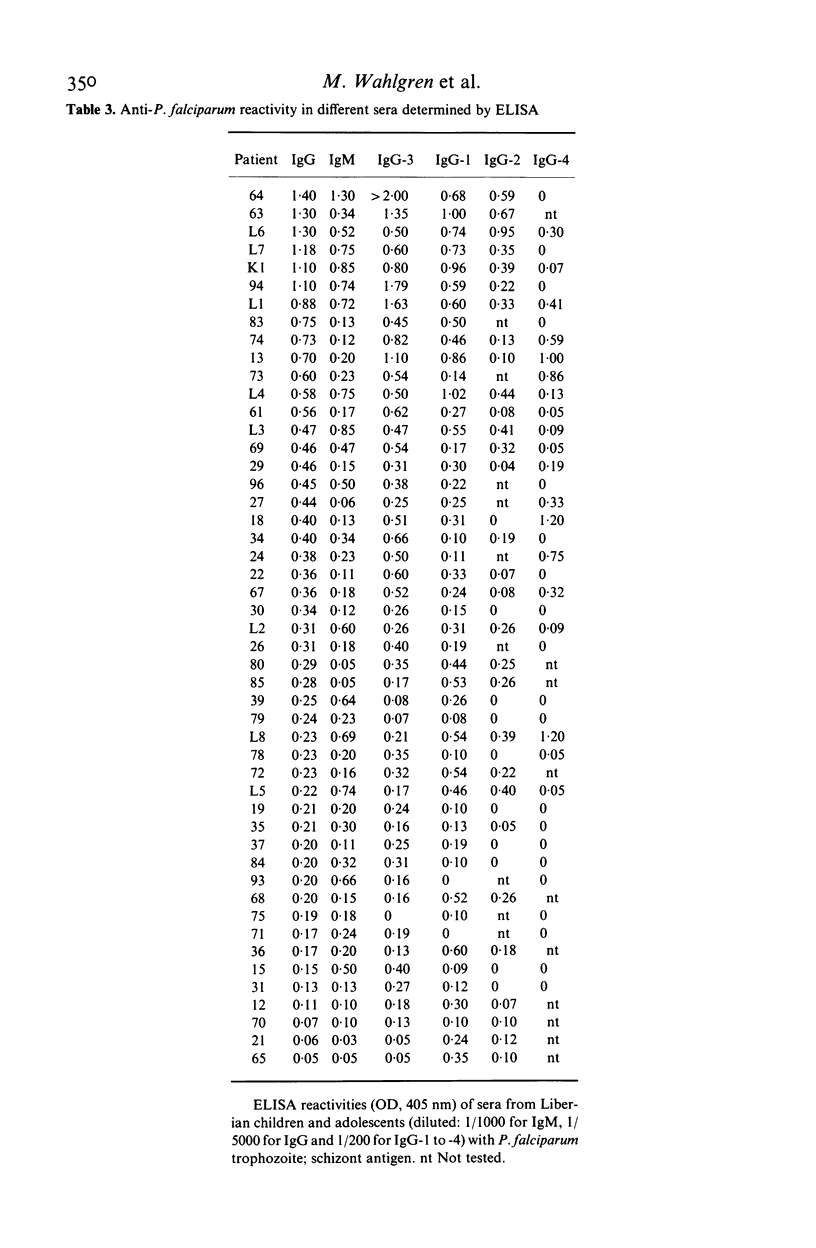
Abstract
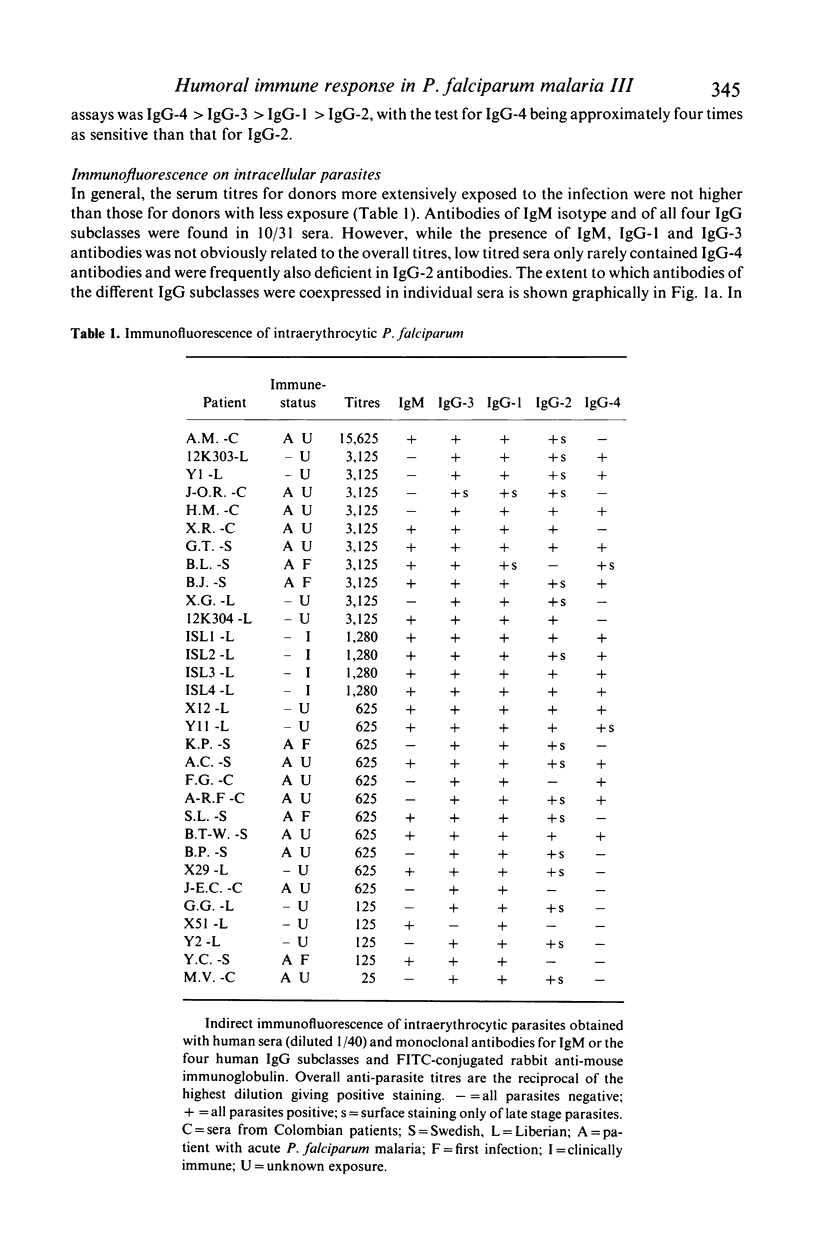
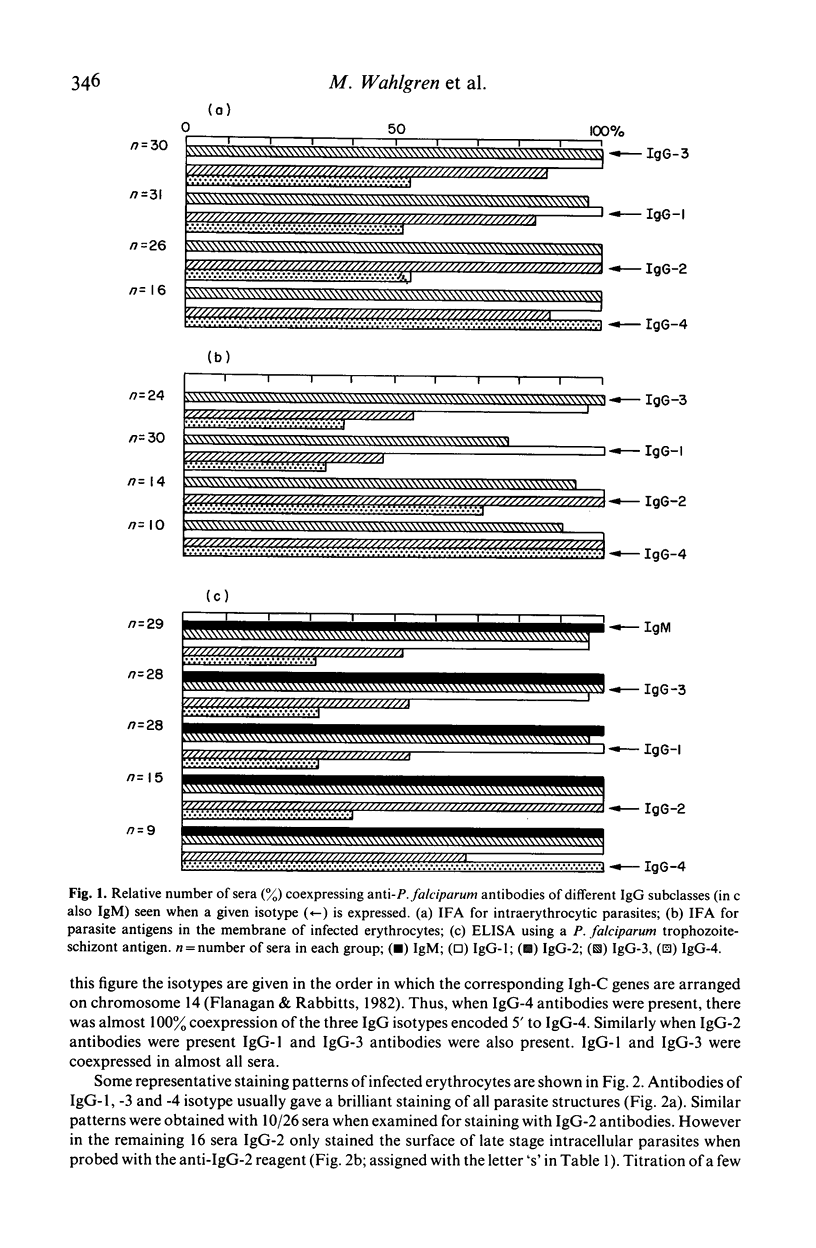
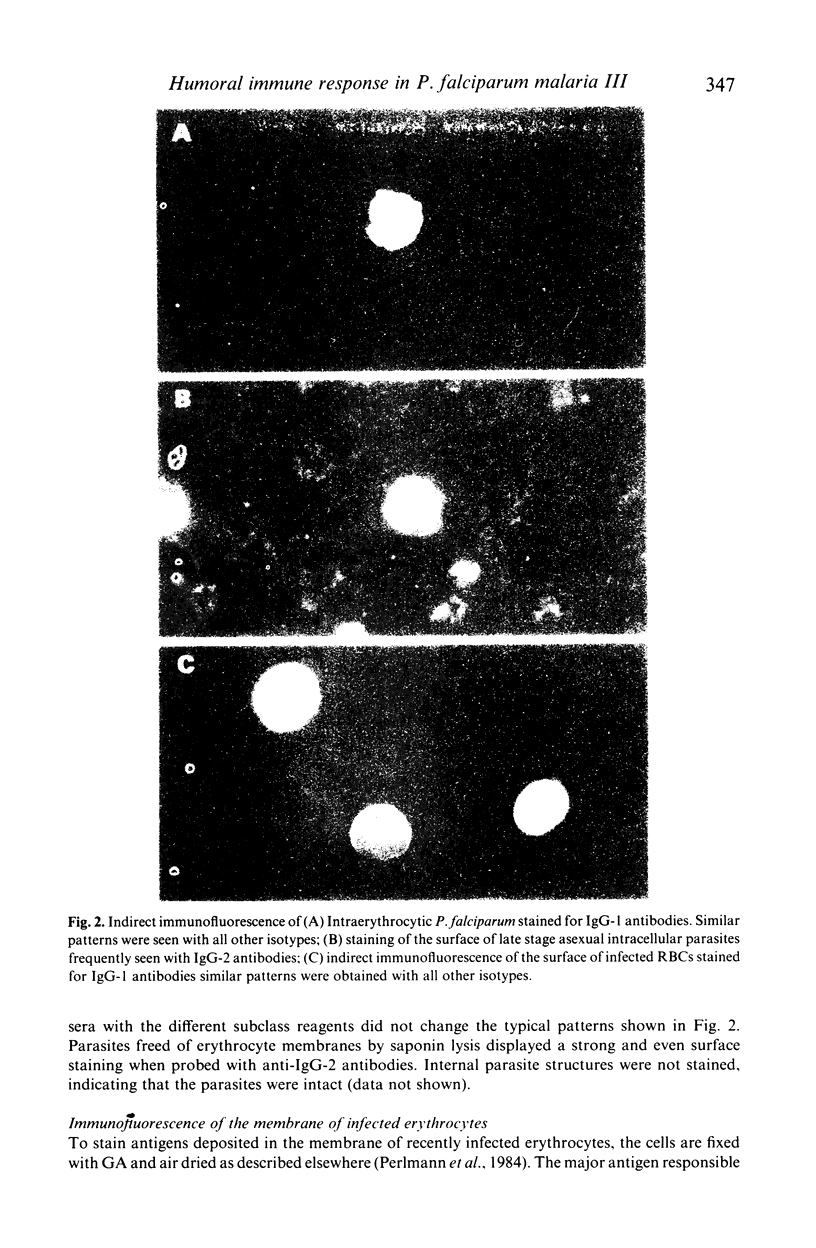
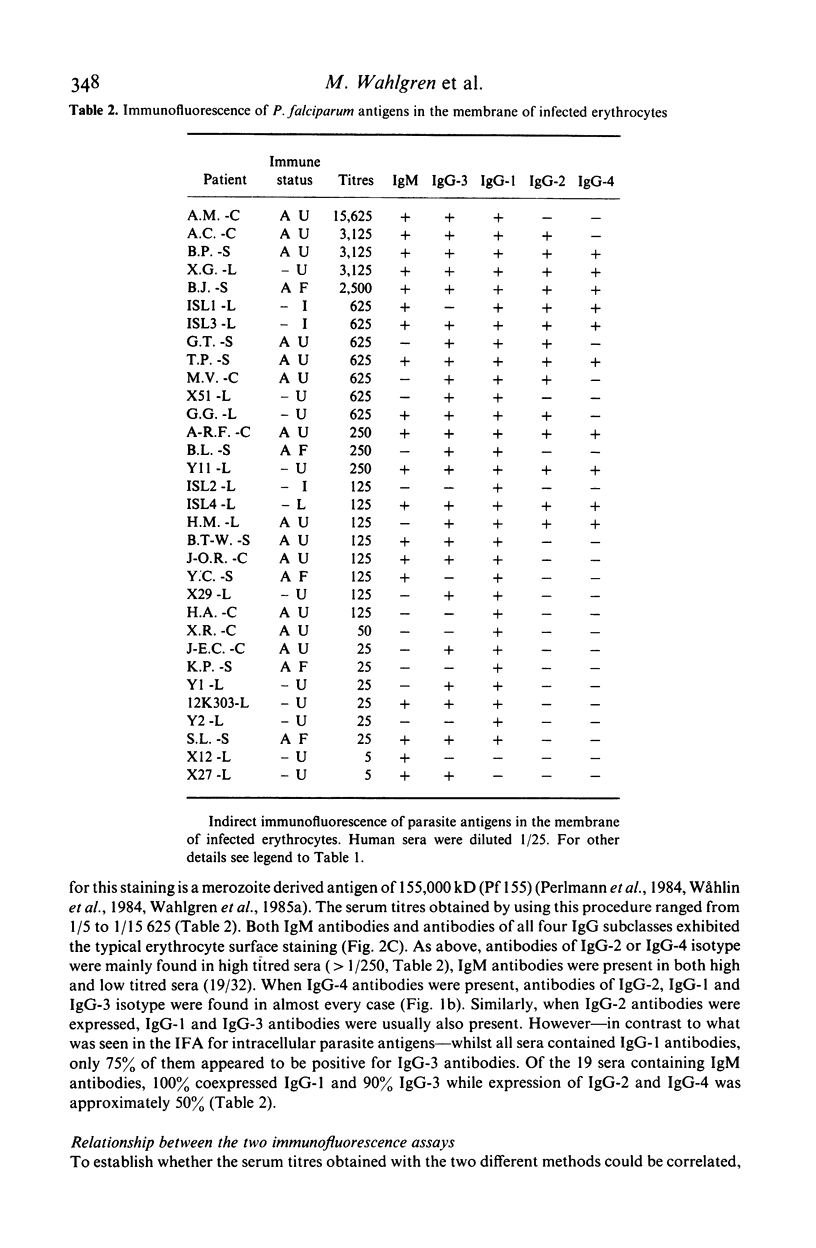
Isotypes (IgM and IgG-1 to 4) of anti-P. falciparum antibodies were investigated in sera of malarial patients or immune donors by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and two indirect immunofluorescence assays (IFAs), one staining intra-erythrocytic parasites of all stages and the other a restricted number of parasite antigens deposited in the membrane of infected erythrocytes by invading merozoites (Perlmann & Wahlgren, 1983; Perlmann et al., 1984, Wahlgren et al., 1985a). There was no correlation in overall antibody titres between the two IFAs. Antibodies of both IgM and all four IgG isotypes were detected in both assays. With the IFA for intracellular parasites a brilliant fluorescence was obtained with antibodies of all isotypes. However IgG-2 antibodies often gave staining restricted to the surface of schizonts. The incidence and reactivity in individual sera of antibodies of the different isotypes did not relate to the immune status of the donors (acute infection or clinically immune) but related well to the degree of malarial exposure as reflected by the overall antibody titres. This, in all three assays, high titred sera frequently contained antibodies of all isotypes while low titred sera usually only contained antibodies of IgM, IgG-1 and IgG-3 isotype. On average, the overall expression of antibodies of different isotypes in individual sera appears to reflect a sequential downstream (5' to 3') activation of the corresponding Igh-C genes in P. falciparum specific B-cell clones.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bich-Thuy L. T., Revillard J. P. Modulation of polyclonally activated human peripheral B cells by aggregated IgG and by IgG-binding factors: differential effect on IgG subclass synthesis. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):544–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkman A., Hedman P., Brohult J., Willcox M., Diamant I., Pehrsson P. O., Rombo L., Bengtsson E. Different malaria control activities in an area of Liberia--effects on malariometric parameters. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1985 Jun;79(3):239–246. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1985.11811914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David P. H., Hadley T. J., Aikawa M., Miller L. H. Processing of a major parasite surface glycoprotein during the ultimate stages of differentiation in Plasmodium knowlesi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Apr;11:267–282. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Rabbitts T. H. Arrangement of human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes implies evolutionary duplication of a segment containing gamma, epsilon and alpha genes. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):709–713. doi: 10.1038/300709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearhart P. J., Hurwitz J. L., Cebra J. J. Successive switching of antibody isotypes expressed within the lines of a B-cell clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5424–5428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Persson M. A., Smith C. I. Subclass distribution of human anti-Staphylococcus aureus alpha toxin antibodies: suggestion of an IgG1, IgA1, IgG4 switch pattern. Scand J Immunol. 1984 Sep;20(3):247–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1984.tb00998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A., Freeman R. R. Biosynthesis and processing of a Plasmodium falciparum schizont antigen recognized by immune serum and a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1528–1538. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M., Paul W. E. Regulation of B-cell growth and differentiation by soluble factors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:307–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., Bird P., Hardie D., Jefferis R., Ling N. R. Monoclonal antibodies (McAbs) to determinants on human gamma chains: properties of antibodies showing subclass restriction or subclass specificity. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):329–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K., Wahlgren M., Troye-Blomberg M., Berzins K., Perlmann H., Perlmann P. Monoclonal anti-parasite and anti-RBC antibodies produced by stable EBV-transformed B cell lines from malaria patients. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):2000–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayumi M., Kuritani T., Kubagawa H., Cooper M. D. IgG subclass expression by human B lymphocytes and plasma cells: B lymphocytes precommitted to IgG subclass can be preferentially induced by polyclonal mitogens with T cell help. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):671–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongini P. K., Paul W. E., Metcalf E. S. T cell regulation of immunoglobulin class expression in the antibody response to trinitrophenyl-ficoll. Evidence for T cell enhancement of the immunoglobulin class switch. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):884–902. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Kunkel H. G. Human immunoglobulins: classes, subclasses, genetic variants, and idiotypes. Adv Immunol. 1973;16:1–59. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A. IgG subclass levels in infancy and childhood. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Jan;68(1):23–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb04424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann H., Berzins K., Wahlgren M., Carlsson J., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Antibodies in malarial sera to parasite antigens in the membrane of erythrocytes infected with early asexual stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1686–1704. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. G., Nahm M. H. Mitogen-induced human IgG subclass expression. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2454–2460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Honjo T. Immunoglobulin class switching. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):801–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons J. G., Fuller C. R., Buchanan P. D., Yount W. J. Distribution of surface, cytoplasmic and secreted IgG subclasses in human lymphoblastoid cell lines and normal peripheral blood lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1981 Jul;14(1):1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Biological activities of immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):259–294. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wåhlin B., Wahlgren M., Perlmann H., Berzins K., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Human antibodies to a Mr 155,000 Plasmodium falciparum antigen efficiently inhibit merozoite invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7912–7916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Dorner M. M., Kunkel H. G., Kabat E. A. Studies on human antibodies. VI. Selective variations in subgroup composition and genetic markers. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):633–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


