Abstract
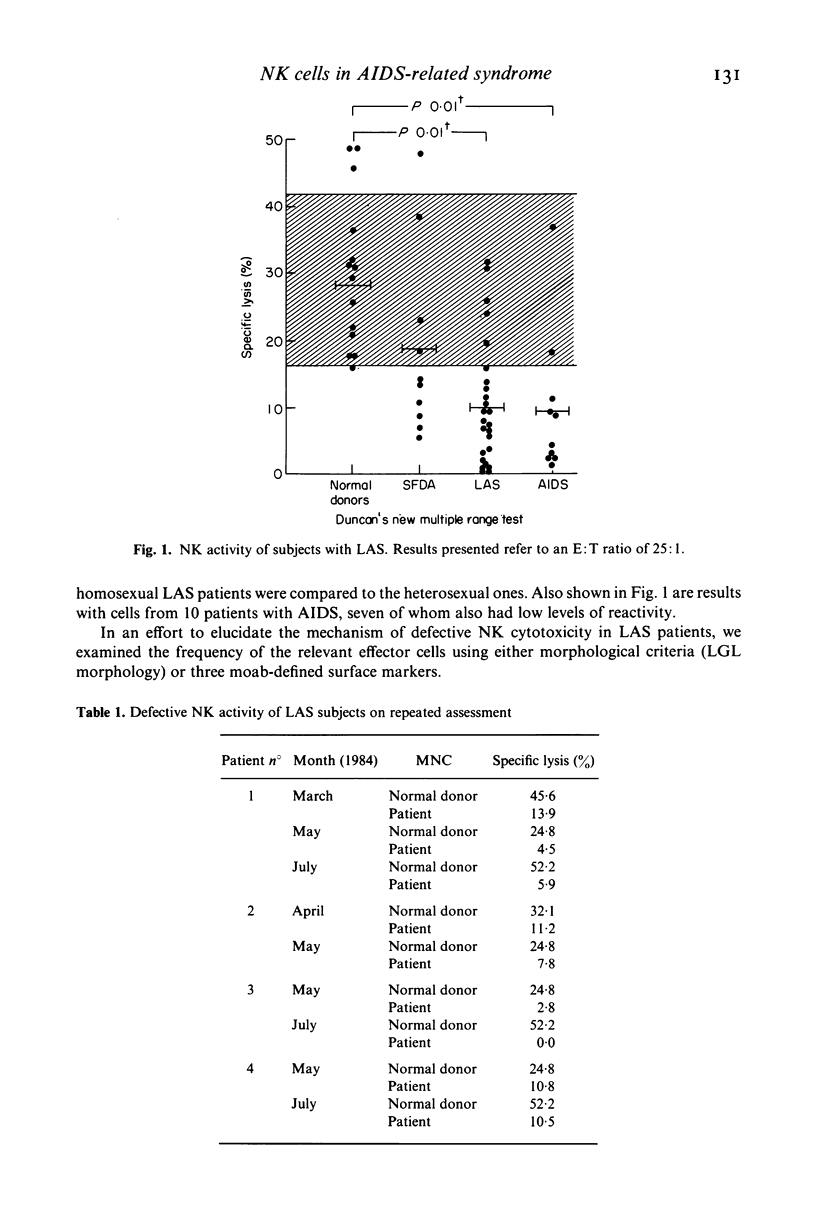
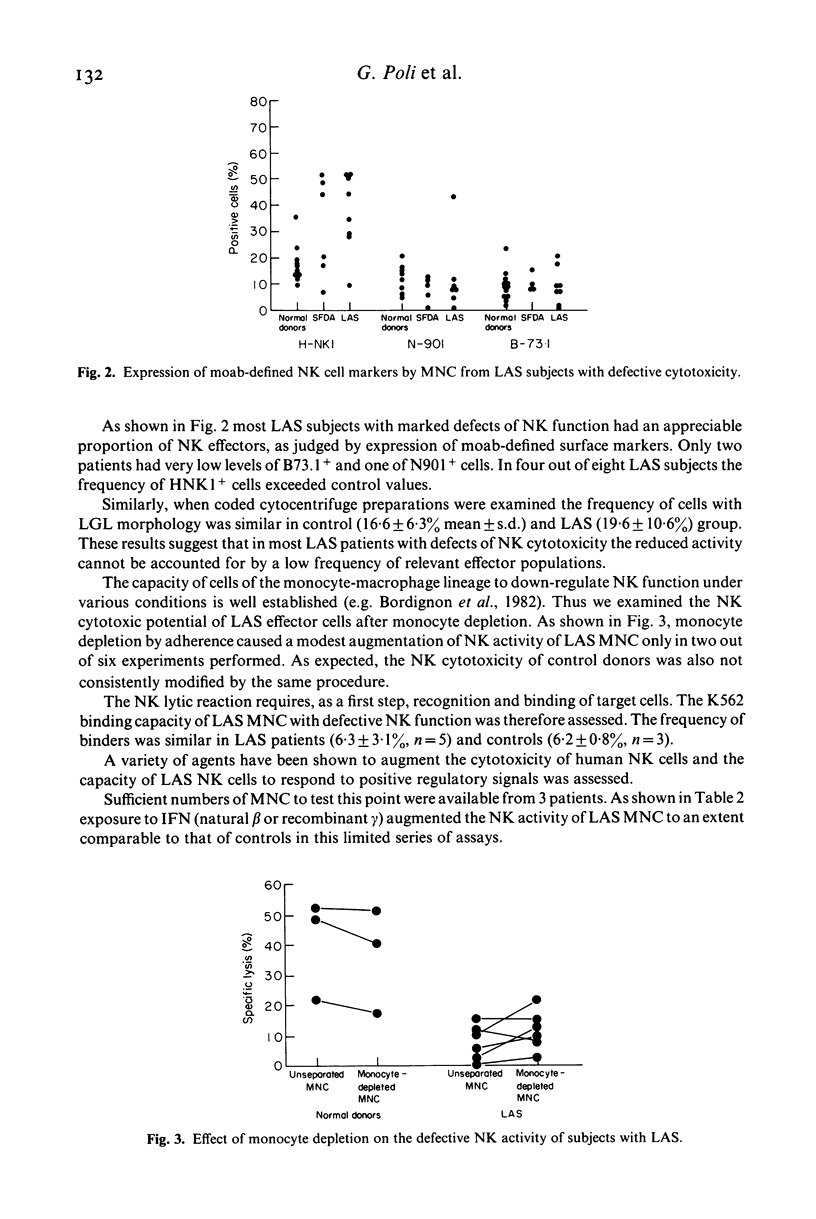
We have investigated 25 intravenous drug abusers with the clinical and laboratory features of lymphadenopathy syndrome (LAS) and 10 AIDS patients for the expression of NK activity. LAS and AIDS patients had low NK cytotoxicity compared to normal donors. The defective NK cytotoxicity was analysed in the eight LAS subjects with most marked depression. NK effectors were identified by morphology (large granular lymphocytes, LGL) and monoclonal antibody-defined surface markers (B73.1, N901, HNK1). LAS patients had normal percentages of LGL and B73.1+ and N901+ cells. with the exception of two subjects with very low frequency of B73.1+ and N901+ cells. The percentage of HNK1+ cells was increased in LAS, probably because of the reactivity of this reagent with a subset of conventional OKT8+ cells, relatively augmented in LAS subjects. Depletion of monocytes did not enhance NK activity consistently. LAS patients had a normal frequency of cells capable of binding K562. In-vitro exposure to interferon beta (natural) or gamma (recombinant) augmented the defective NK activity of LAS subjects. Thus, patients with LAS have defective NK activity that cannot be accounted for by a low frequency of the relevant effector cells or by monocytic suppressors. These observations suggest a functional defect of NK cells at one or more of the post-binding steps required for the completion of killing.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordignon C., Villa F., Allavena P., Introna M., Biondi A., Avallone R., Mantovani A. Inhibition of natural killer activity by human bronchoalveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):587–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S., Gallo R. C. A pathogenic retrovirus (HTLV-III) linked to AIDS. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 15;311(20):1292–1297. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411153112006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colotta F., Peri G., Villa A., Mantovani A. Rapid killing of actinomycin D-treated tumor cells by human mononuclear cells. I. Effectors belong to the monocyte-macrophage lineage. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):936–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstoft J., Malchow-Møller A., Bygbjerg I., Dickmeiss E., Enk C., Halberg P., Haahr S., Jacobsen M., Jensen K., Mejer J. Severe acquired immunodeficiency in European homosexual men. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jul 3;285(6334):17–19. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6334.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Hercend T., Beveridge R., Schlossman S. F. Characterization of an antigen expressed by human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2947–2951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E., Bonavida B. Mechanism of cell-mediated cytotoxicity at the single cell level. I. Estimation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte frequency and relative lytic efficiency. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2861–2869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R. Natural killer cells: their roles in defenses against disease. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):24–30. doi: 10.1126/science.7025208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Djeu J. Y., Dougherty S. F., Oppenheim J. J. Capacity of human large granular lymphocytes (LGL) to produce multiple lymphokines: interleukin 2, interferon, and colony stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2379–2385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Phillips J. H., Warner N. L., Babcock G. F. Subpopulations of human natural killer cells defined by expression of the Leu-7 (HNK-1) and Leu-11 (NK-15) antigens. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1789–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarin A., Galli M., Introna M., Negri C., Mantovani A., Mella L., Ferrante P., Parravicini C., Trombini M., Aiuti F. Outbreak of persistent, unexplained, generalized lymphadenopathy with immunological abnormalities in drug addicts in Milan. Infection. 1984 Nov-Dec;12(6):372–376. doi: 10.1007/BF01645217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Benike C. J., Mark D. F., Koths K., Engleman E. G. Human recombinant interleukin-2 partly reconstitutes deficient in-vitro immune responses of lymphocytes from patients with AIDS. Lancet. 1984 Mar 31;1(8379):698–702. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92220-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C., Fitzgerald P. A., Siegal F. P. Severe acquired immune deficiency syndrome in male homosexuals: diminished capacity to make interferon-alpha in vitro associated with severe opportunistic infections. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):962–966. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metroka C. E., Cunningham-Rundles S., Pollack M. S., Sonnabend J. A., Davis J. M., Gordon B., Fernandez R. D., Mouradian J. Generalized lymphadenopathy in homosexual men. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Nov;99(5):585–591. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-5-585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parravicini C. L., Lazzarin A., Galli M., Berti E., Zerboni R., Costanzi G. C. Lymph node finding in drug abusers. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Dec;82(6):749–750. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.6.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Starr S., Abraham S., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Human natural killer cells analyzed by B73.1, a monoclonal antibody blocking Fc receptor functions. I. Characterization of the lymphocyte subset reactive with B73.1. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2133–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinching A. J. The acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Apr;56(1):1–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitchenik A. E., Fischl M. A., Dickinson G. M., Becker D. M., Fournier A. M., O'Connell M. T., Colton R. M., Spira T. J. Opportunistic infections and Kaposi's sarcoma among Haitians: evidence of a new acquired immunodeficiency state. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Mar;98(3):277–284. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-3-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon M. C., Landay A., Prasthofer E. F., Stagno S. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection in a previously healthy patient with classic hemophilia. Clinical, immunologic, and virologic findings. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Mar;98(3):287–290. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-3-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. M., Chinoy P., Grieco M. H. Differential effects of interferon-alpha 2 and interleukin-2 on natural killer cell activity in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Biol Response Mod. 1984 Aug;3(4):379–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Chess L., Fahey J. L., Fauci A. S., Lachmann P. J., L'Age-Stehr J., Ngu J., Pinching A. J., Rosen F. S., Spira T. J. AIDS--an immunologic reevaluation. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 15;311(20):1286–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411153112005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Lopez C., Hammer G. S., Brown A. E., Kornfeld S. J., Gold J., Hassett J., Hirschman S. Z., Cunningham-Rundles C., Adelsberg B. R. Severe acquired immunodeficiency in male homosexuals, manifested by chronic perianal ulcerative herpes simplex lesions. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1439–1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Perussia B. Human natural killer cells: biologic and pathologic aspects. Lab Invest. 1984 May;50(5):489–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


