Abstract
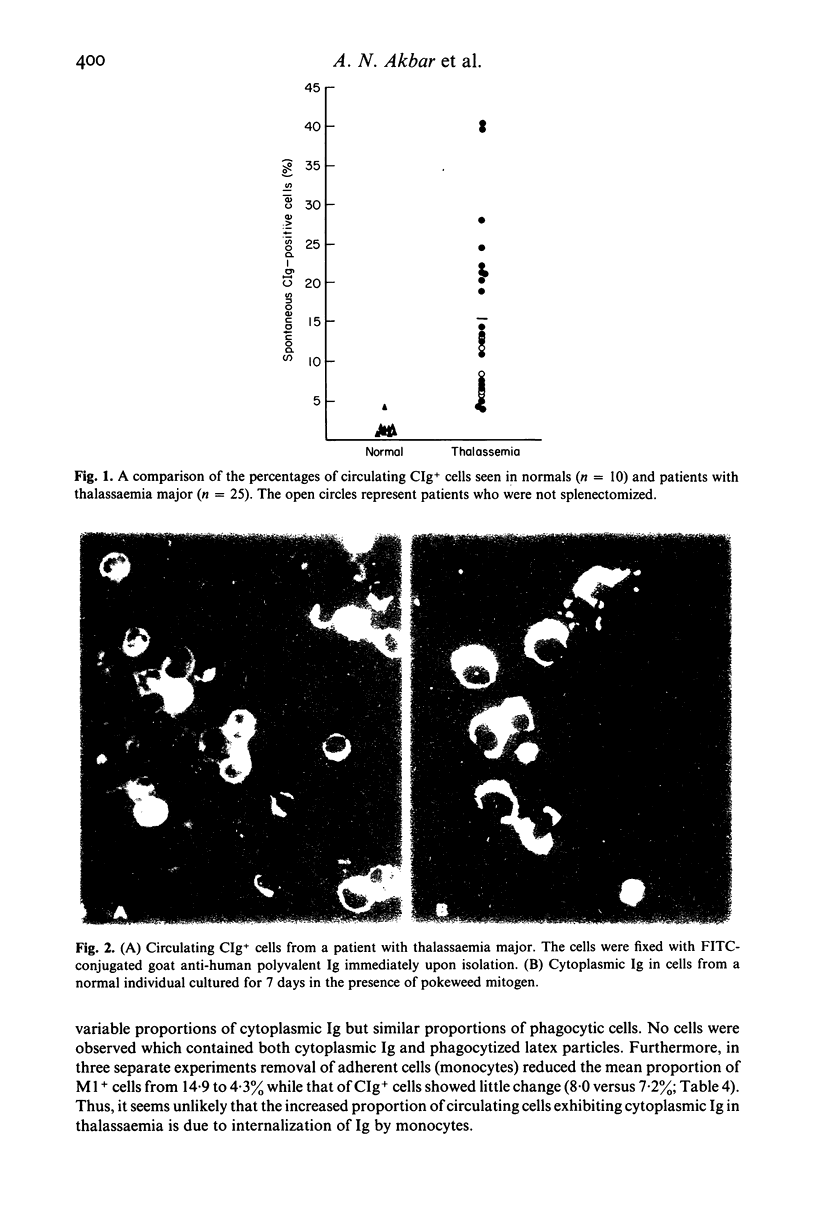
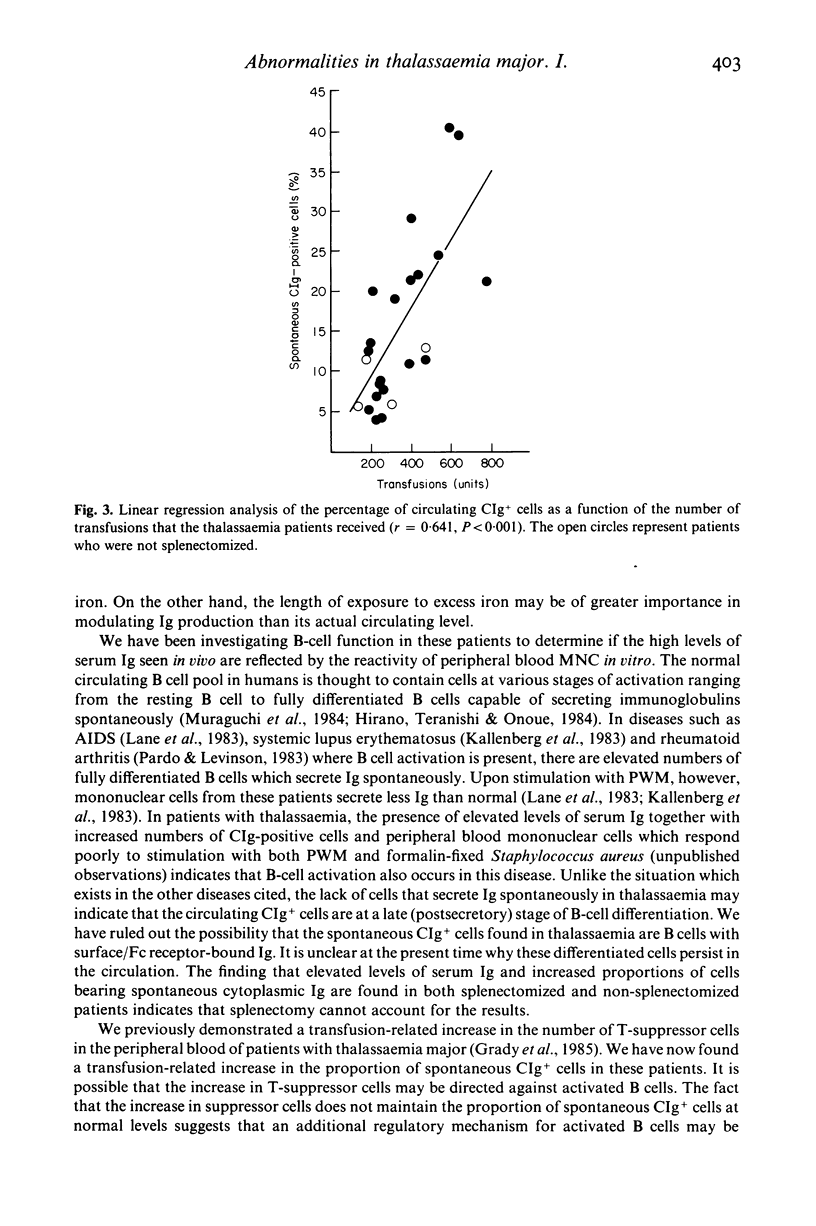
Multiply transfused patients with beta-thalassaemia major have elevated serum immunoglobulin levels and a transfusion-related increase in (T8+) T-suppressor cells. We report here that these patients also have a significantly increased (P less than 0.001) proportion of B-cells that contain cytoplasmic immunoglobulin when visualized immediately upon isolation. On the other hand, the same cell populations do not exhibit an increase in the proportion of immunoglobulin-secreting cells as measured by a reverse haemolytic plaque assay. These results, together with those of ongoing studies, suggest that the cells containing the cytoplasmic immunoglobulin are likely to be terminally differentiated B-cells which persist in the circulation. While the reason for this phenomenon is not yet known, we have found that the increase in these cells is transfusion-related.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akbar A. N., Jones D. B., Wright D. H. Spontaneous and Concanavalin A-induced suppressor activity in control and Hodgkin's disease patients. Br J Cancer. 1984 Mar;49(3):349–356. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines M. G., Lafleur F. L., Holbein B. E. Involvement of transferrin and transferrin receptors in human natural killer effector:target interaction. Immunol Lett. 1983;7(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(83)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brieva J. A., Stevens R. H. Involvement of the transferrin receptor in the production and NK-induced suppression of human antibody synthesis. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1288–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brieva J. A., Targan S., Stevens R. H. NK and T cell subsets regulate antibody production by human in vivo antigen-induced lymphoblastoid B cells. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):611–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantoulakis M., Trichopoulos D., Avgoustaki O., Economidou J. Serum immunoglobulin concentrations before and after splenectomy in patients with homozygous beta-thalassaemia. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jun;31(6):546–550. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.6.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascón P., Zoumbos N. C., Young N. S. Immunologic abnormalities in patients receiving multiple blood transfusions. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Feb;100(2):173–177. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-2-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady R. W., Akbar A. N., Giardina P. J., Hilgartner M. W., de Sousa M. Disproportionate lymphoid cell subsets in thalassaemia major: the relative contributions of transfusion and splenectomy. Br J Haematol. 1985 Apr;59(4):713–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1985.tb07367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano J. H., Piomelli S., Hilgartner M., Giardina P., Karpatkin M., Andrew M., LoIacono N., Seaman C. Chelation therapy in beta-thalassemia major. III. The role of splenectomy in achieving iron balance. J Pediatr. 1981 Nov;99(5):695–699. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Teranishi T., Onoue K. Human helper T cell factor(s). III. Characterization of B cell differentiation factor I (BCDF I). J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):229–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallenberg C. G., Limburg P. C., Van Slochteren C., Van der Woude F. J., The T. H. B cell activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: depressed in vivo humoral immune response to a primary antigen (haemocyanin) and increased in vitro spontaneous immunoglobulin synthesis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Aug;53(2):371–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapadia A., de Sousa M., Markenson A. L., Miller D. R., Good R. A., Gupta S. Lymphoid cell sets and serum immunoglobulins in patients with thalassaemia intermedia: relationship to serum iron and splenectomy. Br J Haematol. 1980 Jul;45(3):405–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb07161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J., Sarnaik S., Gitlin J., Lusher J. Diminished helper/suppressor lymphocyte ratios and natural killer activity in recipients of repeated blood transfusions. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):308–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Masur H., Edgar L. C., Whalen G., Rook A. H., Fauci A. S. Abnormalities of B-cell activation and immunoregulation in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 25;309(8):453–458. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308253090803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modell B. Total management of thalassaemia major. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Jun;52(6):489–500. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.6.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraguchi A., Kehrl J. H., Butler J. L., Fauci A. S. Sequential requirements for cell cycle progression of resting human B cells after activation by anti-Ig. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):176–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckers L. M., Cossman J. Transferrin receptor induction in mitogen-stimulated human T lymphocytes is required for DNA synthesis and cell division and is regulated by interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3494–3498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardo I., Levinson A. I. Circulating immunoglobulin-secreting cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Oct;29(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovo P. A., Miniero R., Barbera C., Sacchetti L., Saitta M. Serum immunoglobulins in homozygous beta-thalassemia. Acta Haematol. 1981;65(1):21–25. doi: 10.1159/000207144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasi C., Wasi P., Thongcharoen P. Serum-immunoglobulin levels in thalassaemia and the effects of splenectomy. Lancet. 1971 Jul 31;2(7718):237–239. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92573-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


