Abstract
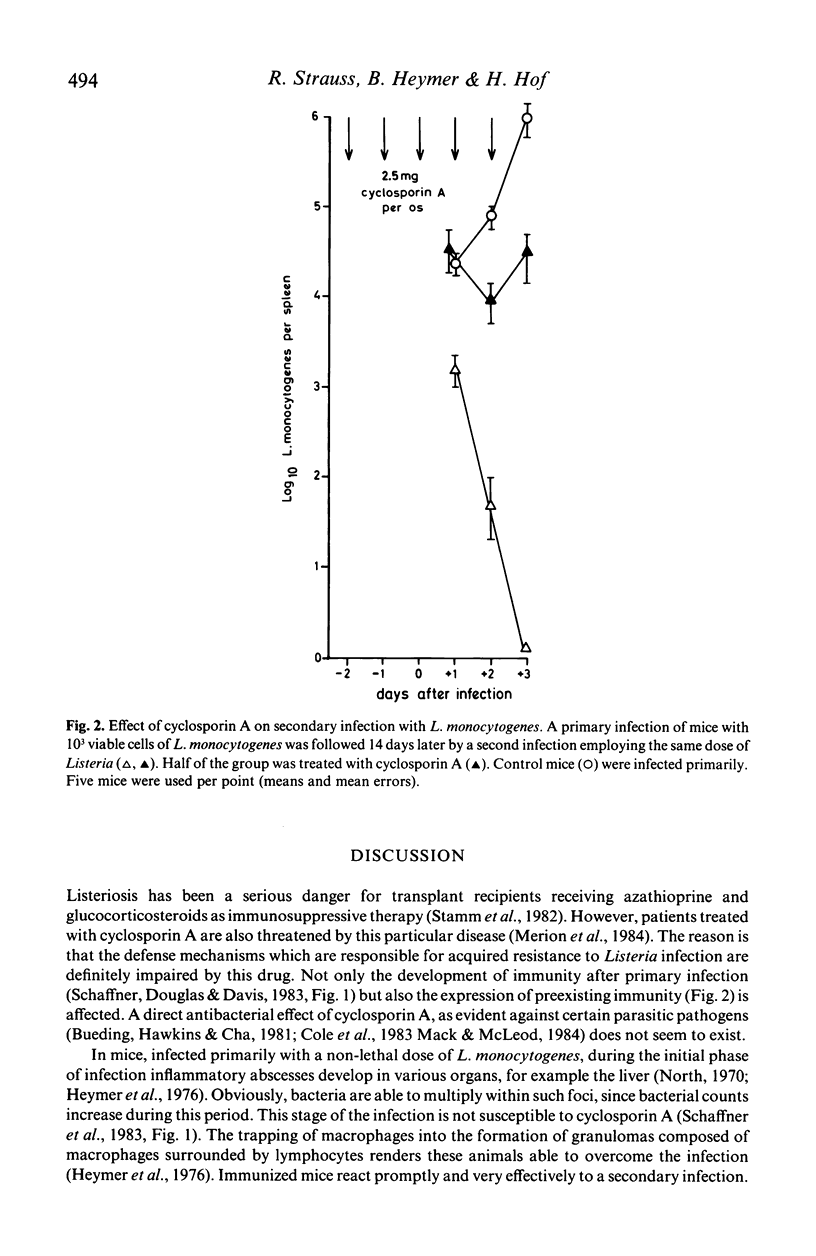
The effects of cyclosporin A on primary and secondary infection of mice with Listeria monocytogenes was studied both at the microbiological and the histomorphological level. This drug, when given in a dose of 100 mg/kg/day, was found to inhibit the development of protective immunity after primary infection as well as the expression of acquired immunity to challenge infection as determined by counting of bacterial numbers in the spleen. The manifestation of delayed type hypersensitivity was also impaired. When the cellular immune system was functionally intact, the formation of granulomas composed of macrophages and lymphocytes enabled the animals to overcome the Listeria infection. In mice treated with cyclosporin A protective granulomatous reaction during secondary infection did not occur. Instead numerous necropurulent lesions developed in the reticuloendothelial organs, such as spleen and liver, of animals unable to control the lethal infection.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmann D. M., Blyth W. A. The effects of cyclosporin A on the induction, expression and regulation of the immune response to herpes simplex virus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Jan;59(1):17–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borel J. F., Feurer C., Gubler H. U., Stähelin H. Biological effects of cyclosporin A: a new antilymphocytic agent. Agents Actions. 1976 Jul;6(4):468–475. doi: 10.1007/BF01973261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bueding E., Hawkins J., Cha Y. N. Antischistosomal effects of cyclosporin A. Agents Actions. 1981 Jul;11(4):380–383. doi: 10.1007/BF01982474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. The role of cell-mediated immunity in bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1221–1250. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman A., Goldman J. M. Effects of cyclosporin A on human granulopoiesis in vitro. Transplantation. 1980 Nov;30(5):386–387. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198011000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymer B., Hobik H. P., Schäfer H., Bültmann B., Spanel R., Haferkamp O. Animal experimental studies on chronic granulomatous inflammation and T-lymphocyte-system. Beitr Pathol. 1975 Nov;156(2):128–144. doi: 10.1016/s0005-8165(75)80146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymer B., Hof H., Emmerling P., Finger H. Morphology and time course of experimental listeriosis in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):832–835. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.832-835.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hof H. Virulence of different strains of Listeria monocytogenes serovar 1/2a. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1984;173(4):207–218. doi: 10.1007/BF02122112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Brinkmann V. Attempts to characterize the T-cell population and lymphokine involved in the activation of macrophage oxygen metabolism in murine listeriosis. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 15;88(2):545–550. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Simon M. M., Hahn H. Specific Lyt 123 cells are involved in protection against Listeria monocytogenes and in delayed-type hypersensitivity to listerial antigens. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):1033–1038. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkl A., Klaus G. G. Selective effects of cyclosporin A on functional B cell subsets in the mouse. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2526–2531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. G., McLeod R. New micromethod to study the effect of antimicrobial agents on Toxoplasma gondii: comparison of sulfadoxine and sulfadiazine individually and in combination with pyrimethamine and study of clindamycin, metronidazole, and cyclosporin A. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):26–30. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh L. C., Thompson A. W. Activity of the mononuclear phagocyte system in cyclosporin A-treated mice. Transplantation. 1980 Nov;30(5):384–386. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198011000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merion R. M., White D. J., Thiru S., Evans D. B., Calne R. Y. Cyclosporine: five years' experience in cadaveric renal transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):148–154. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hermelink H. K., Kaiserling E., Sonntag H. G. Modulation of epithelioid cell granuloma formation to apathogenic mycobacteria by cyclosporin A. Pathol Res Pract. 1982 Oct;175(1):80–96. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(82)80044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The relative importance of blood monocytes and fixed macrophages to the expression of cell-mediated immunity to infection. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):521–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reem G. H., Cook L. A., Vilcek J. Gamma interferon synthesis by human thymocytes and T lymphocytes inhibited by cyclosporin A. Science. 1983 Jul 1;221(4605):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.6407112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumjanek V. M., Smith L. A., Morley J. Modulation by cyclosporin-A of mononuclear cell distribution during experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1984;6(2):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(84)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner A., Douglas H., Davis C. E. Models of T cell deficiency in listeriosis: the effects of cortisone and cyclosporin A on normal and nude BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):450–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm A. M., Dismukes W. E., Simmons B. P., Cobbs C. G., Elliott A., Budrich P., Harmon J. Listeriosis in renal transplant recipients: report of an outbreak and review of 102 cases. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4(3):665–682. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.3.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





